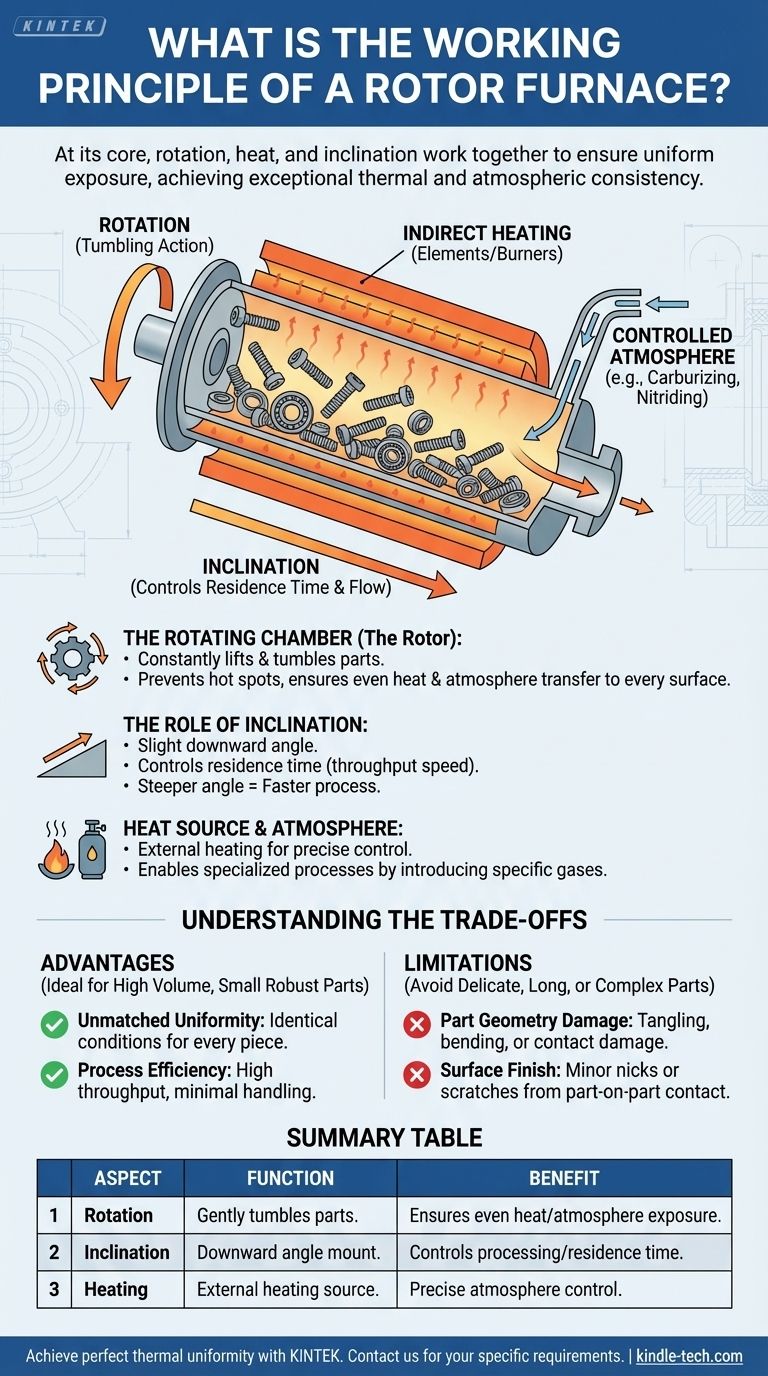
At its core, a rotor furnace operates by using a combination of rotation, heat, and a slight incline to process materials. It consists of a cylindrical chamber (the rotor or retort) that spins slowly on its axis. This constant, gentle tumbling action ensures that every surface of the material being processed is uniformly exposed to the controlled heat and atmosphere inside the furnace.
The defining principle of a rotor furnace is not just about applying heat, but achieving exceptional thermal and atmospheric uniformity. This is accomplished through the continuous, gentle tumbling of the workpiece as it moves through the heated chamber.

Deconstructing the Core Mechanism
To truly understand the furnace, we must look at how its three primary design elements—rotation, inclination, and heating—work in concert.
The Rotating Chamber (The Rotor)
The central component is the cylindrical retort which holds the workpieces. As this chamber rotates, it constantly lifts and tumbles the parts inside.
This motion is critical for preventing hot spots and ensuring that heat is transferred evenly to every single part and every surface of each part. It eliminates the inconsistencies that can occur in static furnaces where some parts may shield others from the heat source.
The Role of Inclination
Rotor furnaces are mounted at a slight downward angle. This tilt is a simple yet brilliant mechanism for process control.
The angle of inclination, combined with the speed of rotation, dictates the residence time—how long the material spends inside the furnace. A steeper angle results in a faster throughput, while a shallower angle increases the processing time for each part. This allows operators to precisely control the duration of the heat treatment cycle.
Heat Source and Atmosphere
The furnace is heated externally, typically by electrical resistance elements or gas burners surrounding the rotating retort. This indirect heating method transfers energy through the retort's wall to the workpieces via conduction and radiation.
Crucially, because the heating is external, the internal atmosphere can be precisely controlled. Specialized gases can be introduced to perform specific metallurgical processes like carburizing, nitriding, or carbonitriding, where the surface chemistry of the steel parts is intentionally altered.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the rotor furnace design is not universally applicable. Its unique mechanism presents clear advantages but also specific limitations.
Advantage: Unmatched Uniformity
For high volumes of small parts, no other batch furnace system can match the part-to-part uniformity of a rotor furnace. The tumbling action guarantees that every piece experiences nearly identical time, temperature, and atmospheric conditions, leading to highly consistent results.
Advantage: Process Efficiency
These furnaces are ideal for processing large quantities of small, bulk-loaded components like screws, bearings, clips, and other fasteners. The continuous-batch nature allows for high throughput with minimal manual handling compared to loading individual parts into racks or baskets.
Limitation: Part Geometry and Damage
The tumbling action that provides such great uniformity is also its main drawback. The process is not suitable for parts that are long, thin, delicate, or complex, as they can become tangled, bent, or damaged by the part-on-part contact.
Limitation: Surface Finish
The same part-on-part contact can cause minor nicks, scratches, or wear on component surfaces. Therefore, rotor furnaces are not recommended for parts where a pristine cosmetic or precision surface finish is a critical requirement.
Is a Rotor Furnace Right for Your Application?
Choosing the correct furnace technology depends entirely on the part's geometry, material, and the desired outcome of the heat treatment process.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, uniform heat treatment of small, robust parts (like fasteners, bearings, or chain links): A rotor furnace is an exceptionally efficient and reliable choice that delivers superior consistency.
- If your primary focus is treating large, delicate, or geometrically complex parts that cannot be tumbled: You must consider alternative technologies like a mesh belt, pusher, or static box furnace.
- If your primary focus is achieving a specific surface chemistry (like case hardening) on many small components: The excellent atmosphere control and thermal uniformity of a rotor furnace make it a superior option.
By understanding the principle of controlled tumbling, you can effectively leverage the unique efficiency of a rotor furnace for the right application.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Rotation | Gently tumbles parts inside the chamber. | Ensures even heat and atmosphere exposure for every part. |
| Inclination | The furnace is mounted at a downward angle. | Controls the processing time (residence time) of the parts. |
| Heating | External heating (e.g., electrical elements). | Allows for precise control of the internal processing atmosphere. |
| Ideal For | Small, robust parts (bearings, screws, fasteners). | Provides unmatched part-to-part uniformity and high throughput. |
Ready to achieve perfect thermal uniformity for your high-volume small parts?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced laboratory equipment, including rotor furnaces, designed to meet the demanding needs of modern labs. Our solutions ensure exceptional process control, efficiency, and consistency for applications like carburizing and nitriding.
If you process small, robust components and require superior results, our experts can help you determine if a rotor furnace is the right choice for your operation.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific heat treatment requirements and discover how our lab equipment can enhance your productivity and quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Does pyrolysis produce carbon monoxide? Harnessing Syngas for Energy and Safety
- What is a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity for Your Industrial Processes
- What is the process of pyrolysis example? Transform Waste into Value with Thermal Decomposition
- What are the three stages of pyrolysis? Turn Waste into Biochar, Bio-Oil & Syngas
- What is the difference between incineration pyrolysis and gasification? Mastering Thermal Conversion Technologies
- What can you do with pyrolysis oil? Turn Waste into Power, Fuel, and Chemicals
- What is the rotary kiln process? A Guide to Efficient High-Temperature Material Processing
- What is the temperature of the rotary furnace? It Depends on the Heating Method



















