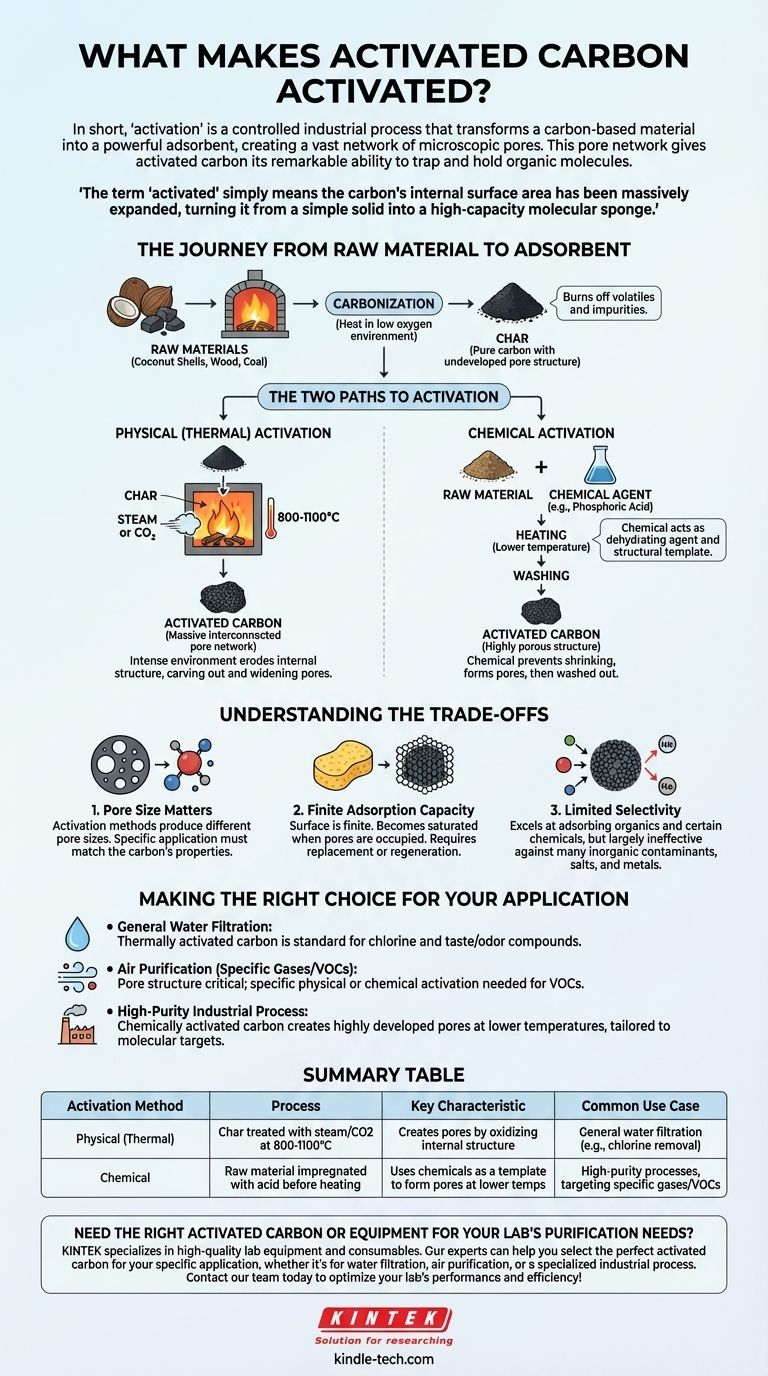
In short, 'activation' is a controlled industrial process that transforms a carbon-based material into a powerful adsorbent. This process uses either high heat or chemical treatment to create an incredibly vast network of microscopic pores within the carbon structure. This pore network is what gives activated carbon its remarkable ability to trap and hold organic molecules.
The term 'activated' does not refer to an electrical charge or chemical reactivity. It simply means the carbon's internal surface area has been massively expanded, turning it from a simple solid into a high-capacity molecular sponge.
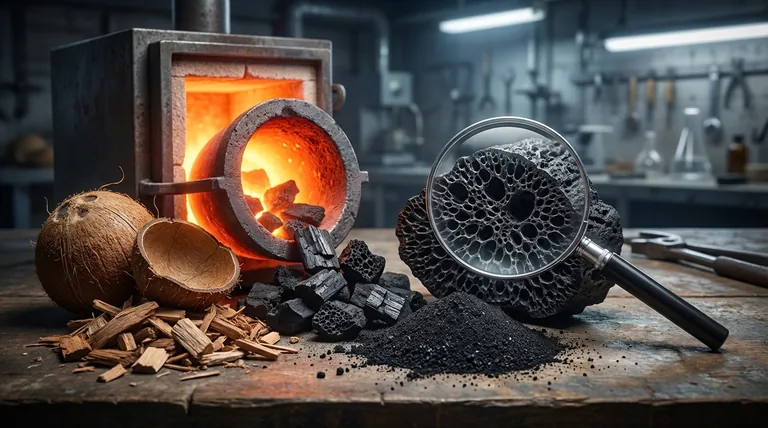

The Journey from Raw Material to Adsorbent
Before carbon can be "activated," it must first be created from a raw organic source. This foundational step sets the stage for the crucial activation process that follows.
Step 1: Carbonization
The process begins with carbon-rich raw materials like coconut shells, wood, or coal. These materials are heated to very high temperatures in an environment with little to no oxygen.
This process, called carbonization, burns off all the volatile compounds and impurities. What remains is a substance called char, which is almost pure carbon, but its internal pore structure is still undeveloped and inefficient.
Step 2: The Activation Process
This is the critical step that creates the vast internal surface area. The char is subjected to one of two primary methods to open up and expand its internal structure, creating a labyrinth of pores.
The Two Paths to Activation
The method chosen for activation directly impacts the final properties of the carbon, such as pore size and distribution, which in turn determines its best application.
Physical (Thermal) Activation
In this method, the carbonized char is exposed to an oxidizing atmosphere, typically steam or carbon dioxide, at extremely high temperatures (usually 800-1100°C).
This intense environment essentially erodes the internal structure of the carbon. The hot gases etch away at the carbon atoms, carving out and widening the existing microscopic pores to create a massive interconnected network.
Chemical Activation
Alternatively, before carbonization, the raw material can be impregnated with a chemical agent, such as phosphoric acid. The mixture is then heated to a lower temperature than in physical activation.
The chemical acts as a dehydrating agent and a structural template. As the material is heated, the chemical prevents it from shrinking and helps to form the porous structure, which is then washed out, leaving behind the highly porous activated carbon.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly effective, activated carbon is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly.
Pore Size Matters
Different activation methods produce different pore size distributions. A carbon activated for capturing large molecules in a liquid might be ineffective at capturing small gas molecules, and vice versa. The specific application must match the carbon's properties.
Finite Adsorption Capacity
The surface of activated carbon is finite. Once all the available pore surfaces are occupied by contaminant molecules, the carbon becomes saturated and can no longer adsorb anything else. At this point, it must be replaced or regenerated.
Limited Selectivity
Activated carbon excels at adsorbing organic compounds and certain chemicals. However, it is largely ineffective against many inorganic contaminants, dissolved salts, and metals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The choice between activation methods is driven entirely by the intended use case, balancing performance requirements with manufacturing costs.
- If your primary focus is general water filtration: Thermally activated carbon is often the standard, effectively removing chlorine and common organic taste-and-odor compounds.
- If your primary focus is purifying air from specific gases: The pore structure is critical, and a specific type of physically or chemically activated carbon may be required to target smaller volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- If your primary focus is a high-purity industrial process: Chemically activated carbon may be chosen for its ability to create a highly developed pore structure at lower temperatures, tailored to very specific molecular targets.
Ultimately, "activation" is the engineered process that unlocks carbon's immense potential as a high-performance purification tool.
Summary Table:
| Activation Method | Process | Key Characteristic | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical (Thermal) | Char is treated with steam/CO2 at 800-1100°C | Creates pores by oxidizing internal structure | General water filtration (e.g., chlorine removal) |
| Chemical | Raw material is impregnated with acid before heating | Uses chemicals as a template to form pores at lower temps | High-purity processes, targeting specific gases/VOCs |
Need the right activated carbon or equipment for your lab's purification needs?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables. Our experts can help you select the perfect activated carbon for your specific application, whether it's for water filtration, air purification, or a specialized industrial process. Contact our team today to optimize your lab's performance and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Three-Necked Round Bottom Flask
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- What is the proper procedure for cleaning a glassy carbon sheet after use? A Definitive Guide to Ensure Reliable Results
- What is the applicable potential range for an RVC glassy carbon sheet? Master Your Electrochemical Analysis
- What are the typical physical specifications for glassy carbon sheets? Unlock Superior Performance for Your Lab
- Why is a glassy carbon disc electrode an indispensable consumable? Ensure Reliable Catalyst Evaluation Today
- What is the porosity of an RVC glassy carbon sheet? Understanding the Critical Difference Between PPI and Porosity



















