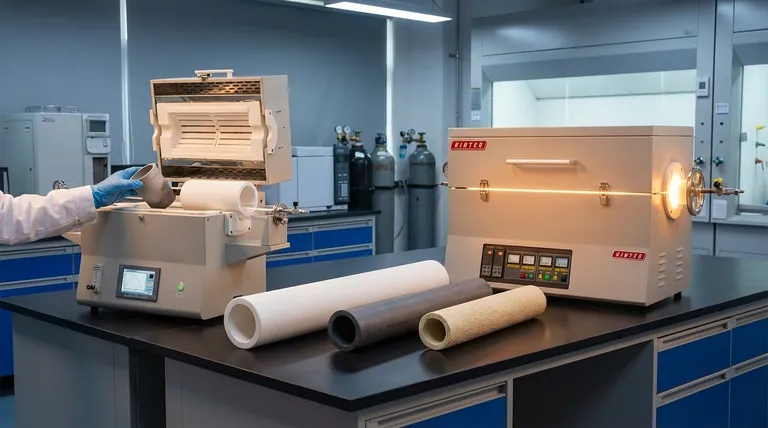
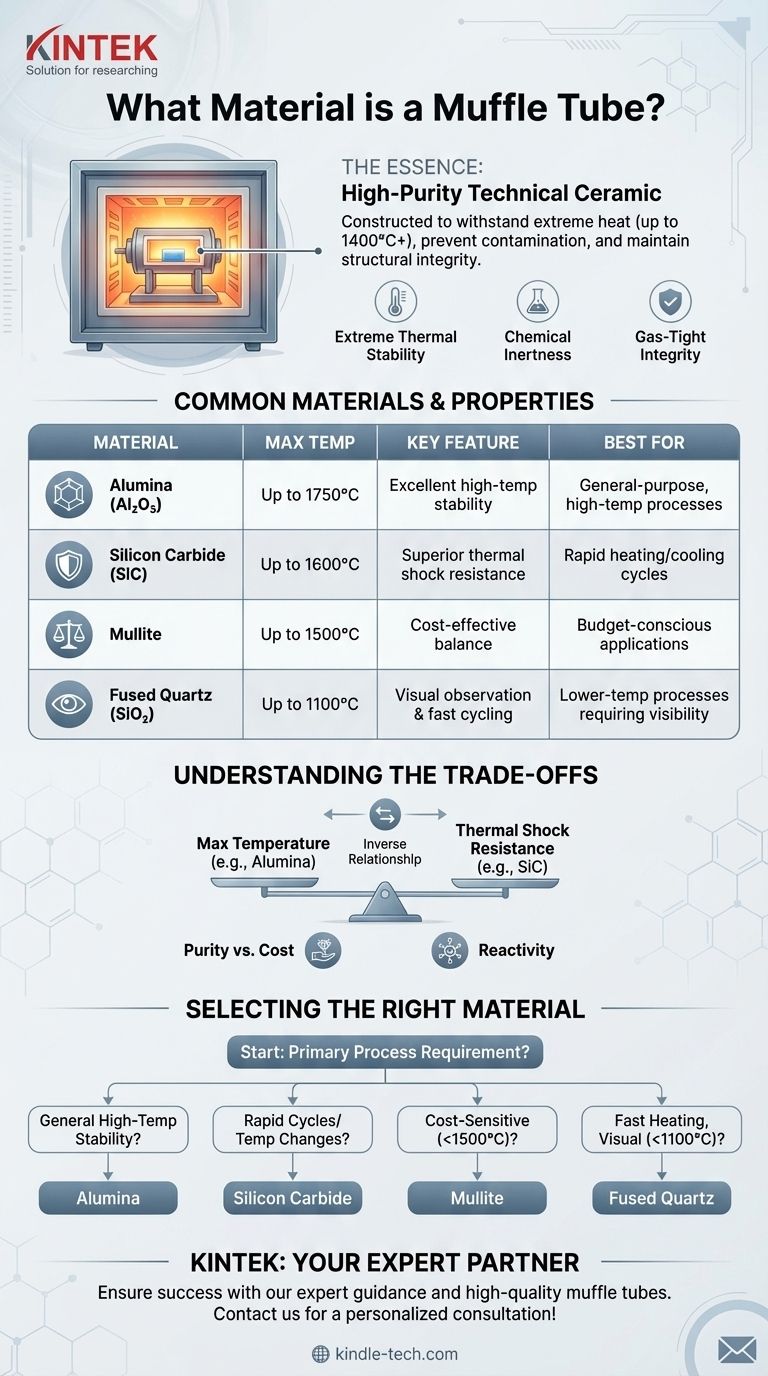
In essence, a muffle tube is constructed from a high-purity technical ceramic. These materials are chosen for their exceptional ability to withstand extreme heat, often up to 1400°C or higher, without melting, deforming, or reacting with the materials being processed. The most common materials used are alumina and silicon carbide, which form a stable and protective inner chamber for high-temperature furnace operations.
The choice of a muffle tube material is not simply about resisting heat. It is a critical decision based on a balance between maximum operating temperature, resistance to thermal shock, and chemical compatibility with your specific process atmosphere.

Why Ceramics are the Industry Standard
The function of a muffle tube is to create an isolated, controlled environment within a furnace. The material used must be able to perform reliably under extreme conditions, which is why technical ceramics are the universal choice.
Extreme Thermal Stability
Ceramics like alumina possess very high melting points. This core property ensures the tube maintains its structural integrity and does not contaminate the sample, even when held at temperatures exceeding 1400°C for extended periods.
Chemical Inertness
A muffle tube must isolate the sample from the furnace's heating elements and, more importantly, must not react with the sample or any process gases introduced. High-purity ceramics are highly inert, preventing unwanted chemical reactions that could compromise the results of a process.
Gas-Tight Integrity
For processes requiring a controlled atmosphere (such as inert gas or a vacuum), the tube material must be non-porous or "gas-tight." High-density ceramics are manufactured to prevent gases from leaking into or out of the tube, ensuring the internal atmosphere remains pure.
A Closer Look at Common Muffle Tube Materials
While "ceramic" is the general answer, the specific type of ceramic used depends heavily on the application's demands.
Alumina (Aluminum Oxide, Al₂O₃)
Alumina is the most common and versatile material for muffle tubes. Its high purity, excellent performance at sustained high temperatures (often up to 1750°C), and good chemical resistance make it the workhorse for general laboratory and industrial use.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Silicon carbide is chosen for more demanding applications. Its key advantage is superior thermal shock resistance, meaning it is far less likely to crack during rapid heating or cooling cycles. It also has excellent thermal conductivity, which can promote more uniform heating.
Mullite (Aluminosilicate)
Mullite is a cost-effective alternative to high-purity alumina. It offers a good balance of thermal properties, including excellent thermal shock resistance, but typically has a lower maximum operating temperature than alumina.
Fused Quartz (SiO₂)
Quartz tubes are used for applications that require very rapid thermal cycling and, crucially, allow for visual observation of the process. However, their maximum service temperature is significantly lower than that of alumina, usually around 1100°C.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the wrong material can lead to failed experiments, damaged equipment, or contaminated samples. Understanding the inherent trade-offs is key.
Temperature vs. Thermal Shock
There is often an inverse relationship between maximum temperature and thermal shock resistance. High-purity alumina is excellent for stable, high-temperature work but can easily crack if cooled too quickly. Silicon carbide, while sometimes having a lower absolute maximum temperature, excels in applications with repeated heating and cooling cycles.
Purity vs. Cost
Higher purity directly correlates with higher cost. A 99.8% pure alumina tube will be significantly more expensive than a mullite tube. For ultra-sensitive processes where any contamination is unacceptable, high-purity material is non-negotiable. For less sensitive, high-volume work, a more economical ceramic may suffice.
Reactivity in Specific Atmospheres
While generally inert, no material is perfect. At very high temperatures, even technical ceramics can react with aggressive atmospheres. For example, quartz can devitrify, and certain reducing atmospheres can degrade specific types of alumina over time. Always verify material compatibility with your specific process gases.
Selecting the Right Material for Your Application
Use your primary process requirement as the deciding factor when choosing a muffle tube.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose, high-temperature stability (up to 1750°C): High-purity Alumina is the industry-standard choice for reliability and chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus involves rapid temperature changes or frequent thermal cycling: Silicon Carbide is the superior choice to prevent cracking and ensure long service life.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive applications below 1500°C: Mullite provides a reliable and economical balance of thermal properties.
- If your primary focus is fast heating and visual monitoring at lower temperatures (below 1100°C): Fused Quartz is the only practical option.
Understanding these material properties empowers you to select the precise tool needed to ensure the integrity and success of your high-temperature process.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | Up to 1750°C | Excellent high-temperature stability | General-purpose, high-temperature processes |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to 1600°C | Superior thermal shock resistance | Rapid heating/cooling cycles |
| Mullite | Up to 1500°C | Cost-effective balance | Budget-conscious applications |
| Fused Quartz (SiO₂) | Up to 1100°C | Visual observation & fast cycling | Lower-temperature processes requiring visibility |
Ensure Your High-Temperature Processes are a Success
Choosing the right muffle tube is critical for your application's integrity, safety, and results. The wrong material can lead to contamination, equipment failure, and wasted time.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance and high-quality muffle tubes tailored to your specific needs—whether you require the extreme temperature stability of alumina or the superior thermal shock resistance of silicon carbide.
Let our experts help you select the perfect tube material. We'll ensure you get a durable, reliable solution that matches your process requirements and budget.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Alumina (Al2O3) Furnace Tube for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of LiNbO3-coated NCA? Enhance Battery Performance
- What specific conditions does a tubular furnace provide for the reduction of Pt catalysts? Optimize Your Catalyst Performance
- What is the role of high-precision laboratory tube furnaces in the development of heterojunction photocatalysts?
- What is the primary industrial objective of utilizing a high-temperature drop tube furnace (HDTF)?
- What is the difference between a tube furnace and a box furnace? Choose the Right Heat Treatment Process
- What experimental environment does a tubular flow reactor provide for evaluating TiOx·MOy coatings? Expert Simulation
- What are the common applications for a tube furnace? Essential for Heat Treatment, Synthesis, and Purification
- How do high-temperature tube furnaces or rotary furnaces facilitate the regeneration of spent activated carbon?



















