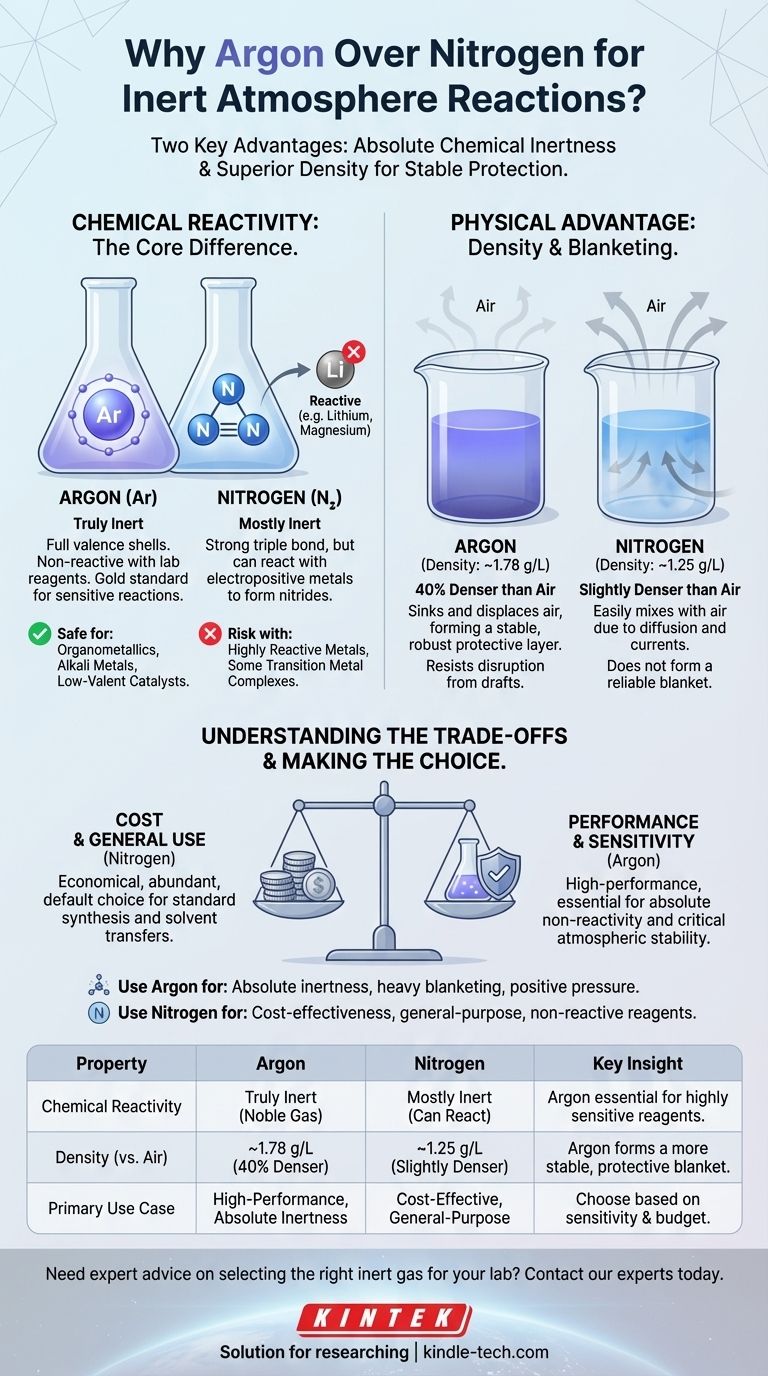
In practice, argon is often considered "better" than nitrogen for inert atmosphere reactions due to two key properties. Argon is a truly inert noble gas, incapable of reacting with lab reagents, while nitrogen can react under certain conditions. Furthermore, argon's higher density allows it to form a more stable and protective "blanket" over a reaction, more effectively displacing air.
The choice between argon and nitrogen is not about which is universally better, but which is more appropriate for a specific task. Nitrogen is the economical workhorse for general-purpose inerting, while argon is the high-performance option for reactions demanding absolute non-reactivity and atmospheric stability.

The Core Difference: Chemical Reactivity
The most fundamental reason to choose one gas over the other comes down to their potential to participate in your reaction.
Argon: The Definition of Inert
Argon is a noble gas. Its valence electron shells are completely full, making it exceptionally stable and non-reactive under virtually all laboratory conditions.
For a chemist, this is the gold standard. You can be confident that argon will not interfere with your reaction, no matter how sensitive the reagents are.
Nitrogen: "Mostly" Inert
Nitrogen gas (N₂) is composed of two nitrogen atoms joined by a very strong triple bond. This bond requires a great deal of energy to break, which is why N₂ is mostly inert and serves well for many applications.
However, it is not completely unreactive. Highly reactive reagents, particularly electropositive metals like lithium, magnesium, and some transition metal complexes, can react with N₂ to form metal nitrides. This unwanted side reaction can reduce your yield or introduce impurities.
The Physical Advantage: Density
Beyond chemical reactivity, the physical behavior of the gas in the lab is a critical factor. Air is a mixture of gases, but it has an average density that we can compare against.
- Argon Density: ~1.78 g/L
- Air Density: ~1.23 g/L
- Nitrogen Density: ~1.25 g/L
How Density Creates a Protective "Blanket"
Argon is approximately 40% denser than air. When you purge a flask with argon, it effectively sinks and displaces the lighter air, pushing it up and out. It then settles over your reaction mixture, forming a stable, heavy blanket that resists disruption.
Nitrogen, in contrast, is only slightly denser than air. It is far more susceptible to mixing with air due to diffusion and minor drafts or convection currents in the room. It does not form the same robust protective layer.
Practical Implications for Lab Setups
This density difference has real-world consequences. In a glovebox or on a Schlenk line, a positive pressure of argon provides a more forgiving atmosphere. If a minor leak occurs, the dense argon will preferentially flow out, preventing lighter air from flowing in.
For techniques that rely on blanketing an open vessel, such as in many electrochemical experiments, argon is vastly superior because it will remain settled over the solution. Nitrogen would simply mix with the surrounding air almost immediately.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the ideal gas requires balancing performance against practical constraints.
Cost: The Deciding Factor for Many
Nitrogen makes up about 78% of the Earth's atmosphere, while argon makes up less than 1%. This difference in abundance makes nitrogen significantly cheaper to produce and purchase.
For large-scale industrial processes or routine lab procedures where extreme inertness is not required, the cost savings of using nitrogen are substantial and often make it the default choice.
Reactivity: When "Mostly" Inert is Good Enough
The potential reactivity of nitrogen only matters if your chemical system is capable of breaking that N≡N triple bond.
For the vast majority of organic reactions, purifications, and solvent transfers, nitrogen is perfectly adequate. The reagents are simply not reactive enough to form nitrides, making argon an unnecessary expense.
Making the Right Choice for Your Reaction
Base your decision on the specific demands of your chemical procedure and the practical realities of your lab.
- If your primary focus is absolute inertness for sensitive reagents: Use argon when working with organometallics (especially those involving Li, Mg), alkali metals, low-valent transition metal catalysts, or any system where nitride formation is a known risk.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and general-purpose use: Use nitrogen for most standard organic synthesis, solvent stills, recrystallizations, and other procedures that do not involve exceptionally reactive species.
- If your primary focus is maintaining a stable atmosphere: Use argon for techniques that require a heavy blanket of gas, such as electrochemistry, or in setups where maintaining a positive pressure against potential leaks is critical.
Ultimately, understanding the distinct chemical and physical properties of each gas empowers you to make the most informed and economical choice for your experiment.
Summary Table:
| Property | Argon | Nitrogen | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Reactivity | Truly inert (noble gas) | Mostly inert, but can react with electropositive metals | Argon is essential for highly sensitive reagents. |
| Density (vs. Air) | ~1.78 g/L (40% denser) | ~1.25 g/L (slightly denser) | Argon forms a more stable, protective blanket. |
| Primary Use Case | High-performance reactions demanding absolute inertness | Cost-effective solution for general-purpose inerting | Choose based on your reaction's sensitivity and budget. |
Need expert advice on selecting the right inert gas for your specific lab application?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-purity lab gases and equipment, including argon and nitrogen systems, to ensure your sensitive reactions are perfectly protected. Our team can help you optimize your setup for maximum yield and safety.
Contact our experts today to discuss your inert atmosphere needs and find the most efficient solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- What is nitrogen atmosphere for annealing? Achieve Oxidation-Free Heat Treatment
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- What is an inert atmosphere heat treatment? Protect Your Metals from Oxidation & Decarburization



















