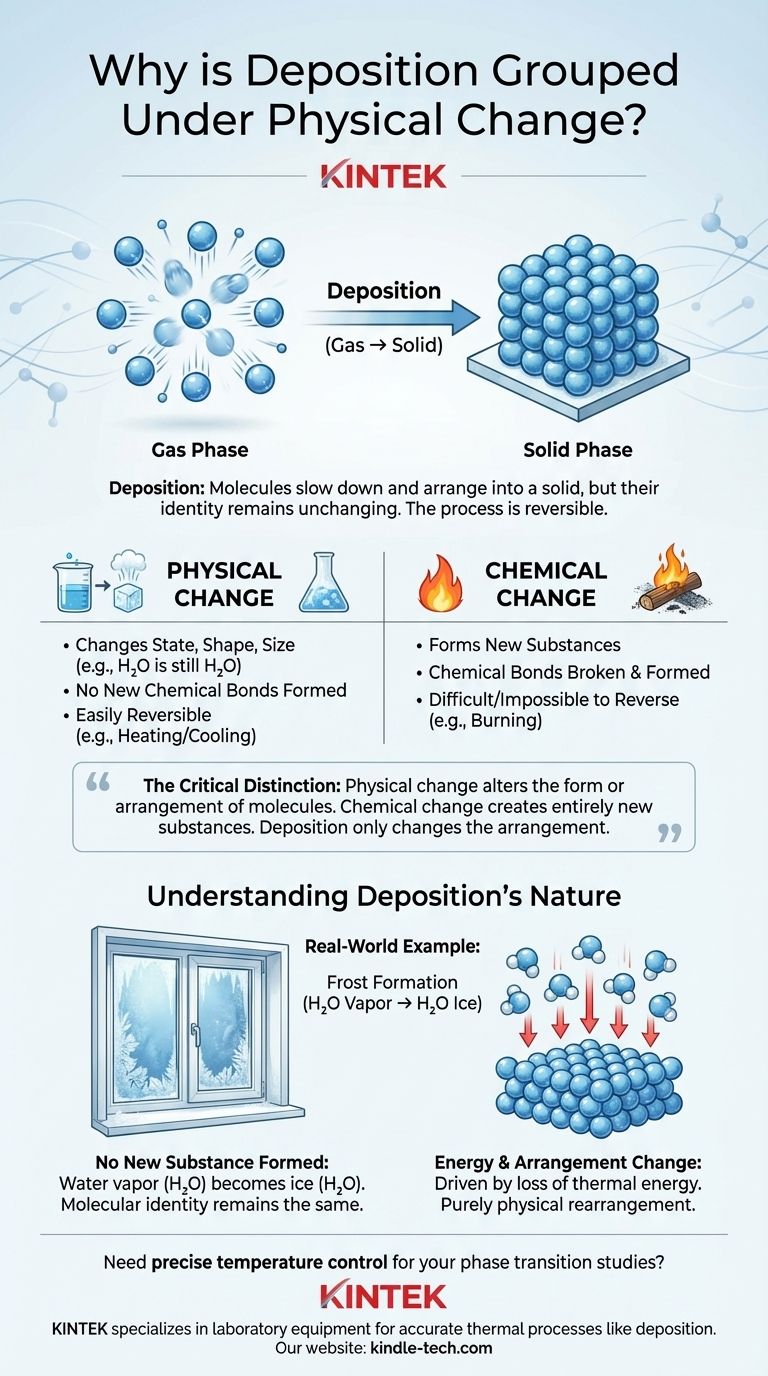
Deposition is classified as a physical change because it only alters the state of a substance, not its fundamental chemical identity. During deposition, molecules of a substance transition directly from a gas to a solid, changing their arrangement and energy level, but the molecules themselves remain intact and unchanged.
The critical distinction is this: a physical change alters the form or arrangement of molecules, while a chemical change breaks and forms bonds to create entirely new substances. Deposition only changes the arrangement.

The Defining Line: Physical vs. Chemical Change
To understand why deposition fits squarely in the physical category, we must first establish a clear definition for both types of changes. The distinction comes down to what happens at the molecular level.
What Constitutes a Physical Change?
A physical change affects a substance's physical properties without altering its chemical composition. These changes are primarily related to energy and the arrangement of particles.
Key characteristics include changes in state (solid, liquid, gas), shape, or size. A classic example is water: ice, liquid water, and water vapor are all H₂O. Only the spacing and energy of the molecules have changed.
These changes are often easily reversible through physical means, like heating or cooling.
What Constitutes a Chemical Change?
A chemical change, or chemical reaction, results in the formation of one or more entirely new substances with different properties and compositions.
This process involves the breaking of existing chemical bonds and the formation of new ones. For instance, when wood burns, it reacts with oxygen to become ash, carbon dioxide, and water—substances chemically distinct from the original wood.
Chemical changes are typically difficult or impossible to reverse through simple physical means.
Analyzing Deposition at the Molecular Level
When we apply this framework to deposition, its classification becomes clear.
The Process of Deposition Explained
Deposition is the direct phase transition of a substance from a gas to a solid, completely skipping the intermediate liquid phase.
A common real-world example is the formation of frost. On a cold morning, water vapor in the air (a gas) comes into contact with a surface below the freezing point, like a windowpane, and turns directly into ice crystals (a solid).
No New Substances are Formed
This is the most critical point. The water vapor in the air has the chemical formula H₂O. The ice crystals that form as frost also have the chemical formula H₂O.
The molecular identity of the substance has not changed. No chemical bonds within the water molecules were broken, and no new substances were created.
It's a Change in Energy and Arrangement
The transition is driven by a loss of thermal energy. The high-energy, fast-moving water molecules in the gaseous state lose energy upon contacting the cold surface.
This energy loss causes them to slow down and arrange themselves into a fixed, ordered crystalline structure—the solid state. The change is purely one of physical arrangement and energy, not chemical makeup.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Misconceptions
Confusing physical and chemical changes is common, especially when a dramatic visual change occurs.
The "New Look" Fallacy
A substance undergoing deposition, like invisible water vapor forming visible frost, can look like a new material has been created. However, a change in appearance is a hallmark of a physical change.
Always focus on the chemical composition, not the visual form. Color, texture, and state are physical properties that can change without any chemical reaction occurring.
Reversibility as a Strong Indicator
Deposition is a reversible process. The reverse process, where a solid turns directly into a gas, is called sublimation. For example, dry ice (solid CO₂) sublimates into CO₂ gas.
The ability to reverse the process by simply adding energy (heating) without a chemical reaction is a powerful clue that you are dealing with a physical change.
How to Correctly Classify Any Change
To determine whether a process is physical or chemical, ask yourself a series of targeted questions.
- If your primary focus is identifying a physical change: Ask, "Is the underlying chemical formula of the substance the same before and after the change?"
- If your primary focus is identifying a chemical change: Ask, "Have chemical bonds been broken or formed to create a new substance with different properties?"
- When in doubt about a process: Ask, "Can this change be easily reversed by simple physical means, such as heating, cooling, or dissolving?"
Focusing on the unchanging identity of the molecules is the key to accurately distinguishing between physical and chemical processes.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Physical Change | Chemical Change |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Identity | Remains the same (e.g., H₂O stays H₂O) | Changes (new substances formed) |
| Bond Alteration | No breaking/forming of chemical bonds | Bonds broken and new ones formed |
| Reversibility | Easily reversible (e.g., heating/cooling) | Difficult or impossible to reverse |
| Example Process | Deposition (gas → solid), freezing | Burning, rusting, digestion |
Need precise temperature control for your phase transition studies? KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables designed for accurate thermal processes like deposition and sublimation. Whether you're researching material science or conducting educational experiments, our reliable tools ensure consistent results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your lab's needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating



















