In an incubator, heat transfer is primarily driven by convection, but it is a system where all three forms of heat transfer—convection, conduction, and radiation—work together. The specific balance and method, especially the type of convection used, determine the incubator's performance and suitability for different applications.
The central challenge for an incubator isn't just generating heat, but distributing it uniformly to create a stable environment. While all three heat transfer methods are present, the choice between natural (gravity) convection and forced (fan-assisted) convection is the single most important factor defining an incubator's performance.
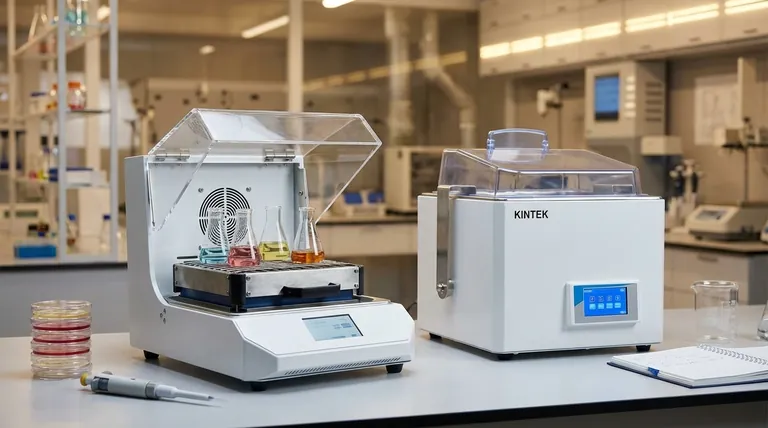

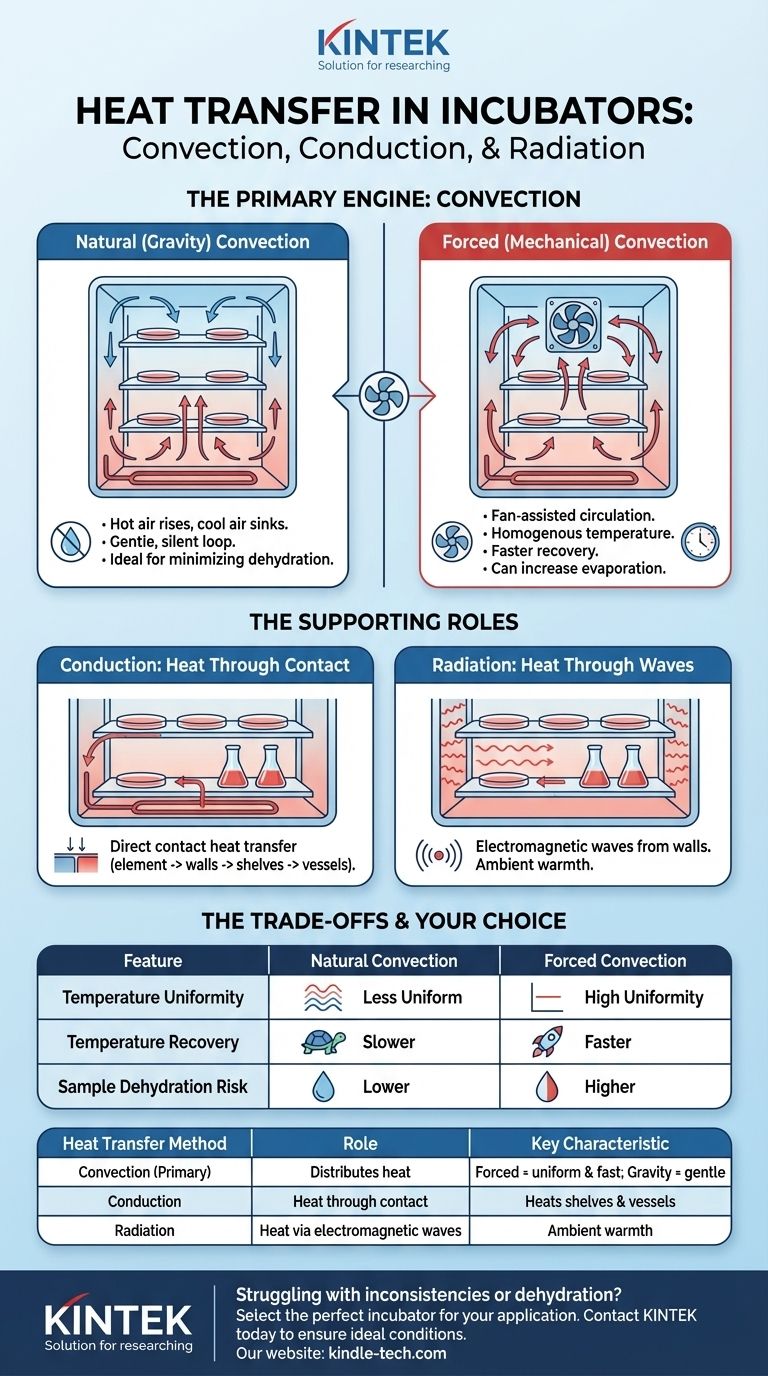
The Primary Engine: Convection
Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of a fluid, in this case, the air inside the chamber. It is the main mechanism for distributing heat from the heating element to your samples.
Natural (Gravity) Convection
In a natural or "gravity" convection incubator, air circulation relies on a simple principle: hot air is less dense and rises, while cooler, denser air sinks.
A heating element, typically at the bottom of the chamber, warms the adjacent air. This air rises, transfers some of its heat to the chamber and samples, cools, and then sinks back down to be reheated, creating a gentle, continuous loop.
This method is silent and reduces the risk of samples drying out, as the air movement is slow.
Forced (Mechanical) Convection
Forced convection incubators use a fan to actively and continuously circulate the air inside the chamber.
This mechanical circulation creates a much more homogenous temperature throughout the entire incubator, eliminating the hot and cold spots that can occur in gravity convection models. It also allows the incubator to recover its target temperature much more quickly after the door has been opened.
The Supporting Roles: Conduction and Radiation
While convection is the primary distributor, conduction and radiation are constantly at play, contributing to the overall thermal stability.
Conduction: Heat Through Contact
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct physical contact.
Heat is first conducted from the electrical heating element to the incubator's inner walls and floor. The shelves then conduct heat to any vessels (like petri dishes or flasks) resting on them. Finally, the air molecules themselves conduct heat to the surfaces of your samples.
Radiation: Heat Through Waves
Radiation is the transfer of heat via electromagnetic waves. It doesn't require a medium like air or water.
The heated inner walls of the incubator radiate thermal energy in all directions. This energy is absorbed by the shelves and the samples within the chamber, helping to maintain their temperature. Think of it as the subtle warmth you feel from a brick wall that's been in the sun, even after the sun has gone down.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between a fan-assisted (forced convection) and a fan-less (gravity convection) incubator involves critical trade-offs that directly impact your work.
The Case for Forced Convection (Fan-Assisted)
Forced convection provides superior temperature uniformity and stability. The constant air movement ensures every corner of the incubator is at virtually the same temperature.
This design also offers much faster temperature recovery. When you open the door, the fan can quickly recirculate the air to bring the chamber back to its setpoint, minimizing stress on your samples.
The Risk of Dehydration
The primary drawback of forced convection is an increased rate of sample evaporation and dehydration. The moving air, similar to a breeze on a hot day, can wick moisture away from cultures, especially in open plates or over long incubation periods.
The Case for Gravity Convection (No Fan)
Gravity convection is ideal for applications where sample dehydration is a major concern, such as open-plate cell culture. The gentle, slow air movement minimizes evaporation.
These units are also mechanically simpler, often less expensive, and operate silently.
The Risk of Inconsistency
The main limitation is temperature stratification. The top of the incubator can be significantly warmer than the bottom, creating inconsistent conditions for samples placed on different shelves. Recovery times after a door opening are also much slower.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right incubator means matching the heat transfer method to your specific application.
- If your primary focus is sensitive cell cultures or preventing sample drying: A gravity convection incubator is often the safest and most effective choice.
- If your primary focus is absolute temperature uniformity and rapid recovery: A forced convection (fan-assisted) incubator is technically superior for ensuring consistent conditions across all samples.
- If you are running robust applications like bacterial cultures in sealed flasks: The benefits of a forced convection unit typically outweigh the minimal risk of dehydration.
- If you need to incubate a large number of plates that require identical conditions: Forced convection is essential to eliminate temperature variations between shelves.
Understanding these principles empowers you to select and operate your incubator not just as a hot box, but as a precision instrument tailored to your needs.
Summary Table:
| Heat Transfer Method | Role in Incubator | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Convection (Primary) | Distributes heat via air movement | Forced (fan) = uniform & fast; Gravity (natural) = gentle & low evaporation |
| Conduction | Heat transfer through direct contact | Heats shelves and sample vessels |
| Radiation | Heat transfer via electromagnetic waves | Provides ambient warmth from heated walls |
Struggling with temperature inconsistencies or sample dehydration in your incubator? The right heat transfer method is critical for your results. KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables, offering a range of incubators tailored to your specific application—whether you need the uniform heating of forced convection or the gentle environment of gravity convection. Let our experts help you select the perfect instrument for your cell culture, bacterial growth, or other lab needs. Contact KINTEK today to ensure your samples are in the ideal environment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Shaking Incubators for Diverse Laboratory Applications
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Hybrid Tissue Grinding Mill
People Also Ask
- Why is a constant temperature shaker required during the impregnation of manganese salts onto activated carbon?
- What role does a laboratory constant temperature shaker play in the fungal strain cultivation stage? Boost Mycelium Growth
- What is the purpose of a constant temperature incubator shaker? Master Quercetin Adsorption on Nanocomposites
- Why is a constant temperature shaking incubator necessary for antibacterial experiments? Ensure Valid Results
- What is the importance of a constant temperature shaking incubator? Ensure Precise Bacterial Growth and Membrane Tests


















