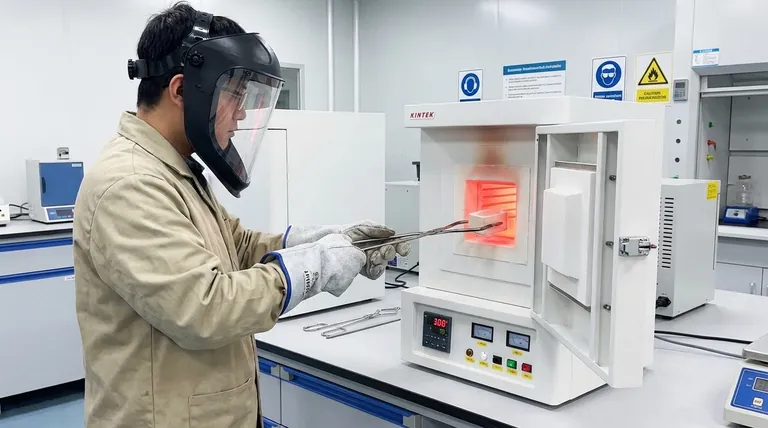
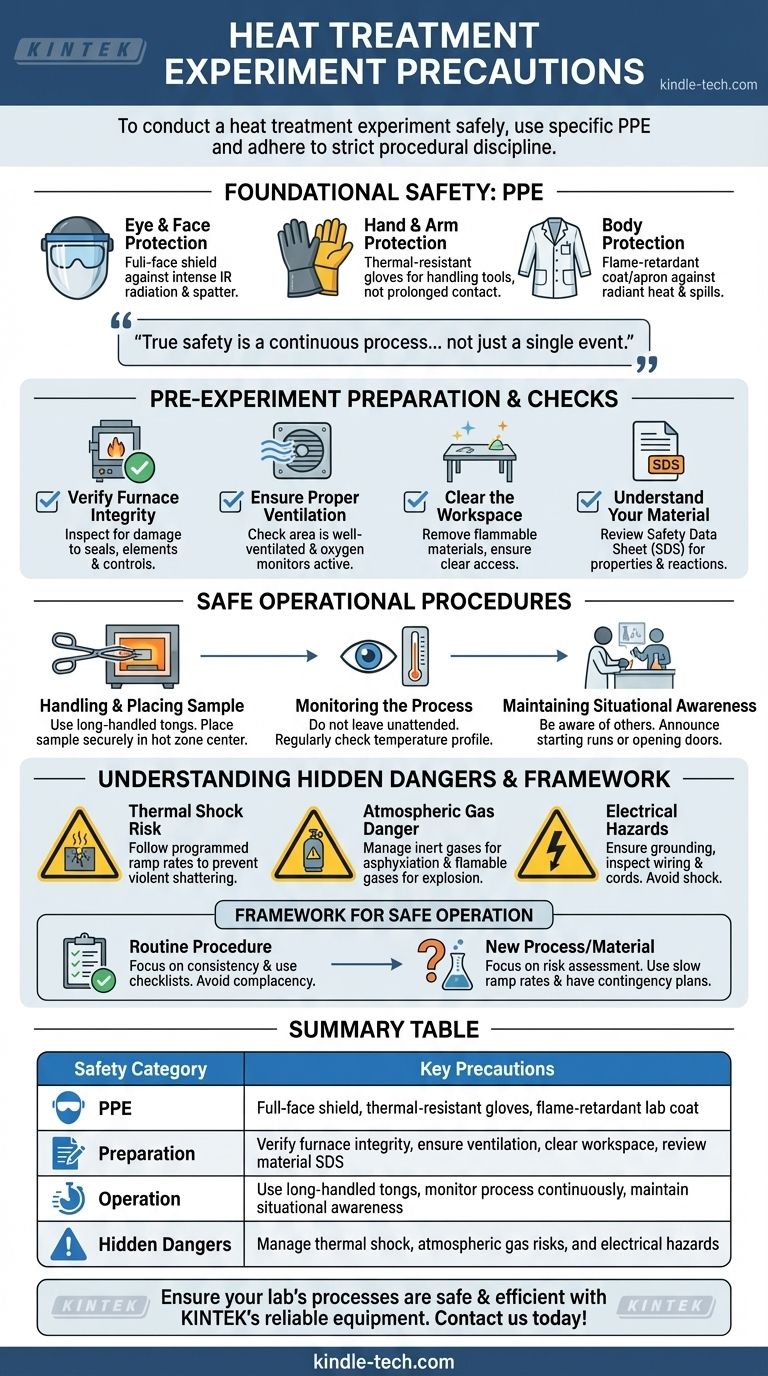
To conduct a heat treatment experiment safely, you must use specific Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) and adhere to strict procedural discipline. This includes wearing a full-face shield, thermal-resistant gloves, and a flame-retardant lab coat or apron. These precautions are the first line of defense against the significant thermal and electrical hazards inherent in the process.
The most common experimental failures and injuries are not caused by a single catastrophic event, but by a lapse in systematic procedure. True safety is a continuous process that begins before the furnace is turned on and ends long after it has cooled.

Foundational Safety: Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Your PPE is the essential barrier between you and the high-energy environment of the furnace. Never begin work without verifying you have the correct gear and that it is in good condition.
Eye and Face Protection
A full-face shield is non-negotiable. It protects against the intense infrared (IR) radiation from the hot zone, which can damage your eyes over time. It also provides a critical barrier against potential thermal spatter or projectile fragments from a fracturing sample.
Hand and Arm Protection
You need heavy, thermal-resistant gloves, often made from aramid fibers like Kevlar or Nomex. These are for handling tools or parts being placed into or removed from the furnace. They are not for prolonged contact with hot surfaces.
Body Protection
Wear a flame-retardant lab coat or, for higher-risk operations, a full leather or aluminized apron. This protects your body from intense radiant heat and is a crucial defense against accidental spills of hot materials or contact with hot surfaces.
Pre-Experiment Preparation and Checks
The safest experiments are those that are well-planned. A few minutes of preparation can prevent hours of downtime or a serious accident.
Verify Furnace and Controller Integrity
Before starting, visually inspect the furnace for any damage to the insulation, door seals, or heating elements. Confirm that the temperature controller and over-temperature protection circuits are functioning correctly.
Ensure Proper Ventilation
Ensure the area is well-ventilated, especially if the material being treated may off-gas fumes. If using atmospheric gases like nitrogen or argon, verify there are no leaks and that oxygen monitors are active if required.
Clear the Workspace
The area around the furnace must be completely clear of flammable materials, tripping hazards, and clutter. You need unobstructed access to the furnace and a clear path to exit in an emergency.
Understand Your Material
Know the properties of the material you are heating. Some materials can release toxic fumes, expand significantly, or become reactive at high temperatures. Reviewing the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) is a mandatory step.
Safe Operational Procedures
During the experiment, your primary tool is disciplined attention. Complacency is the greatest risk.
Handling and Placing the Sample
Use long-handled tongs to place and retrieve your sample. Never put your hands or head inside the furnace chamber, even when it is at a lower temperature. Place the sample securely in the center of the hot zone to ensure uniform heating.
Monitoring the Process
Do not leave a heat treatment process unattended. Regularly check the temperature display to ensure it follows the desired profile. As noted, keeping observation windows clean is critical for visually monitoring the sample without opening the door.
Maintaining Situational Awareness
Be aware of who is in the lab and what they are doing. Announce when you are starting a high-temperature run or opening the furnace door.
Understanding the Hidden Dangers
Beyond the obvious hazard of high heat, several other risks must be managed.
The Risk of Thermal Shock
Placing a room-temperature sample into a fully heated furnace or removing a hot sample into open air can cause it to shatter violently. This is thermal shock. Always follow a programmed heating and cooling ramp rate appropriate for your material.
The Danger of Atmospheric Gases
Many treatments use inert gases (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent oxidation. These gases can displace oxygen in an enclosed space, creating an asphyxiation hazard. Flammable gases like hydrogen present a significant explosion risk and require specialized safety protocols.
Electrical Hazards
The furnace is a high-power electrical device. The risk of shock is most acute during maintenance or if wiring becomes damaged. Ensure the equipment is properly grounded and never operate a furnace with frayed power cords or a compromised electrical panel.
A Framework for Safe Operation
Your approach to safety should adapt to the nature of the task. Use these guidelines to frame your actions.
- If you are performing a routine, established procedure: Focus on consistency and using a checklist. Complacency is your biggest enemy, so treat every run with the same level of discipline as the first.
- If you are developing a new process or using a new material: Your focus is on risk assessment. Start with slow ramp rates, lower peak temperatures, and have a clear contingency plan if the material behaves unexpectedly.
By treating safety as an integral part of the scientific method, you protect not only yourself but also the integrity of your experimental results.
Summary Table:
| Safety Category | Key Precautions |
|---|---|
| PPE | Full-face shield, thermal-resistant gloves, flame-retardant lab coat |
| Preparation | Verify furnace integrity, ensure ventilation, clear workspace, review material SDS |
| Operation | Use long-handled tongs, monitor process continuously, maintain situational awareness |
| Hidden Dangers | Manage thermal shock, atmospheric gas risks, and electrical hazards |
Ensure your lab's heat treatment processes are safe and efficient with KINTEK's reliable equipment and expertise.
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab furnaces, safety accessories, and consumables designed for precise thermal processing. Our products are engineered with safety features to help you maintain strict procedural discipline and protect your team.
Contact us today to discuss your laboratory's specific heat treatment needs. Let our experts help you select the right equipment and safety solutions to achieve reliable results while minimizing risks.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature at the bottom of the blast furnace? Unlocking the Heart of Iron Production
- Why is an object coated with gold before SEM imaging? To Prevent Charging and Achieve Clear SEM Images
- Why is RF sputtering often used for oxide film deposition? Achieve Superior Insulating Film Quality
- What is the difference between fusion and sintering? Master Material Joining Methods
- How do you clean a sputtering chamber? Master the Critical Protocol for Purity and Yield
- Is biofuel production expensive? The True Cost of Sustainable Energy Explained
- What is the importance of determining the melting point of a substance? Identify Compounds & Assess Purity
- What role does a laboratory magnetic stirrer play in the acidification pretreatment of aluminum sludge? Speed Recovery



















