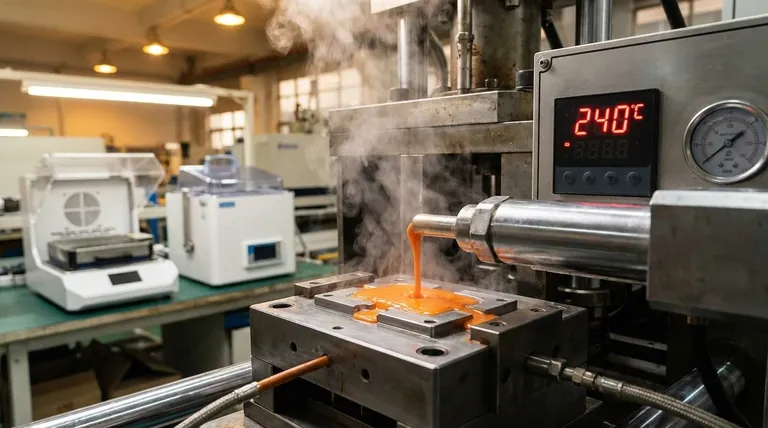
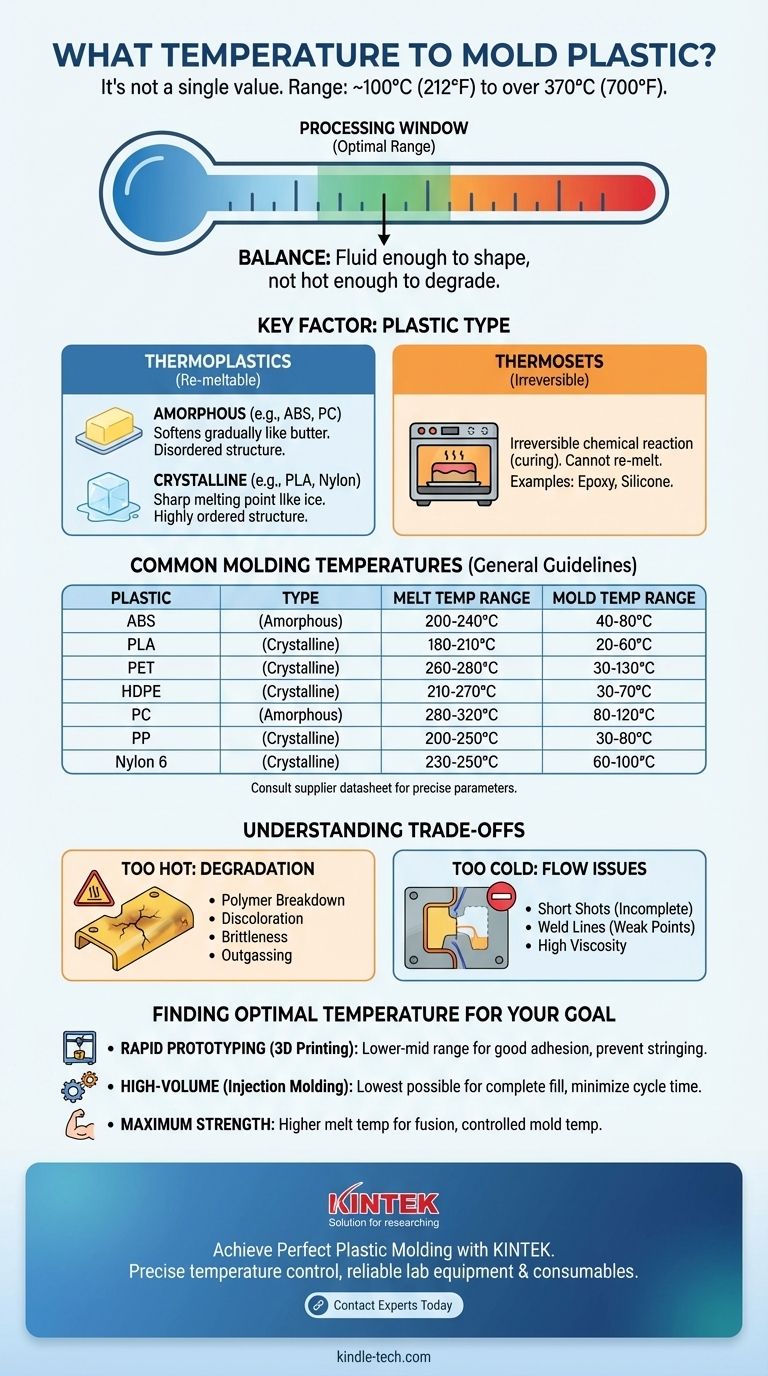
The temperature required to mold plastic is not a single value; it varies dramatically from approximately 100°C (212°F) to over 370°C (700°F). The precise temperature depends entirely on the specific type of plastic being used, the manufacturing process (like injection molding or 3D printing), and the desired properties of the final product. Each polymer has a unique processing window that must be respected to achieve a successful result.
The core principle is that every plastic has a specific "processing window"—a temperature range where it's fluid enough to be shaped but not so hot that it begins to degrade. Finding this optimal temperature is a critical balance between the material's inherent properties and the demands of the manufacturing process.

The Critical Factor: Plastic Type
The most significant variable dictating molding temperature is the chemical structure of the plastic itself. This determines how the material behaves when heated and cooled.
Thermoplastics vs. Thermosets
Plastics are broadly divided into two families. Thermoplastics can be melted and reformed multiple times without significant chemical change, much like ice can be melted into water and refrozen. This group includes common materials like Polyethylene (PE), Polypropylene (PP), and ABS.
Thermosets, on the other hand, undergo an irreversible chemical reaction (curing) when heated. Once set, they cannot be re-melted. This process is more like baking a cake; you can't turn it back into batter. Examples include epoxy, silicone, and polyurethane.
Amorphous vs. Crystalline Structures
Within thermoplastics, a material's molecular structure further defines its melting behavior. Amorphous plastics, like Polycarbonate (PC), have a disordered molecular structure. They don't have a sharp melting point but instead soften gradually over a wide temperature range, like butter.
Crystalline plastics, like Nylon (PA), have highly ordered, tightly packed molecular structures. They behave more like ice, maintaining a solid state until they reach a very specific, sharp melting point where they quickly become liquid.
A Guide to Common Molding Temperatures
For thermoplastics used in injection molding, both the temperature of the melted plastic (Melt Temperature) and the temperature of the mold itself (Mold Temperature) are critical. The mold temperature is kept significantly cooler to control the solidification rate, which affects the part's final finish, dimensions, and strength.
| Plastic Name | Type | Typical Melt Temperature Range | Typical Mold Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) | Amorphous | 200 - 240°C (392 - 464°F) | 40 - 80°C (104 - 176°F) |
| PLA (Polylactic Acid) | Crystalline | 180 - 210°C (356 - 410°F) | 20 - 60°C (68 - 140°F) |
| PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) | Crystalline | 260 - 280°C (500 - 536°F) | 30 - 130°C (86 - 266°F) |
| HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) | Crystalline | 210 - 270°C (410 - 518°F) | 30 - 70°C (86 - 158°F) |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | Amorphous | 280 - 320°C (536 - 608°F) | 80 - 120°C (176 - 248°F) |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Crystalline | 200 - 250°C (392 - 482°F) | 30 - 80°C (86 - 176°F) |
| Nylon 6 (PA6) | Crystalline | 230 - 250°C (446 - 482°F) | 60 - 100°C (140 - 212°F) |
Note: These are general guidelines. Always consult the specific material supplier's datasheet for the most accurate processing parameters.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a temperature is not just about making the plastic liquid; it's a careful balancing act to control the material's behavior and avoid defects.
Too Hot: The Dangers of Degradation
Exceeding the recommended processing window can cause the polymer chains to break down. This thermal degradation can lead to several problems.
You might see discoloration (especially yellowing or browning), a loss of impact strength making the part brittle, and outgassing that can cause surface blemishes like silver streaks.
Too Cold: The Problems of Flow and Fusion
If the temperature is too low, the plastic's viscosity will be too high. It won't flow easily enough to fill the entire mold cavity, resulting in an incomplete part known as a "short shot."
Even if the mold fills, cold plastic can create weak points called weld lines where two flow fronts meet but fail to fuse together properly, compromising the part's structural integrity.
Finding the Optimal Temperature for Your Project
The ideal temperature setting depends on your specific goal, as you are always balancing speed, quality, and material properties.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping (like 3D printing): Prioritize good layer adhesion and dimensional accuracy, which often means running at the lower to middle end of the recommended temperature range to prevent stringing and deformation.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production (injection molding): Aim for the lowest possible melt temperature that still allows for complete mold filling to minimize cycle time and save energy.
- If your primary focus is maximum part strength: Ensure the melt temperature is high enough for complete molecular fusion at weld lines and use a controlled mold temperature to manage crystalline structure and reduce internal stresses.
Ultimately, achieving a successful plastic part requires treating the manufacturer's datasheet as your starting point and then making small, methodical adjustments to perfect the process for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Plastic Name | Type | Typical Melt Temperature Range | Typical Mold Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | Amorphous | 200 - 240°C (392 - 464°F) | 40 - 80°C (104 - 176°F) |
| PLA | Crystalline | 180 - 210°C (356 - 410°F) | 20 - 60°C (68 - 140°F) |
| PET | Crystalline | 260 - 280°C (500 - 536°F) | 30 - 130°C (86 - 266°F) |
| HDPE | Crystalline | 210 - 270°C (410 - 518°F) | 30 - 70°C (86 - 158°F) |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | Amorphous | 280 - 320°C (536 - 608°F) | 80 - 120°C (176 - 248°F) |
| Polypropylene (PP) | Crystalline | 200 - 250°C (392 - 482°F) | 30 - 80°C (86 - 176°F) |
| Nylon 6 (PA6) | Crystalline | 230 - 250°C (446 - 482°F) | 60 - 100°C (140 - 212°F) |
Achieve Perfect Plastic Molding with KINTEK
Navigating the precise temperature requirements for your plastic materials is critical for avoiding defects like degradation or incomplete filling. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your laboratory's unique needs. Whether you're involved in rapid prototyping, high-volume production, or research requiring maximum part strength, our expertise ensures you achieve optimal results.
Let us help you:
- Select the right equipment for precise temperature control and consistent performance.
- Optimize your process with reliable consumables that meet stringent material specifications.
- Enhance your lab's efficiency with solutions designed for accuracy and durability.
Don't let temperature challenges compromise your project's success. Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your plastic molding applications and deliver the quality your work demands.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Shaking Incubators for Diverse Laboratory Applications
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Bomb Type Probe for Steelmaking Production Process
- 10L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- How does a constant temperature incubator shaker facilitate the enzymatic hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials?
- What role does a constant temperature orbital shaker play in biomass processing? Maximize Your Fermentation Yields
- Why is a constant temperature shaker required during the impregnation of manganese salts onto activated carbon?
- What function does a constant temperature shaker perform during adsorption performance tests? Ensure Data Accuracy
- What role does a laboratory constant temperature shaker play in the fungal strain cultivation stage? Boost Mycelium Growth



















