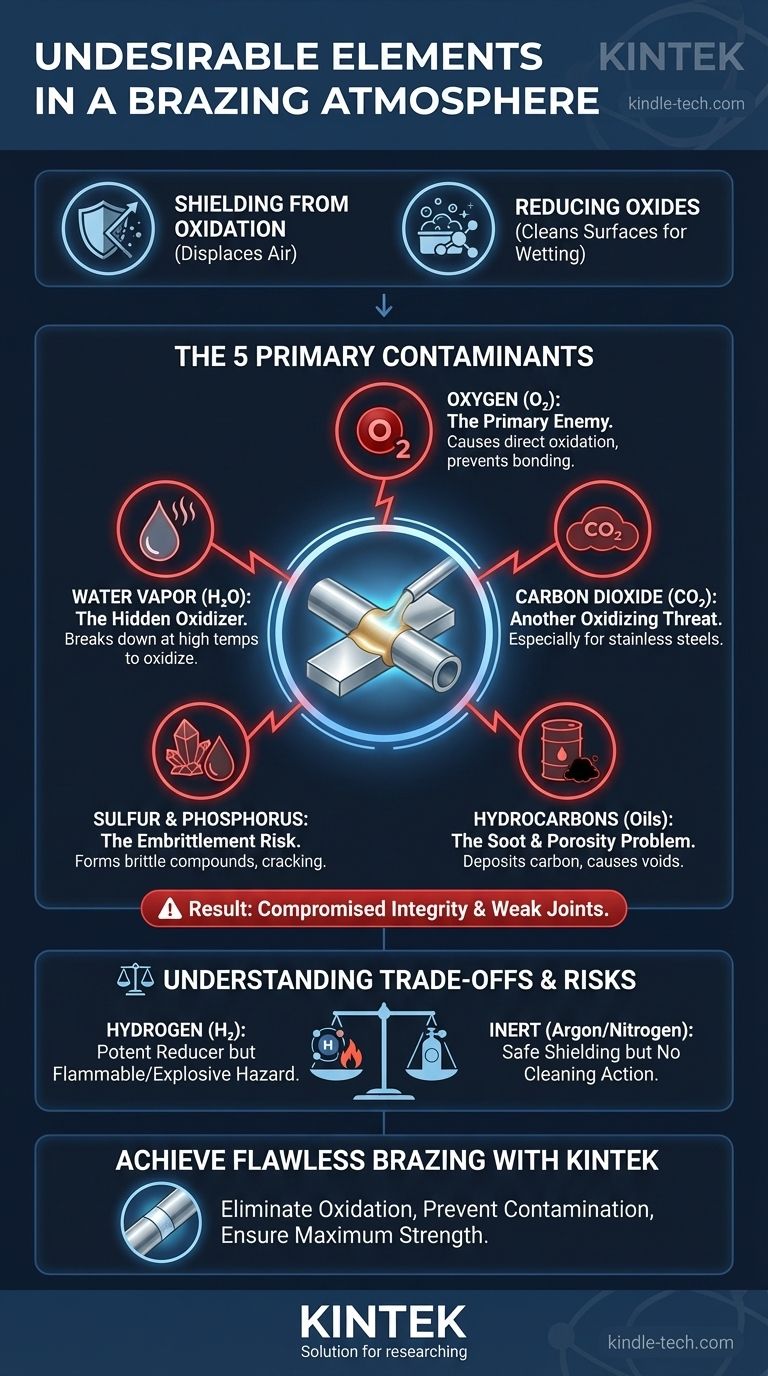
In brazing, the most undesirable elements in an atmosphere are those that cause oxidation and contamination. Chief among these are oxygen (O₂), water vapor (H₂O), and carbon dioxide (CO₂), as they actively prevent the braze filler metal from bonding with the base metals. Other harmful contaminants include sulfur compounds and residual oils or lubricants, which can compromise the integrity and strength of the final joint.
The fundamental purpose of a brazing atmosphere is to protect parts from oxidation and allow the filler metal to flow freely. Therefore, any atmospheric component that introduces oxygen or otherwise contaminates the metal surfaces at brazing temperatures is highly undesirable as it directly undermines the success of the process.

The Core Function of a Brazing Atmosphere
To understand what makes an atmosphere undesirable, we must first establish its purpose. A controlled atmosphere in brazing serves two critical functions.
### Function 1: Shielding from Oxidation
As metals are heated, their rate of reaction with oxygen in the air increases dramatically. This reaction forms a layer of metallic oxide on the surface.
A proper brazing atmosphere, typically composed of inert or reducing gases, displaces the surrounding air. This creates a protective shield that prevents these oxides from forming on the parts during the heating cycle.
### Function 2: Reducing Existing Oxides
An ideal atmosphere goes beyond simple protection; it actively cleans the parts. Reducing atmospheres, such as those containing hydrogen (H₂), can chemically react with and remove light, pre-existing oxides from the metal surfaces.
This cleaning action, known as "reduction," is crucial for promoting wetting, which is the ability of the molten braze filler metal to spread smoothly across the base metal surfaces.
Key Undesirable Contaminants and Their Effects
Any gas or vapor that interferes with the core functions of shielding and reducing is a contaminant. The level of harm depends on the specific base metals being joined.
### Oxygen (O₂): The Primary Enemy
Oxygen is the most direct cause of oxidation. Even small leaks in a furnace or contaminated gas supply can introduce enough oxygen to form oxide films that act as a barrier, preventing the braze filler metal from adhering to the parts.
### Water Vapor (H₂O): The Hidden Oxidizer
Water vapor is a particularly insidious contaminant. At the high temperatures required for brazing, water molecules (H₂O) can break down, releasing their oxygen to aggressively oxidize the metal surfaces.
The concentration of water vapor is measured by its dew point—the temperature at which the vapor would condense into liquid water. A lower dew point indicates a drier, and therefore better, brazing atmosphere.
### Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): Another Oxidizing Threat
Similar to water vapor, carbon dioxide can become an oxidizing agent at brazing temperatures, especially for metals containing chromium, manganese, or titanium (like stainless steels). The CO₂ can break down and release oxygen, creating stubborn oxides.
### Sulfur and Phosphorus Compounds: The Embrittlement Risk
Sulfur can be introduced from contaminated gas supplies or from residual cutting oils left on the parts. It can react with certain base metals, like nickel alloys, to form low-melting-point compounds along the grain boundaries, leading to severe cracking and a brittle joint.
### Hydrocarbons (Oils and Lubricants): The Soot and Porosity Problem
If parts are not thoroughly cleaned, residual oils and lubricants will vaporize during heating. These hydrocarbon molecules can break down and deposit carbon (soot) onto the part surface, inhibiting filler metal flow. They can also decompose into gases that become trapped in the joint, causing porosity.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Dangers
Choosing an atmosphere involves balancing its effectiveness with its cost and safety considerations. What is undesirable in one context may be a necessary risk in another.
### The Hydrogen Dilemma: Potent Reducer, Potential Hazard
Hydrogen is an excellent reducing agent, making it highly desirable for cleaning oxides from difficult-to-braze materials like stainless steels.
However, as a pure gas or in high concentrations, hydrogen is flammable and explosive when mixed with air. Furnaces using hydrogen require sophisticated safety systems to monitor for oxygen and to burn off excess gas, adding complexity and cost to the operation.
### Inert vs. Active Atmospheres: A Balancing Act
Inert atmospheres, like pure argon, are excellent for shielding but provide no cleaning action. They are safe but can't remove pre-existing oxides.
Active atmospheres, like a nitrogen-hydrogen blend, provide both shielding and reducing. The trade-off is the added complexity and safety risk associated with handling hydrogen. The choice depends on the cleanliness of the parts and the type of metal being brazed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ensuring a clean atmosphere is about controlling inputs: the purity of your supplied gas, the integrity of your furnace, and the cleanliness of your parts.
- If your primary focus is brazing common carbon steels: A less pure atmosphere (e.g., generated from an endothermic gas generator) may be acceptable, as the oxides formed are more easily reduced.
- If your primary focus is brazing stainless steels or alloys with chromium: You must use a very dry, high-purity atmosphere with a low dew point (typically below -40°C / -40°F) to prevent the formation of stubborn chromium oxides.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint integrity for critical applications: A vacuum atmosphere or a high-purity inert gas like argon is often the best choice, as it introduces the fewest potential contaminants.
Ultimately, controlling the brazing atmosphere is the single most important factor in achieving consistent, high-quality, and reliable brazed joints.
Summary Table:
| Undesirable Contaminant | Primary Negative Effect |
|---|---|
| Oxygen (O₂) | Causes surface oxidation, prevents filler metal wetting |
| Water Vapor (H₂O) | Acts as a hidden oxidizer at high temperatures |
| Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) | Oxidizes metals like stainless steel, forms stubborn oxides |
| Sulfur Compounds | Causes embrittlement and cracking in nickel alloys |
| Hydrocarbons (Oils) | Creates soot and porosity, inhibiting joint formation |
Achieve flawless brazing results with KINTEK's expertise.
Don't let atmospheric contaminants compromise your brazed joints. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed to create and maintain the ideal brazing atmosphere for your specific metals and application requirements. Our solutions help you eliminate oxidation, prevent contamination, and ensure maximum joint strength and reliability.
Whether you are brazing carbon steels, stainless steels, or high-performance alloys, we can help you select the right atmosphere control system for consistent, high-quality results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your brazing process and discover how we can enhance your joint integrity and production efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is meant by inert atmosphere? A Guide to Preventing Oxidation & Ensuring Safety
- What is the role of an atmosphere-controlled tube furnace in Cu-Mo sintering? Achieve High-Purity Densification
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- How does an atmosphere furnace facilitate the post-treatment of nickel-plated carbon fibers? Ensure Peak Bonding
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2



















