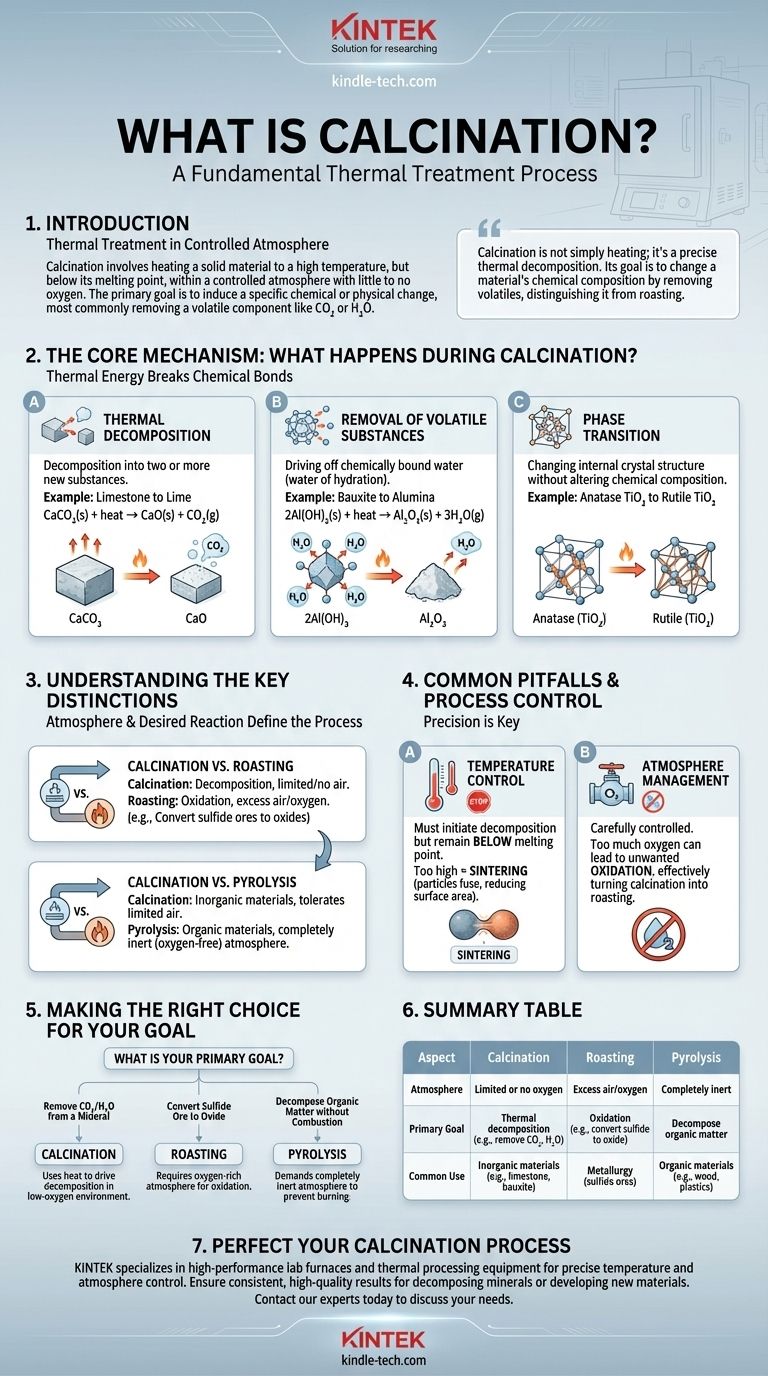
In materials science and metallurgy, calcination is a fundamental thermal treatment process. It involves heating a solid material to a high temperature, but below its melting point, within a controlled atmosphere that has little to no oxygen. This process is not designed to melt the material but to induce a specific chemical or physical change, most commonly to remove a volatile component like carbon dioxide or water.
Calcination is not simply heating; it's a precise thermal decomposition. Its primary goal is to change a material's chemical composition by removing volatile components, distinguishing it from other heat treatments like roasting, which involves chemical reaction with the furnace atmosphere.

The Core Mechanism: What Happens During Calcination?
Calcination works by providing enough thermal energy to break chemical bonds, leading to a predictable transformation of the solid material. This change typically falls into one of three categories.
Thermal Decomposition
This is the most common purpose of calcination. The heat causes the material to decompose into two or more new substances.
The quintessential example is the production of lime (calcium oxide) from limestone (calcium carbonate). When heated, the calcium carbonate breaks down, releasing carbon dioxide gas and leaving behind solid calcium oxide.
CaCO₃(s) + heat → CaO(s) + CO₂(g)
Removal of Volatile Substances
Calcination is highly effective at driving off chemically bound water (water of hydration) from minerals.
For instance, in the production of alumina from bauxite, calcination is used to convert aluminum hydroxides into aluminum oxide (alumina) by removing the water molecules.
2Al(OH)₃(s) + heat → Al₂O₃(s) + 3H₂O(g)
Phase Transition
Less commonly, calcination is used to change a material's internal crystal structure (its phase) without altering its chemical composition.
This process increases the material's stability or modifies its properties. For example, heating anatase, a form of titanium dioxide (TiO₂), converts it into the more stable and industrially valuable rutile phase.
Understanding the Key Distinctions
The term "calcination" is often confused with other heat treatments. The critical difference lies in the atmosphere used and the desired chemical reaction.
Calcination vs. Roasting
The most common point of confusion is between calcination and roasting. While both use heat, their goals and atmospheres are opposite.
Roasting is performed in an excess of air or oxygen. Its purpose is to react the solid with oxygen, typically to convert sulfide ores into oxides.
Calcination, conversely, is performed in the absence or a very limited supply of air. Its purpose is decomposition, not oxidation.
Calcination vs. Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is another thermal decomposition process, but it is defined by its use of a completely inert (oxygen-free) atmosphere.
It is most often associated with the decomposition of organic materials, like producing charcoal from wood. Calcination is typically used for inorganic materials like minerals and can tolerate a limited amount of air, whereas pyrolysis cannot.
Common Pitfalls and Process Control
Successfully executing calcination requires precise control over key variables. Failure to do so can lead to an incomplete reaction or unwanted byproducts.
Temperature Control is Critical
The process temperature must be high enough to initiate decomposition but remain below the material's melting point.
If the temperature is too high, it can cause sintering, where particles begin to fuse. This reduces the surface area and reactivity of the final product, which is often undesirable.
Atmosphere Management
The amount of air or reactive gas in the furnace इज carefully controlled. Introducing too much oxygen can lead to unwanted oxidation, effectively turning a calcination process into a roasting process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal treatment is entirely dependent on your starting material and the desired chemical end-product.
- If your primary focus is removing CO₂ or water from a mineral: Calcination is the correct process, as it uses heat to drive decomposition in a low-oxygen environment.
- If your primary focus is converting a sulfide ore to an oxide: Roasting is the necessary process, as it requires an oxygen-rich atmosphere to facilitate an oxidation reaction.
- If your primary focus is decomposing organic matter without combustion: Pyrolysis is the correct choice, as it demands a completely inert atmosphere to prevent the material from burning.
Ultimately, choosing the right thermal treatment hinges on understanding whether you want to remove a part of the material or react it with something new.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Calcination | Roasting | Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Limited or no oxygen | Excess air/oxygen | Completely inert |
| Primary Goal | Thermal decomposition (e.g., remove CO₂, H₂O) | Oxidation (e.g., convert sulfide to oxide) | Decompose organic matter |
| Common Use | Inorganic materials (e.g., limestone, bauxite) | Metallurgy (sulfide ores) | Organic materials (e.g., wood, plastics) |
Ready to perfect your calcination process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and thermal processing equipment designed for precise temperature and atmosphere control. Whether you're decomposing minerals or developing new materials, our solutions ensure consistent, high-quality results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover the right equipment for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is ceramic used in making furnace? Achieve Superior Heat Resistance and Efficiency
- What is the temperature of a muffle furnace? It's Not a Single Number—Find Your Perfect Range
- What is the heating range of a muffle furnace? From 800°C to 1800°C for Your Lab Needs
- What are the advantages of a muffle furnace? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Precision in Your Lab
- What are the precautions of muffle furnace? Essential Safety Protocols for Your Lab



















