A crucible furnace is a high-temperature chamber designed to melt materials held within a separate, removable container called a crucible. Its primary use is to liquefy substances like metals, alloys, glass, or ceramics for applications ranging from small-scale casting and alloying to laboratory analysis and materials research. The furnace provides the heat, while the crucible contains the material, preventing contamination and simplifying the process of pouring the molten substance.
The core value of a crucible furnace is not just its ability to generate high heat, but its unique combination of versatility and precision for small-batch operations. It isolates the material being melted, allowing for a clean, controlled process suitable for a wide range of substances where larger industrial furnaces would be impractical or inefficient.

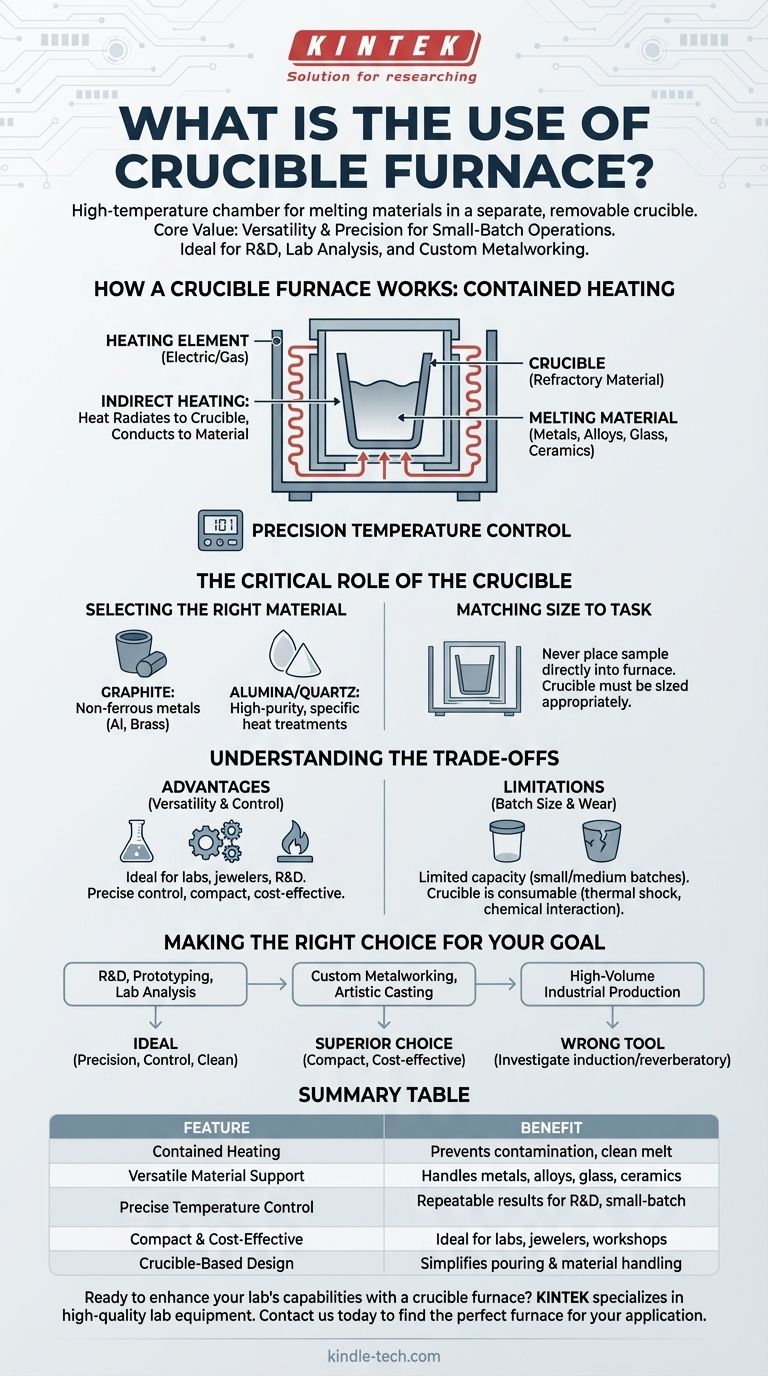
How a Crucible Furnace Works: A Principle of Contained Heating
A crucible furnace operates on a straightforward principle: indirect heating. Instead of applying heat directly to the material, the furnace heats the crucible, which in turn transfers that thermal energy to the contents inside.
The Core Components
The system is defined by two essential parts. The first is the heating element, which can be powered by electricity (resistance coils) or gas burners. The second is the crucible, a pot made from refractory materials like graphite, silicon carbide, or alumina that can withstand extreme temperatures without reacting with the melt.
The Melting Process
The material to be melted is placed inside the crucible, which is then set inside the furnace. The heating element raises the temperature of the furnace chamber, and the heat radiates to the crucible. This energy is conducted through the crucible walls, raising the internal temperature until the material reaches its melting point and becomes liquid.
Precision Through Temperature Control
Modern furnaces include sophisticated temperature control systems. These are critical for preventing overheating, which can damage the alloy or the crucible, and underheating, which results in an incomplete melt. This control makes the process repeatable and reliable.
The Critical Role of the Crucible
The crucible is not merely an accessory; it is a critical component that directly influences the success and quality of the melt. Choosing the correct crucible is as important as setting the right temperature.
Selecting the Right Material
The crucible's material must be chemically compatible with the substance being melted and capable of withstanding the required temperatures.
- Graphite is common for non-ferrous metals like aluminum and brass.
- Alumina or Quartz are often used for high-purity applications or specific heat treatments where carbon contamination from graphite would be an issue.
Matching Size to the Task
The crucible must be sized appropriately for the furnace and the sample. An oversized crucible heats inefficiently, while an undersized one limits the batch size. Critically, a sample should never be placed directly into the furnace tube without a crucible, as this will damage the furnace and contaminate the material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any tool, a crucible furnace has distinct advantages and clear limitations. Understanding these is key to using it effectively.
The Advantage: Versatility and Control
For laboratories, small foundries, jewelers, or R&D facilities, the crucible furnace is invaluable. Its ability to melt a wide variety of materials with precise temperature control in a compact, cost-effective unit is its primary strength.
The Limitation: Batch Size
The most significant drawback is its limited capacity. Crucible furnaces are designed for small- to medium-sized batches. They are fundamentally unsuited for the high-volume needs of large-scale industrial production, where continuous or much larger batch furnaces are required.
The Reality: Crucible Wear and Tear
Crucibles are consumable items. They degrade over time due to thermal shock (rapid heating and cooling) and chemical interaction with molten materials. A regular inspection and replacement schedule is necessary for safe and effective operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge, you must align the furnace's capabilities with your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is research, prototyping, or lab analysis: The crucible furnace is ideal due to its precision, control, and ability to handle diverse, small-volume materials cleanly.
- If your primary focus is custom metalworking or artistic casting: Its compact size, ease of operation, and cost-effectiveness make it a superior choice for small workshops and studios.
- If your primary focus is high-volume industrial production: A crucible furnace is the wrong tool; you should investigate larger-scale technologies like induction or reverberatory furnaces.
Understanding the crucible furnace as a complete system—not just a heater—is the key to unlocking its full potential for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Contained Heating | Prevents contamination and ensures a clean melt |
| Versatile Material Support | Handles metals, alloys, glass, and ceramics |
| Precise Temperature Control | Enables repeatable results for R&D and small-batch work |
| Compact & Cost-Effective | Ideal for labs, jewelers, and small workshops |
| Crucible-Based Design | Simplifies pouring and material handling |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a crucible furnace? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including crucible furnaces designed for precision melting and material research. Whether you're in R&D, metalworking, or materials science, our solutions deliver the control and reliability you need. Contact us today to find the perfect furnace for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control



















