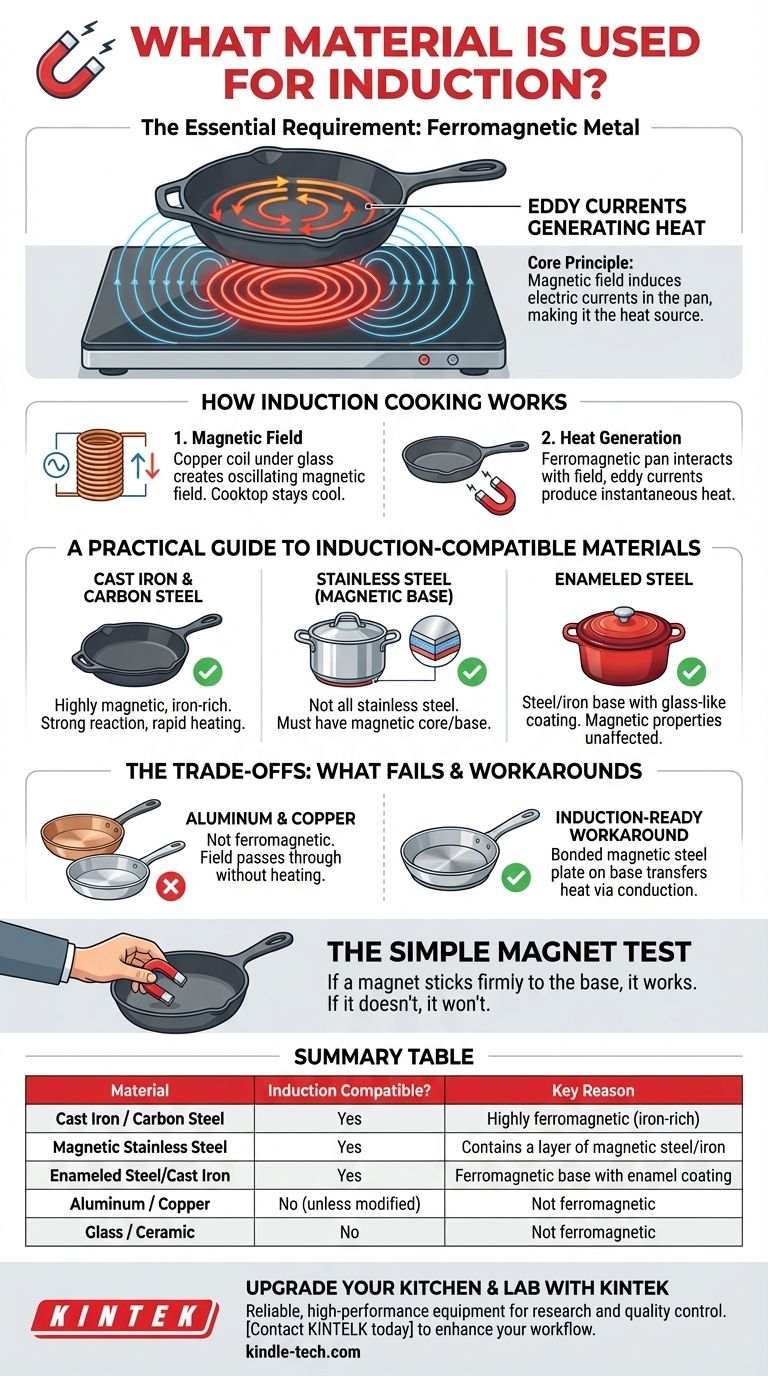
The essential requirement for induction cookware is that it must be made of a ferromagnetic metal. This means materials like cast iron, carbon steel, and certain types of stainless steel will work. Materials that are not magnetic, such as aluminum, copper, and glass, are not compatible on their own.
The core principle is simple: induction cooktops use a magnetic field to generate heat directly within the cookware itself. If a magnet sticks firmly to the base of your pan, it will work with an induction cooktop.

How Induction Cooking Actually Works
To understand which materials are compatible, it's helpful to understand the mechanism that makes induction cooking so efficient. It's a fundamentally different process than thermal conduction used by gas or electric coil stovetops.
The Role of the Magnetic Field
Underneath the flat glass surface of an induction cooktop is a coil of copper wire. When you turn the cooktop on, an alternating electric current flows through this coil, creating a rapidly oscillating magnetic field.
This magnetic field itself does not produce heat. The cooktop surface remains cool to the touch until a compatible pot is placed on it.
Why the Cookware Heats Itself
When you place a ferromagnetic (iron-based) pan on the cooktop, the magnetic field penetrates the metal of the pan. This induces powerful, swirling electric currents, known as eddy currents, within the cookware.
The pan's natural electrical resistance fights against these currents, and this struggle generates significant, instantaneous heat. The pan becomes its own heat source, which is then transferred directly to the food.
A Practical Guide to Induction-Compatible Materials
Knowing the science makes it easy to identify the right materials for the job.
Cast Iron and Carbon Steel
These materials are the most natural partners for induction. They are rich in iron (ferrous metal), making them highly magnetic.
Their high iron content allows for a strong reaction to the magnetic field, resulting in rapid and powerful heating.
Stainless Steel: The Critical Detail
This is the most common point of confusion. Not all stainless steel is magnetic.
Stainless steel is an alloy, and its magnetic properties depend on its composition. To be induction-compatible, it must have a magnetic base or core. High-quality stainless steel cookware designed for induction often has a multi-ply construction with a layer of magnetic steel or iron sealed in the base.
Enameled Steel
Enameled cookware, such as a classic Dutch oven, is almost always induction-compatible.
The cookware is fundamentally made of a steel or cast iron base, which is ferromagnetic. The enamel is simply a glass-like coating that does not interfere with the underlying magnetic properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
Some materials fail on induction cooktops, and some manufacturers use workarounds to achieve compatibility.
Why Aluminum and Copper Fail
Aluminum and copper are excellent heat conductors, but they are not ferromagnetic. A magnet will not stick to them.
Because they are not magnetic, the induction cooktop's magnetic field passes through them without inducing the necessary eddy currents to generate heat.
The "Induction-Ready" Workaround
You will often find aluminum or copper pans advertised as "induction-ready."
Manufacturers achieve this by bonding a plate of magnetic stainless steel or iron to the bottom of the pan. This bottom layer interacts with the cooktop, gets hot, and then transfers that heat to the rest of the aluminum or copper pan via conduction.
The Simple Magnet Test
The most reliable way to determine if your current or potential cookware will work is with a simple magnet. If a common refrigerator magnet sticks firmly to the bottom of the pan, it will work on an induction cooktop. If it doesn't stick or the pull is very weak, it will not work.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of cookware depends on your cooking style and maintenance preferences.
- If your primary focus is heat retention and searing: Cast iron is your best choice due to its mass and powerful heating ability on induction.
- If your primary focus is versatility and easy maintenance: A high-quality, multi-ply stainless steel set with a magnetic base offers excellent performance and is typically dishwasher safe.
- If your primary focus is non-stick performance or a specific color: Look for aluminum pans with a bonded magnetic steel base or enameled steel cookware.
By understanding the simple physics of magnetism, you can confidently select the perfect cookware for your induction cooktop.
Summary Table:
| Material | Induction Compatible? | Key Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Cast Iron / Carbon Steel | Yes | Highly ferromagnetic (iron-rich) |
| Magnetic Stainless Steel | Yes | Contains a layer of magnetic steel/iron |
| Enameled Steel/Cast Iron | Yes | Ferromagnetic base with enamel coating |
| Aluminum / Copper | No (unless modified) | Not ferromagnetic |
| Glass / Ceramic | No | Not ferromagnetic |
Upgrade Your Kitchen with the Right Equipment
Just as you need the right cookware for an induction cooktop, your laboratory needs reliable, high-performance equipment to achieve precise results. KINTEK specializes in supplying top-tier lab equipment and consumables, serving the diverse needs of research and quality control laboratories.
Let us help you equip your lab for success. Contact KINTELK today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Oscillating Orbital Shaker
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a vibratory sieve shaker? Achieve Precise Particle Size Analysis
- What is the use of vibratory sieve shaker? Achieve Precise Particle Size Analysis for Your Lab
- What is the frequency of a vibrating screen? Unlock Optimal Material Separation Efficiency
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis
- What is the principle of vibratory sieve shaker? Achieve Accurate Particle Size Analysis




