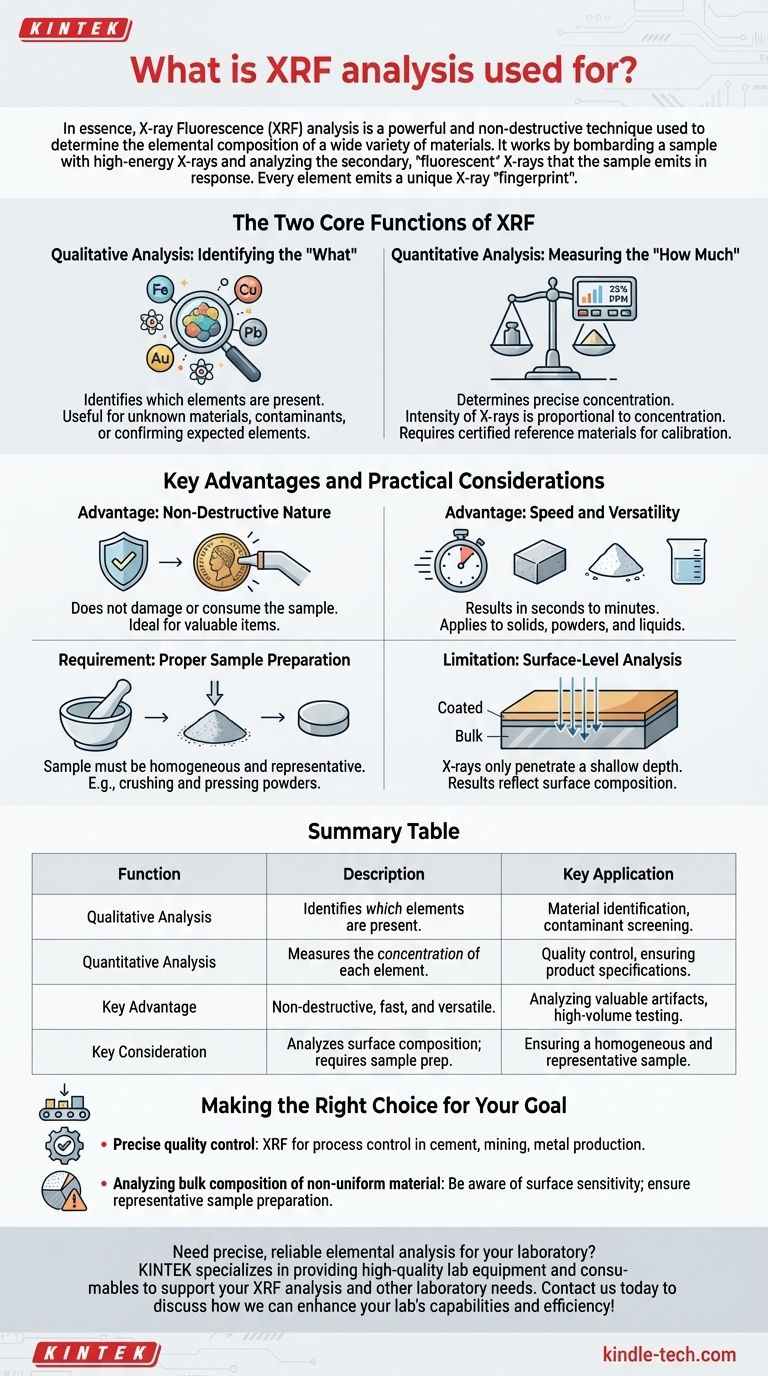
In essence, X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) analysis is a powerful and non-destructive technique used to determine the elemental composition of a wide variety of materials. It works by bombarding a sample with high-energy X-rays and analyzing the secondary, "fluorescent" X-rays that the sample emits in response. This allows you to identify which elements are present and, with proper calibration, exactly how much of each element exists.
The core principle of XRF is that every element emits a unique X-ray "fingerprint" when excited. By reading these fingerprints, the analyzer can rapidly create a detailed list of the elements within a sample and their relative concentrations.
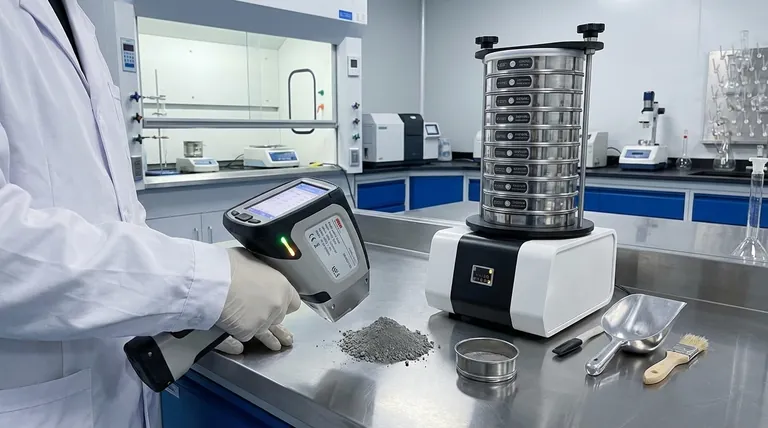

The Two Core Functions of XRF
XRF analysis is typically performed in one of two modes, depending on the information you need to extract from the sample.
Qualitative Analysis: Identifying the "What"
Qualitative analysis is the process of identifying which elements are present in a sample, without regard to their specific amounts.
Each element on the periodic table emits fluorescent X-rays at a specific, characteristic energy level. The XRF instrument detects these energy levels, effectively creating a list of all the elements it can see in the material.
This function is incredibly useful for identifying unknown materials, screening for contaminants, or confirming the presence of expected elements.
Quantitative Analysis: Measuring the "How Much"
Quantitative analysis goes a step further to determine the precise concentration of each identified element.
The intensity of the characteristic X-rays emitted by an element is directly proportional to its concentration in the sample. A stronger signal means more of that element is present.
To get accurate numbers, the instrument's reading of the unknown sample is compared against measurements from certified reference materials with known concentrations. This calibration allows the device to report elemental composition in percentages or parts-per-million (PPM).
Key Advantages and Practical Considerations
While powerful, the effectiveness of XRF depends on understanding both its benefits and its operational requirements.
Advantage: Non-Destructive Nature
A major benefit of XRF is that it is typically non-destructive. The analysis does not damage or consume the sample, making it ideal for testing valuable items like jewelry, archaeological artifacts, or critical industrial components that must be returned to service.
Advantage: Speed and Versatility
XRF analyzers can deliver results in seconds to minutes, making them highly efficient for high-volume testing, such as in quality control or scrap metal sorting. The technique can be applied to solids, powders, and liquids, highlighting its versatility.
Requirement: Proper Sample Preparation
The accuracy of an XRF measurement is directly impacted by the quality of the sample. For the most reliable quantitative results, the sample must be homogeneous and representative of the entire material.
Common preparation steps include crushing and grinding powders, then pressing them into a solid pellet. This ensures the surface being measured is flat and uniform, minimizing analytical errors.
Limitation: Surface-Level Analysis
XRF is fundamentally a surface analysis technique. The X-rays only penetrate a shallow depth into the material, meaning the results reflect the composition of the surface, not necessarily the bulk material underneath.
This is a critical consideration for coated, corroded, or non-homogeneous materials, where the surface may be different from the interior.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Use this guide to determine if XRF is the appropriate tool for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is rapid material identification and sorting: XRF is an exceptional choice for quickly confirming alloy grades, checking raw material purity, or screening for restricted elements in consumer goods.
- If your primary focus is precise quality control: XRF provides the accurate, quantitative data needed for process control in industries like cement, mining, or metal production to ensure products meet exact specifications.
- If your primary focus is analyzing the bulk composition of a non-uniform material: Be aware of XRF's surface sensitivity and ensure your sample preparation creates a truly representative surface for analysis.
Ultimately, understanding these core functions and limitations allows you to effectively leverage XRF as a powerful tool for elemental analysis.
Summary Table:
| Function | Description | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Qualitative Analysis | Identifies which elements are present. | Material identification, contaminant screening. |
| Quantitative Analysis | Measures the concentration of each element. | Quality control, ensuring product specifications. |
| Key Advantage | Non-destructive, fast, and versatile. | Analyzing valuable artifacts, high-volume testing. |
| Key Consideration | Analyzes surface composition; requires sample prep. | Ensuring a homogeneous and representative sample. |
Need precise, reliable elemental analysis for your laboratory?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to support your XRF analysis and other laboratory needs. Our expertise ensures you have the right tools for accurate material identification and quality control.
Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's capabilities and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
People Also Ask
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research
- Why is a laboratory electromagnetic vibratory sieve shaker used? Optimize Walnut Shell Chemical Pretreatment
- What function does a sieving system perform during HPS powder pretreatment? Ensure Uniform Particle Size Distribution
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy

















