The paradox of graphite lies in its dual nature: it is one of the softest materials known, yet it possesses one of the highest melting points. This behavior stems from its unique atomic structure, where carbon atoms are held by immensely strong covalent bonds within flat sheets, requiring a massive amount of energy to break and melt the substance.
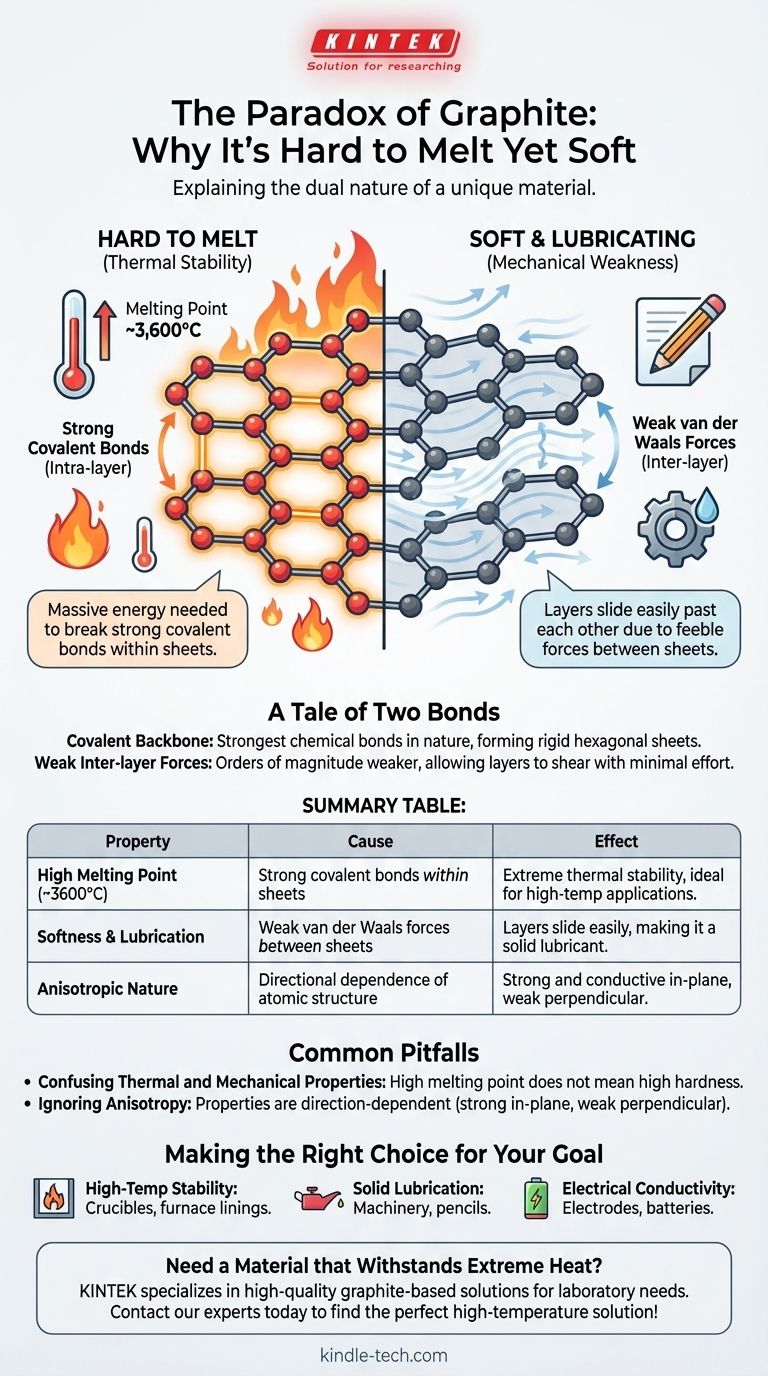
Graphite's properties are a tale of two forces. The extreme strength of the covalent bonds within its atomic layers dictates its high melting point, while the profound weakness of the forces between those layers explains why it feels soft and acts as a lubricant.
A Tale of Two Bonds: The Source of Graphite's Strength
Graphite's resistance to melting is rooted in the fundamental way its carbon atoms are connected. This internal architecture is incredibly robust.
The Covalent Backbone
Each carbon atom in a graphite layer is linked to three others by covalent bonds. These bonds, which involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, are among the strongest types of chemical bonds in nature.
To melt a substance, you must provide enough thermal energy to break the bonds holding its atoms in a fixed, solid structure. Because graphite's covalent bonds are so strong, the energy required to disrupt them is immense, resulting in a melting point of around 3,600°C (6,500°F).
The Hexagonal Sheets
These covalently bonded atoms form vast, flat sheets arranged in a hexagonal, honeycomb-like lattice. You can think of each sheet as a single layer of the wonder-material graphene.
Within these sheets, the structure is rigid and exceptionally stable. The strength isn't just in one direction; it's distributed across the entire two-dimensional plane.
Solving the Paradox: Why Is It Also Soft?
The explanation for graphite's softness is found not within its strong atomic sheets, but in the space between them.
Weak Inter-layer Forces
While the atoms within a sheet are powerfully bonded, the sheets themselves are stacked on top of one another with very little holding them together. They are attracted only by weak intermolecular forces known as van der Waals forces.
These forces are orders of magnitude weaker than the covalent bonds inside the sheets.
The Sliding Layers
Because the attraction between the layers is so feeble, the sheets can easily slide past one another with minimal effort. This sliding action is what we perceive as softness and what makes graphite an excellent solid lubricant.
When you write with a pencil, you are simply shearing off thousands of these weakly-connected layers and depositing them onto the paper.
Intra-layer vs. Inter-layer
This distinction is the key to understanding graphite. Intra-layer forces (covalent bonds) are incredibly strong, giving graphite its thermal stability. Inter-layer forces (van der Waals) are incredibly weak, giving it mechanical softness.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding graphite means avoiding the common oversimplification that a material is either "strong" or "weak." Its properties are highly dependent on the context and direction.
Confusing Thermal and Mechanical Properties
It's a common mistake to assume a high melting point must correlate with high mechanical hardness. Graphite is the classic counterexample.
Its thermal stability (resistance to melting) is governed by its strong covalent bonds. Its mechanical properties (softness and shear strength) are governed by its weak inter-layer forces.
Ignoring Anisotropy
Graphite is a highly anisotropic material, meaning its properties are direction-dependent.
It is extremely strong and conducts heat and electricity well along the plane of its atomic sheets. However, it is mechanically weak and a poor conductor perpendicular to those sheets.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
This dual nature makes graphite a uniquely versatile material, but its application must be aligned with its specific directional properties.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability: Graphite is an excellent choice for applications like crucibles or furnace linings because its strong covalent bonds resist thermal breakdown.
- If your primary focus is solid lubrication: Graphite's weakly bonded, sliding layers make it ideal for reducing friction in machinery, locks, or as the "lead" in pencils.
- If your primary focus is electrical conductivity: The structure allows electrons to move freely along the sheets, making graphite a useful material for electrodes, batteries, and brushes in electric motors.
Recognizing that a material's macroscopic properties are a direct result of its atomic structure is the key to solving any engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Property | Cause | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| High Melting Point (~3600°C) | Strong covalent bonds within atomic sheets | Extreme thermal stability, ideal for high-temperature applications |
| Softness & Lubrication | Weak van der Waals forces between sheets | Layers slide easily, making it a solid lubricant |
| Anisotropic Nature | Directional dependence of atomic structure | Strong and conductive in-plane, weak perpendicular to it |
Need a Material that Withstands Extreme Heat?
Graphite's unique properties make it an ideal choice for high-temperature furnaces, crucibles, and other demanding lab equipment. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including graphite-based solutions, to meet your specific laboratory needs.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect high-temperature solution for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the mechanical properties of graphite? Harnessing Rigidity and Managing Brittleness
- Why can graphite conduct heat? Unlocking Its Anisotropic Thermal Properties
- How does an induction graphitization furnace facilitate the transformation of unburned carbon into synthetic graphite?
- Why graphite has high thermal conductivity? Unlock Superior Heat Management with Its Unique Structure
- What are the industrial applications of graphite? From Metallurgy to Semiconductors



















