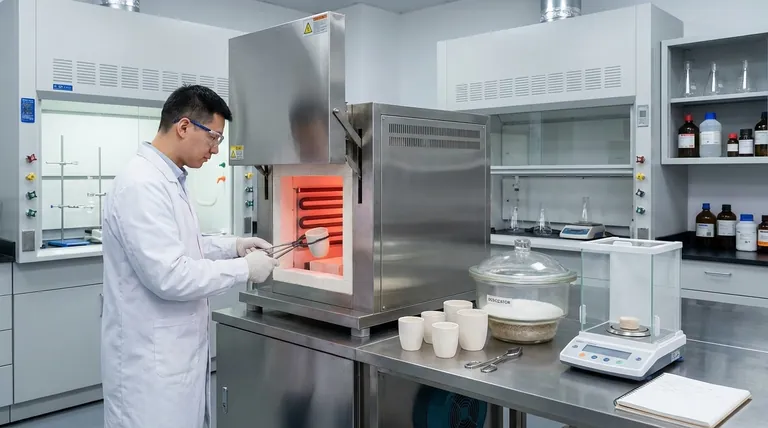
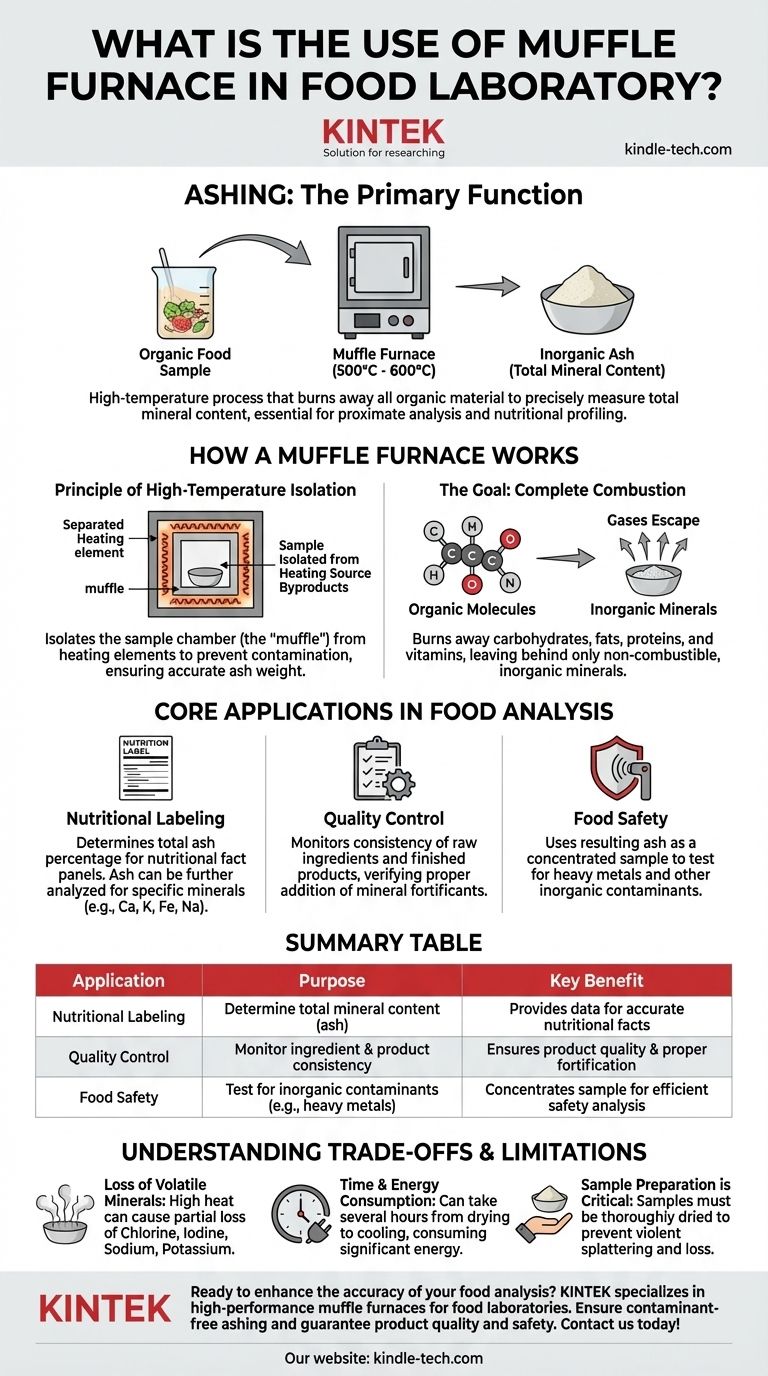
In a food laboratory, a muffle furnace is primarily used for ashing: a high-temperature process that burns away all organic material from a food sample to precisely measure its total mineral content. This fundamental procedure, part of a standard proximate analysis, is essential for determining the nutritional profile and overall quality of food products.
The core function of a muffle furnace is not just to heat a sample, but to completely incinerate its organic components in a controlled, contaminant-free environment. This leaves behind only the inorganic residue—the "ash"—which represents the food's total mineral content.

What is a Muffle Furnace and How Does It Work?
A muffle furnace is essentially a high-temperature oven designed for analytical processes that require thermal decomposition. Its design is critical to its function in a food lab.
The Principle of High-Temperature Isolation
The furnace heats samples to very high temperatures, typically between 500°C and 600°C for food ashing. This extreme heat provides the energy needed to break down and completely combust all organic matter.
Unlike a simple oven, the sample chamber (the "muffle") is physically isolated from the heating elements. This prevents any combustion byproducts from the heating source from contaminating the food sample, ensuring the final ash weight is accurate.
The Goal: Complete Combustion
The process systematically burns away all organic compounds—carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, and other organic acids. These materials are primarily composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen, which convert into gases and escape.
What remains in the crucible is a small amount of light-colored powder known as ash. This ash is the collection of non-combustible, inorganic minerals present in the original food sample.
The Core Application in Food Analysis: Ashing
While muffle furnaces have many industrial uses, their role in food science is almost entirely centered on ash analysis. This single measurement provides critical insights.
Determining Total Mineral Content
The primary output of ashing is the total ash percentage, a quantitative measure of the total mineral content. This value is a required component on many nutritional fact panels and is a key indicator of a food's nutritional composition.
A Foundation for Nutritional Labeling
The ash itself serves as a concentrated sample for further testing. Analysts can dissolve the ash and use more advanced techniques (like Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy) to identify and quantify specific minerals, such as calcium, potassium, iron, and sodium, for detailed nutritional labeling.
A Key Part of Proximate Analysis
Ashing is one of the six fundamental tests in proximate analysis, the standard suite of chemical tests used to evaluate a food's nutritional makeup. The other components are moisture, crude protein, crude fat, crude fiber, and carbohydrates. Together, these values provide a complete nutritional profile.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While essential, the ashing process is not without its analytical considerations. Understanding these limitations is key to interpreting the results correctly.
Loss of Volatile Minerals
The extremely high temperatures can cause some minerals to vaporize and be lost along with the organic gases. Elements like chlorine, iodine, and to some extent, sodium and potassium, can be partially lost, leading to a slight underestimation of the true total mineral content.
Time and Energy Consumption
Ashing is not a quick process. It can take several hours, from initial sample drying to the extended time in the furnace and final cooling in a desiccator. This makes it both time-consuming and energy-intensive.
Sample Preparation is Critical
The accuracy of the result depends heavily on proper sample preparation. Samples must be thoroughly dried before being placed in the furnace to prevent violent splattering, which causes sample loss. Incorrect handling can easily invalidate the results.
Applying Ash Analysis in Your Laboratory
The data from a muffle furnace is foundational for several key objectives within a food production or research environment.
- If your primary focus is nutritional labeling: Use the total ash value as a key metric for the food's profile and as the starting point for quantifying specific essential minerals.
- If your primary focus is quality control: Regularly monitor the ash content of raw ingredients and finished products to ensure consistency and verify the proper addition of mineral fortificants.
- If your primary focus is food safety: Use the resulting ash as a concentrated sample to efficiently test for the presence of heavy metals or other inorganic contaminants.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace provides a foundational measurement that underpins the nutritional integrity, quality, and safety of food products.
Summary Table:
| Application | Purpose | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Nutritional Labeling | Determine total mineral content (ash) | Provides data for accurate nutritional facts |
| Quality Control | Monitor ingredient & product consistency | Ensures product quality and proper fortification |
| Food Safety | Test for inorganic contaminants (e.g., heavy metals) | Concentrates sample for efficient safety analysis |
Ready to enhance the accuracy of your food analysis?
A reliable muffle furnace is the cornerstone of precise nutritional labeling and quality control. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including muffle furnaces designed for the rigorous demands of food laboratories. Our solutions ensure contaminant-free ashing for accurate mineral content measurement, helping you guarantee product quality and safety.
Contact us today to find the perfect furnace for your lab's needs and ensure the integrity of your food products. Get in touch with our experts now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the parts of a muffle furnace? Uncover the Core Components for Precision Heating
- How long does heating take on a muffle furnace? Unlock the Key Factors for Your Lab's Efficiency
- What is the primary use of furnace in the chemical industry? Master Thermal Treatment for Material Transformation
- What is the heating mechanism of a muffle furnace? Achieve Clean, Uniform High-Temperature Processing
- What is the difference between a lab furnace and a lab oven? Choose the Right Heating Tool for Your Lab



















