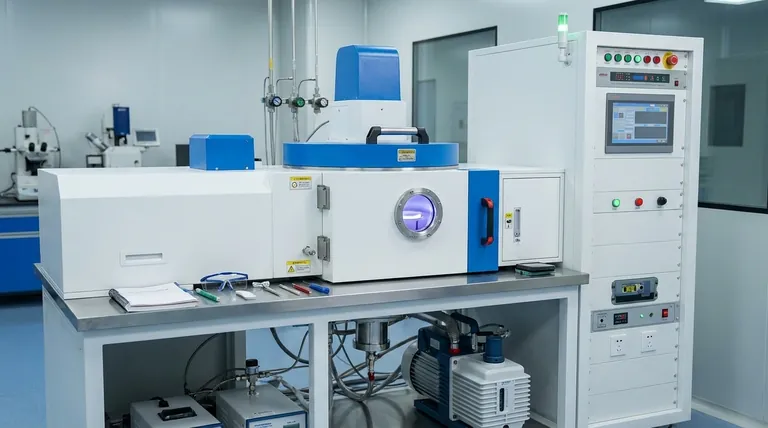
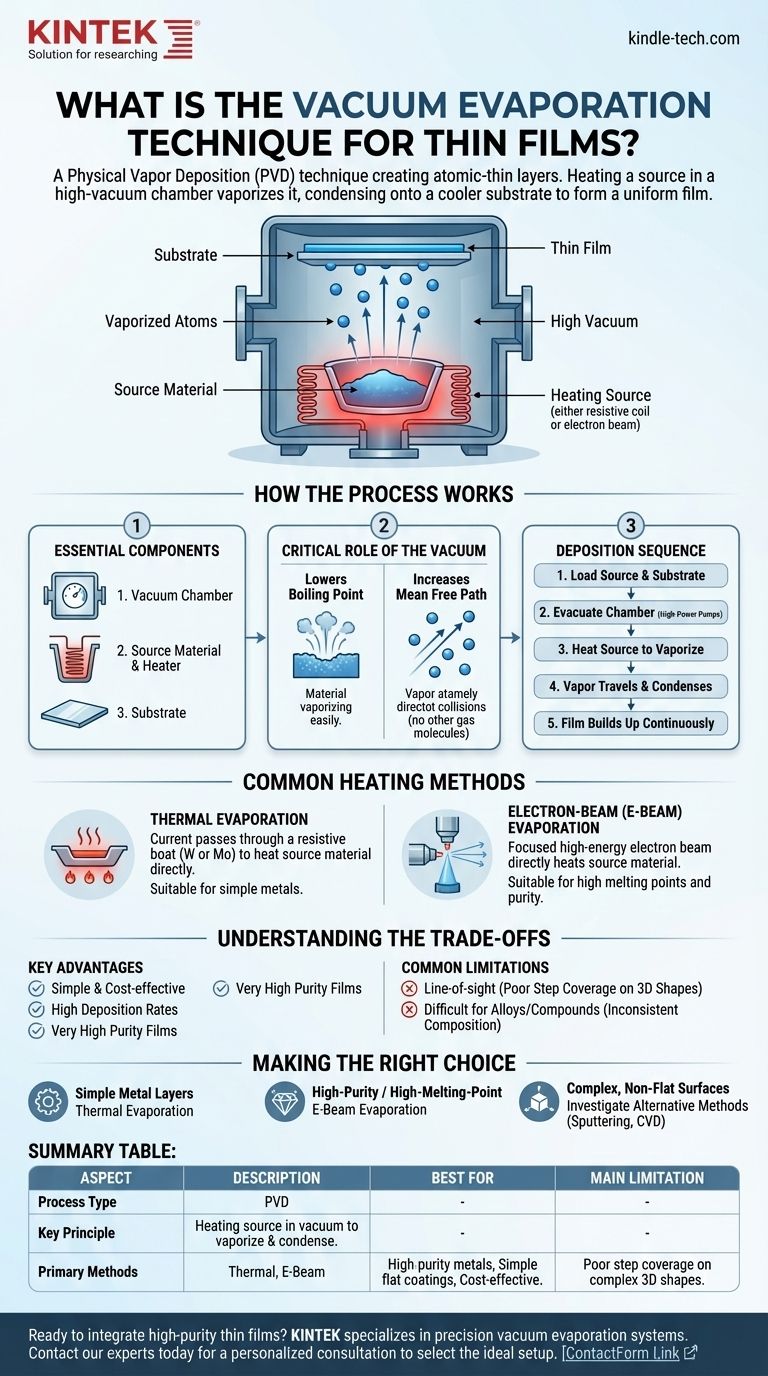
At its core, vacuum evaporation is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) technique used to create extremely thin layers of material, often just atoms thick. The process involves heating a source material inside a high-vacuum chamber until it vaporizes. These vaporized atoms then travel through the vacuum and condense onto a cooler target surface, known as a substrate, forming a uniform thin film.
The essential principle of vacuum evaporation is using a vacuum to both lower a material's boiling point and clear a path for its vapor to travel directly to a target. This allows for the controlled, line-of-sight deposition of a pure material layer.

How the Process Works
To understand vacuum evaporation, it's best to break it down into its core components and the sequence of events. The elegance of the technique lies in its physical simplicity.
The Essential Components
Every vacuum evaporation system consists of three key parts working together:
- A vacuum chamber that houses the entire process.
- A source material (evaporant) and a method to heat it.
- A substrate, which is the object being coated.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
Creating a high vacuum is the most critical step. Removing air and other gas molecules from the chamber accomplishes two essential goals.
First, it dramatically lowers the boiling point of the source material. Just as water boils at a lower temperature at high altitudes, all materials vaporize more easily in a vacuum.
Second, and more importantly, it increases the mean free path of the vaporized atoms. This means the evaporated atoms can travel directly from the source to the substrate in a straight line without colliding with other gas molecules, which would otherwise scatter them and introduce impurities into the film.
The Deposition Sequence
The process follows a straightforward sequence:
- The source material and the substrate are placed inside the vacuum chamber.
- High-power pumps evacuate the chamber to create a vacuum.
- The source material is heated until it begins to vaporize (or sublime).
- The vapor travels in a straight line and condenses on the cooler substrate.
- Over time, these condensed atoms build up to form a continuous thin film.
Common Heating Methods
The primary distinction between different types of vacuum evaporation lies in how the source material is heated.
Thermal Evaporation
This is the most common and straightforward method. The source material is placed in a small, electrically resistive "boat" or crucible, typically made of tungsten or molybdenum.
A high electrical current is passed through the boat, causing it to heat up rapidly due to resistance. This heat is transferred to the source material, causing it to evaporate.
Electron-Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation
For materials with very high melting points (like platinum or ceramics), thermal evaporation is insufficient. E-beam evaporation uses a focused, high-energy beam of electrons to directly heat the source material.
This method deposits energy with incredible precision and intensity, allowing for the vaporization of a wider range of materials. It is also considered a "cleaner" process, as the surrounding crucible is not heated to the same degree, reducing the risk of contamination.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any technical process, vacuum evaporation has clear advantages and specific limitations that make it suitable for some applications but not others.
Key Advantages
Vacuum evaporation is widely used because it is relatively simple and cost-effective, especially for standard thermal systems.
The process can achieve high deposition rates, making it efficient for production. It also produces films of very high purity since the process occurs in a vacuum with minimal contaminants.
Common Limitations
The most significant drawback is its line-of-sight nature. Because the vapor travels in a straight line, it cannot easily coat complex, three-dimensional shapes or the sides of features on a substrate. This results in poor step coverage.
Furthermore, it can be difficult to deposit alloys or compound materials consistently. If the source material is made of elements with different boiling points, the more volatile element will evaporate first, changing the composition of the resulting film over time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition technique depends entirely on the requirements of the final film and the geometry of the part being coated.
- If your primary focus is creating simple metal layers for optics or electronics: Thermal evaporation is an excellent, cost-effective, and reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is depositing high-purity films or high-melting-point materials: E-beam evaporation provides the necessary energy and control.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, non-flat surfaces uniformly: You should investigate alternative methods like sputtering or chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
Vacuum evaporation remains a foundational and powerful technique for creating the high-purity thin films that enable much of modern technology.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) |
| Key Principle | Heating a source material in a vacuum to vaporize it, forming a thin film on a substrate. |
| Primary Methods | Thermal Evaporation, Electron-Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation |
| Best For | High-purity metal layers, simple coatings on flat surfaces, cost-effective production. |
| Main Limitation | Poor step coverage on complex, 3D shapes due to line-of-sight deposition. |
Ready to integrate high-purity thin films into your R&D or production line? The right lab equipment is critical for success. KINTEK specializes in precision vacuum evaporation systems and consumables, serving the exact needs of laboratories in materials science, optics, and semiconductor research. Our experts can help you select the ideal thermal or e-beam evaporation setup to achieve your deposition goals efficiently and reliably. Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and receive a personalized consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Coating Solution for Sensitive Materials
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is plasma CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Sensitive Materials



















