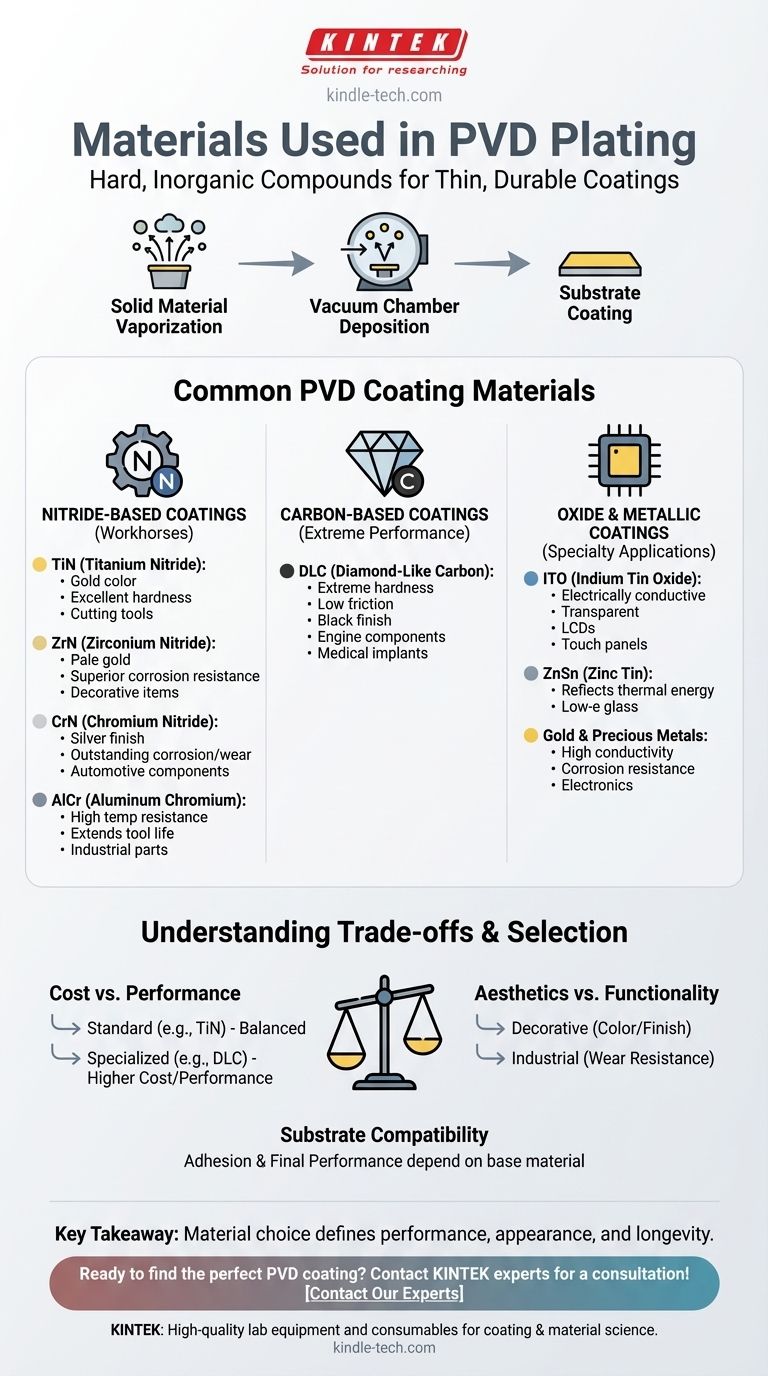
In short, PVD plating primarily uses hard, inorganic materials like nitrides and carbon compounds to create thin, durable coatings. The most common materials include Titanium Nitride (TiN), Zirconium Nitride (ZrN), Chromium Nitride (CrN), and Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC), each chosen for specific properties like hardness, color, and corrosion resistance.
The key takeaway is that the material used in PVD is not an afterthought; it is the central decision that defines the final product's performance, appearance, and longevity. The process is versatile enough to use almost any inorganic material, but a select group has become industry standard for their proven results.

The Principles Behind PVD Material Selection
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a vacuum deposition process where a solid material is vaporized and then condensed onto a substrate as a thin film. This technique allows for precise control over the coating's characteristics.
What Makes a Material Suitable for PVD?
The PVD process can deposit a vast range of inorganic materials and even some organic ones. However, the most effective and widely used materials are chosen for their ability to form a dense, well-adhered layer that enhances the underlying part.
The Goal Dictates the Material
The choice of material is driven entirely by the intended application. A material chosen to protect a high-speed cutting tool from heat and wear will be different from one chosen to give a watch a durable, decorative finish.
A Breakdown of Common PVD Coating Materials
While the list of potential materials is long, most applications rely on a core group known for their exceptional properties. These can be categorized by their chemical composition.
Nitride-Based Coatings (The Workhorses)
Nitrides are compounds of a metal with nitrogen, renowned for their extreme hardness and wear resistance.
- Titanium Nitride (TiN): Known for its distinct gold color and excellent all-around performance. It significantly increases hardness and is widely used on cutting tools, hardware parts, and decorative items.
- Zirconium Nitride (ZrN): Offers a pale gold or brass-like finish. It provides superior corrosion resistance compared to TiN and is often used in similar applications.
- Chromium Nitride (CrN): Provides a bright, metallic silver finish with outstanding corrosion and wear resistance. It's a common choice for automotive components, watches, and jewelry.
- Aluminum Chromium (AlCr): Engineered to withstand high temperatures, this coating is a primary choice for extending the service life of industrial tools and machine parts operating under extreme stress.
Carbon-Based Coatings (For Extreme Performance)
These coatings leverage the unique properties of carbon to achieve exceptionally low friction and high hardness.
- Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC): As its name implies, DLC is an extremely hard, low-friction material with a distinctive black finish. It is the go-to choice for high-performance applications like engine components, medical implants, and premium tools where reducing friction is critical.
Oxide and Metallic Coatings (For Specialty Applications)
This category includes materials chosen for unique optical or electrical properties rather than pure mechanical strength.
- Indium Tin Oxide (ITO): A crucial material in modern electronics. ITO is unique because it is both electrically conductive and optically transparent, making it essential for LCDs, plasma displays, and touch panels.
- Zinc Tin (ZnSn): Primarily used in the manufacturing of low-emissivity (low-e) glass for windows. This coating reflects thermal energy, improving insulation.
- Gold (and other precious metals): Used for both their classic decorative appearance and their functional properties, such as high conductivity and corrosion resistance in electronics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a PVD material involves balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" material, only the most appropriate one for a specific goal.
Cost vs. Performance
Standard coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN) offer a fantastic balance of performance and cost-effectiveness for many applications. More specialized materials like Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) provide superior performance but at a significantly higher price point.
Aesthetics vs. Functionality
For decorative items like watches or faucets, the color and finish (e.g., the silver of CrN or the gold of TiN) are primary drivers. For an industrial drill bit, the high-temperature wear resistance of a material like AlCr is the only thing that matters, regardless of its appearance.
Substrate Compatibility
The base material being coated plays a role in material selection. The adhesion and final performance of the PVD layer depend on its chemical and physical compatibility with the substrate it is being applied to.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final decision should be guided by the primary objective you need to achieve for your product.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance for tools: Prioritize nitride coatings like TiN and AlCr, or select DLC for the most demanding high-performance applications.
- If your primary focus is a decorative finish with high durability: Consider TiN or ZrN for gold tones and CrN for a classic, resilient silver or chrome finish.
- If your primary focus is specialized electronic or optical properties: Your choice is defined by the function, such as using transparent, conductive ITO for displays or ZnSn for thermal glass.
Ultimately, selecting the correct PVD material is how you transform a standard component into a high-performance, durable, and visually appealing product.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Examples | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitride-Based | Titanium Nitride (TiN), Zirconium Nitride (ZrN), Chromium Nitride (CrN) | Extreme Hardness, Wear & Corrosion Resistance | Cutting Tools, Automotive Parts, Decorative Hardware |
| Carbon-Based | Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) | Extreme Hardness, Low Friction, Black Finish | High-Performance Engine Components, Medical Implants |
| Oxide/Metallic | Indium Tin Oxide (ITO), Gold | Electrically Conductive, Optically Transparent, Corrosion Resistance | LCD Displays, Touch Panels, Electronics |
Ready to find the perfect PVD coating for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your coating and material science needs. Whether you're developing cutting tools, decorative finishes, or advanced electronic components, our expertise can help you select and apply the ideal PVD material to enhance your product's performance, durability, and appearance.
Let's discuss your project requirements and achieve superior results together. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
People Also Ask
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers
- What is the process of CVD diamond coating? Grow a Superior, Chemically-Bonded Diamond Layer
- What is CVD diamond coating? Grow a Super-Hard, High-Performance Diamond Layer
- What is diamond coating film? A Thin Layer of Diamond for Extreme Performance
- Is diamond coating permanent? The Truth About Its Long-Lasting Durability



















