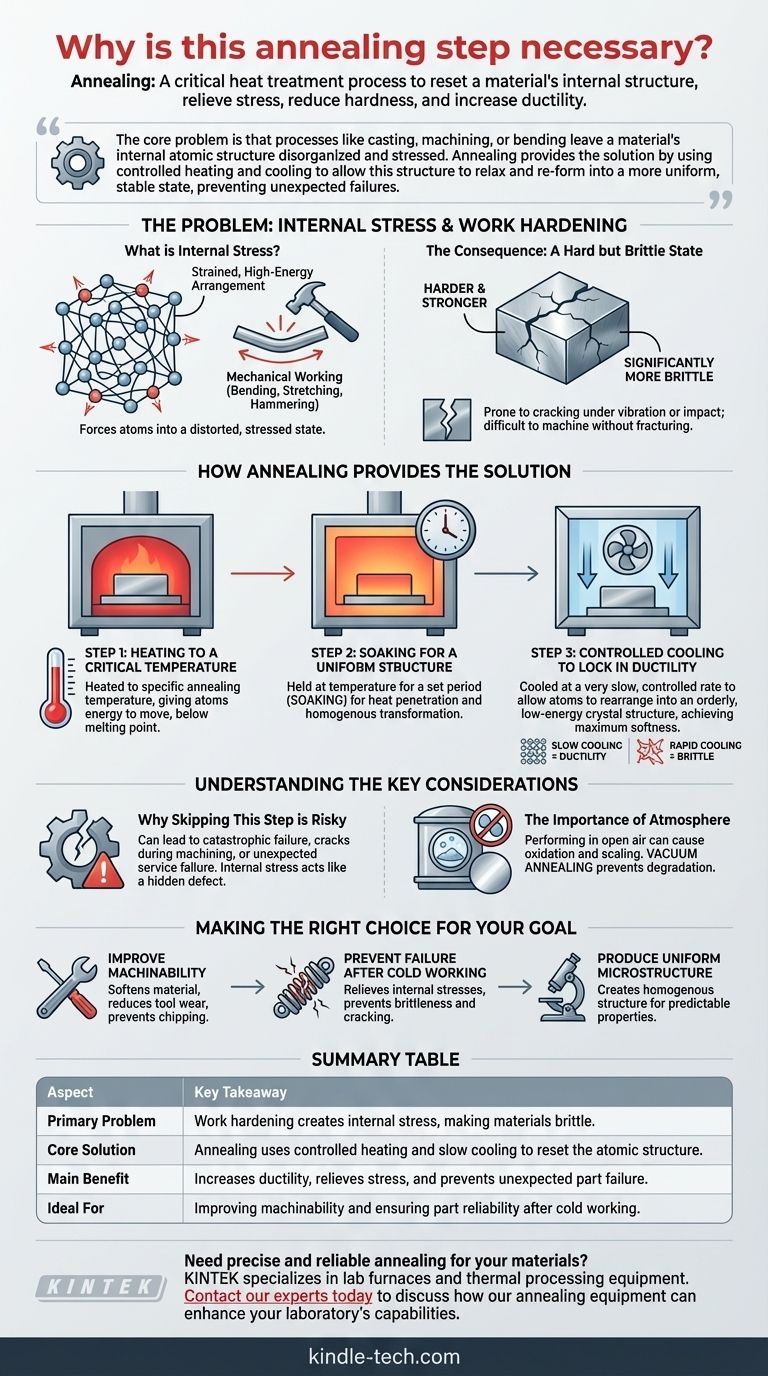
In short, annealing is a critical heat treatment process used to fundamentally reset a material's internal structure. It is necessary to relieve built-up internal stresses, reduce hardness, and increase ductility. This makes the material significantly less brittle and much easier to work with for subsequent manufacturing steps.
The core problem is that processes like casting, machining, or bending leave a material's internal atomic structure disorganized and stressed. Annealing provides the solution by using controlled heating and cooling to allow this structure to relax and re-form into a more uniform, stable state, preventing unexpected failures.
The Problem: Internal Stress and Work Hardening
What is Internal Stress?
When a material is mechanically worked—bent, stretched, or hammered—its internal crystal structure becomes distorted. This process, often called work hardening or strain hardening, forces the atoms into a strained, high-energy arrangement.
Imagine the material's internal grain structure as a neat, orderly grid. Work hardening tangles and stretches that grid, creating immense tension on an atomic level.
The Consequence: A Hard but Brittle State
This stressed state makes the material harder and stronger, but it comes at a great cost: it also becomes significantly more brittle.
A work-hardened part is prone to cracking under vibration or impact. Its internal tension makes it unpredictable and difficult to machine or form any further without fracturing.
How Annealing Provides the Solution
Annealing is a three-stage process designed to systematically erase this internal stress and restore the material's workability.
Step 1: Heating to a Critical Temperature
The material is heated in a furnace to a specific annealing temperature. This temperature is high enough to give the atoms enough energy to move and break free from their distorted positions, but it remains below the material's melting point.
Step 2: Soaking for a Uniform Structure
The material is held at this high temperature for a set period, a step known as soaking. This is crucial to ensure that the heat penetrates the entire part, not just the surface.
This soaking period allows the entire internal structure to achieve a complete, homogenous transformation into a new, stress-free grain structure.
Step 3: Controlled Cooling to Lock in Ductility
Finally, the material is cooled at a very slow, controlled rate. This slow cooling is the key to achieving maximum softness and ductility.
It allows the atoms to rearrange themselves into a large, orderly, and low-energy crystal structure, bringing the material to or near its equilibrium state. Rapid cooling, by contrast, would trap stress and create a harder, more brittle material.
Understanding the Key Considerations
Why Skipping This Step is Risky
Failing to anneal a work-hardened component can lead to catastrophic failure. The part may crack during subsequent machining steps, or worse, fail unexpectedly once it is put into service. The internal stress acts like a hidden defect, waiting for a trigger.
The Importance of Atmosphere
For many materials, especially reactive metals, performing this process in open air is detrimental. The high temperatures would cause the material to react with oxygen or nitrogen, leading to scaling, contamination, and a loss of desirable properties.
This is why vacuum annealing is often used. By removing the air, the process can be performed without degrading the material's surface or chemistry.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Annealing is not just one process but a tool used to achieve specific outcomes. The exact temperature and cooling rate are tailored to the material and the desired end-state.
- If your primary focus is improving machinability: Annealing is necessary to soften the material, which reduces tool wear and prevents chipping during cutting.
- If your primary focus is preventing failure after cold working: Annealing is essential to relieve the internal stresses that make the material brittle and prone to cracking.
- If your primary focus is producing a uniform microstructure: Annealing is used to create a homogenous internal structure required for predictable mechanical, physical, or electrical properties.
Ultimately, understanding the necessity of annealing is understanding how to control a material's most fundamental properties.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Primary Problem | Work hardening creates internal stress, making materials brittle. |
| Core Solution | Annealing uses controlled heating and slow cooling to reset the atomic structure. |
| Main Benefit | Increases ductility, relieves stress, and prevents unexpected part failure. |
| Ideal For | Improving machinability and ensuring part reliability after cold working. |
Need precise and reliable annealing for your materials?
KINTEK specializes in lab furnaces and thermal processing equipment designed for controlled heat treatment. Whether your goal is stress relief, improving machinability, or achieving a uniform microstructure, our solutions ensure consistent, high-quality results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our annealing equipment can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and prevent material failure.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is sputtering technology? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- How does a sputtering machine work? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision for Your Coatings
- What are the three most important factors in material heat treatment? Master Temperature, Time, and Cooling for Superior Properties
- What is a sputtering machine? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What temperature does titanium vaporize at? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Resistance for Aerospace



















