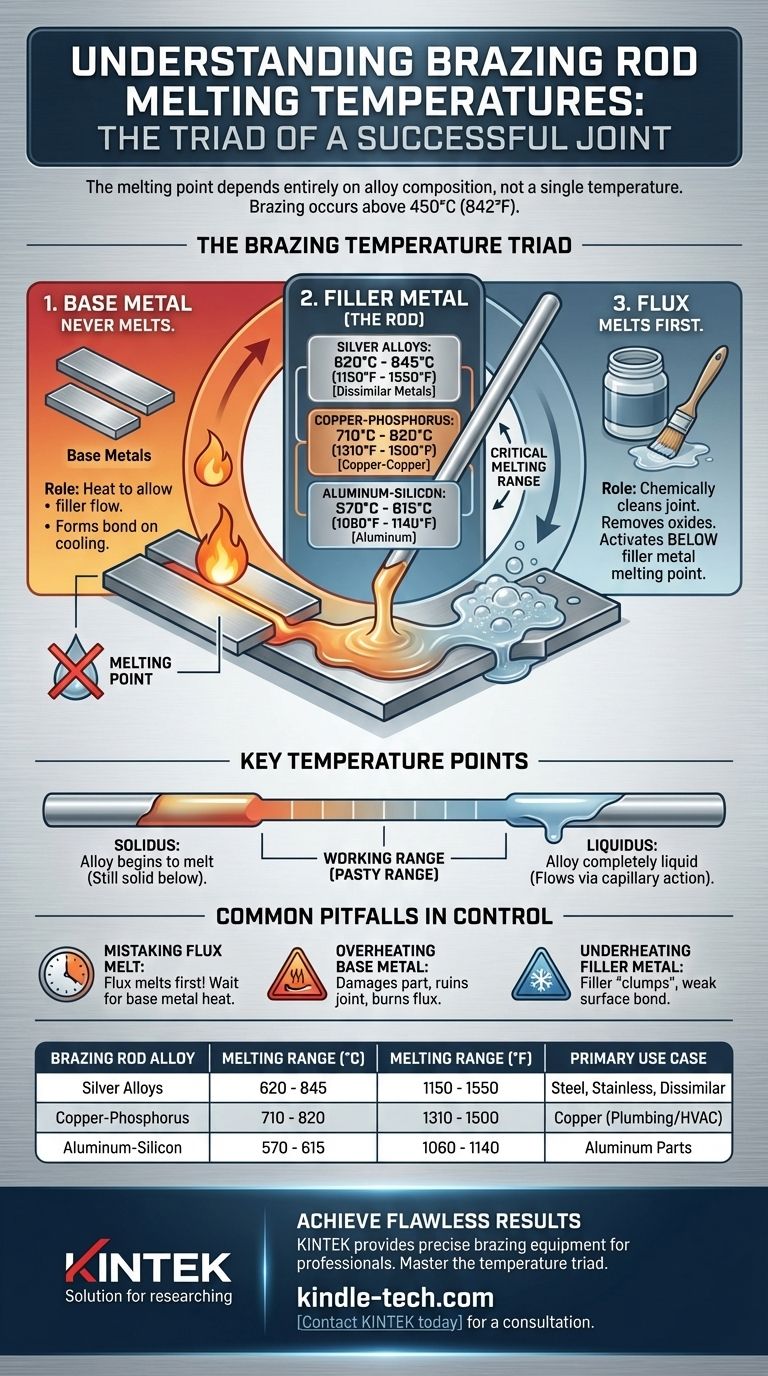
The melting point of a brazing rod depends entirely on its specific alloy composition. By definition, the process of brazing uses a filler metal that melts above 450°C (842°F) but below the melting point of the base metals being joined. Therefore, there is no single temperature; a silver-based rod will melt at a different temperature than a copper-phosphorus or aluminum-silicon rod.
The core principle of brazing is a controlled temperature hierarchy: the flux must melt first to clean the joint, followed by the filler metal (rod), all while keeping the base metals solid. A successful braze depends on understanding this sequence, not just a single melting point.
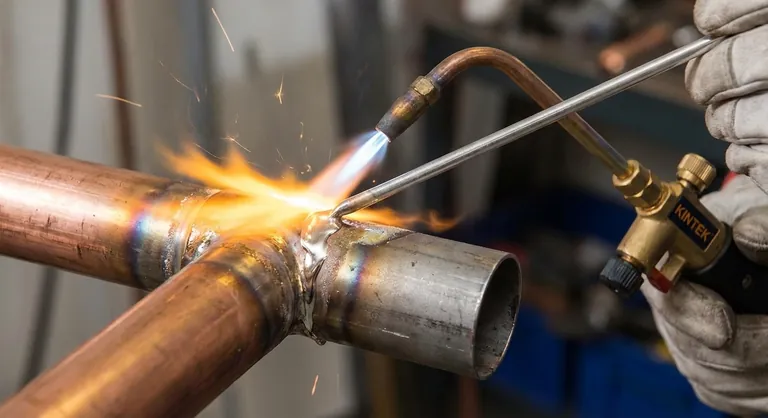

The Brazing Temperature Triad
A strong brazed joint is created by the interaction of three key elements, each with a distinct role related to temperature. The process is a sequence, not a single event.
The Role of the Base Metal
The base metals are the pieces you intend to join. In brazing, the base metals should never reach their melting point.
Their role is to get hot enough to allow the molten filler metal to flow into the joint through capillary action, forming a strong metallurgical bond upon cooling.
The Filler Metal (The Brazing Rod)
This is the brazing rod itself. Its melting range is the most critical factor and varies widely by type.
- Silver Alloys: A common choice for joining dissimilar metals like steel and copper. Melting ranges are typically between 620°C and 845°C (1150°F and 1550°F).
- Copper-Phosphorus Alloys: Often used for joining copper to copper without flux. They melt in the range of 710°C to 820°C (1310°F to 1500°F).
- Aluminum-Silicon Alloys: Specifically for brazing aluminum. These melt at a lower range, around 570°C to 615°C (1060°F to 1140°F), which is just below aluminum's melting point.
The Function of Flux
Flux is a chemical cleaning agent. Its job is to remove oxides from the surface of the base metals so the filler can bond properly.
Crucially, flux is designed to melt and become active at a temperature below the melting point of the filler metal. The temperature you cited, 565-572°C (1049-1062°F), is a typical melting range for a brazing flux, not the brazing rod itself.
Key Temperature Points to Understand
When you look at a technical data sheet for a brazing rod, you will see two temperatures listed. Understanding both is essential for proper technique.
The 'Solidus' Temperature
This is the temperature at which the alloy first begins to melt. Below this point, the filler metal is completely solid.
The 'Liquidus' Temperature
This is the temperature at which the alloy becomes completely liquid. Proper flow into the joint via capillary action will only occur at or above this temperature.
Why the Working Range Matters
The temperature gap between the solidus and liquidus is the alloy's "working range" or "pasty range." Alloys with a small gap transition quickly from solid to liquid, which is ideal for tight-fitting joints. A wider gap allows more time to work the filler into a larger joint before it fully solidifies.
Common Pitfalls in Temperature Control
Achieving the correct temperature is the most common challenge in brazing. Misunderstanding the process leads to failed joints.
Mistaking Flux Melt for Brazing Temperature
The most frequent mistake is seeing the flux melt and bubble, and then immediately applying the brazing rod. The base metals are not yet hot enough for the filler to flow properly. The flux melting is simply your indicator that the joint is approaching the correct brazing temperature.
Overheating the Base Metal
Applying too much heat for too long can damage or distort the base metals. In extreme cases, you can melt the workpiece, which ruins the joint and the part. It can also burn away the flux, leaving the joint unprotected from oxidation.
Underheating the Filler Metal
If the base metals are not hot enough when you introduce the rod, the filler will "clump" and fail to flow into the joint. This results in a weak, unreliable bond that sits on the surface rather than penetrating the gap.
Matching Your Rod to Your Goal
The correct rod and temperature are dictated by the materials you are joining.
- If your primary focus is joining copper pipes for plumbing or HVAC: Use a copper-phosphorus rod. These are economical and self-fluxing on copper, simplifying the process.
- If your primary focus is joining steel, stainless steel, or dissimilar metals: A silver-based brazing alloy is the most versatile and reliable choice due to its strength and lower melting point.
- If your primary focus is joining aluminum parts: You must use a specialized aluminum-silicon filler alloy and its corresponding flux, as the temperature window is very narrow.
Ultimately, a successful braze is achieved by heating the base metal evenly, allowing the heat of the work—not the flame—to melt the filler rod.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Rod Alloy | Common Melting Range (°C) | Common Melting Range (°F) | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Silver Alloys | 620°C - 845°C | 1150°F - 1550°F | Joining steel, stainless steel, dissimilar metals |
| Copper-Phosphorus Alloys | 710°C - 820°C | 1310°F - 1500°F | Joining copper to copper (common in plumbing/HVAC) |
| Aluminum-Silicon Alloys | 570°C - 615°C | 1060°F - 1140°F | Joining aluminum parts |
Achieve Flawless Brazing Results with the Right Equipment
Understanding the precise melting points of your brazing rods is only half the battle. Consistent, high-quality joints require reliable and precise heating equipment.
KINTEK specializes in lab and workshop equipment, including brazing torches and temperature control systems designed for professionals who demand accuracy. We provide the tools you need to master the temperature triad—ensuring your flux, filler metal, and base metals interact perfectly for strong, durable bonds every time.
Let us help you elevate your brazing process. Whether you're working in HVAC, plumbing, or specialized metal fabrication, our expertise ensures you have the right equipment for your specific alloys and applications.
Contact KINTEL today for a consultation on the ideal brazing solutions for your workshop or laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Wafer Holders for Lab and Semiconductor Processing
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Tweezers
- Custom-Made Alumina Zirconia Special-Shaped Ceramic Plates for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Processing
- Polyethylene Separator for Lithium Battery
People Also Ask
- How should the PTFE electrode stand and its components be cleaned after use? A Step-by-Step Guide to Prevent Contamination
- What is the correct way to place items into a PTFE cleaning basket? Master the Art of Perfect, Repeatable Cleaning
- What inspections should be performed on the PTFE electrode stand before use? Ensure Safe & Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- How can corrosion of the sample holder be prevented when using corrosive chemicals? Protect Your Lab's Integrity
- What are the temperature and pressure limitations for using the sample holder? Essential Guide for Lab Safety



















