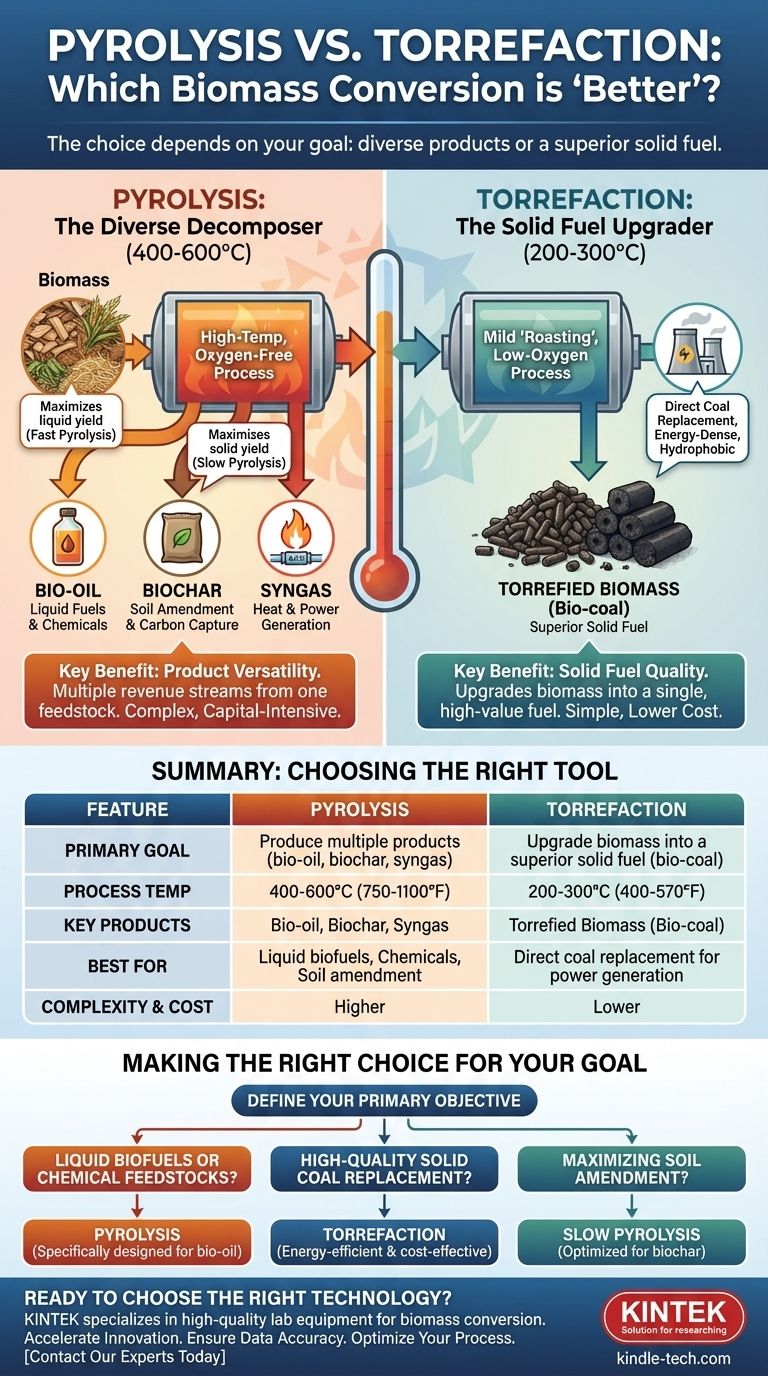
To put it simply, pyrolysis is considered "better" than torrefaction when the goal is to create a diverse range of valuable products, especially liquid bio-oil for fuel or chemicals and biochar for soil amendment. Torrefaction is a less intensive process focused solely on upgrading solid biomass into a coal-like fuel, not on creating liquid or specialized solid products.
The choice between pyrolysis and torrefaction is not a question of which is universally "better," but which is the right tool for the job. Pyrolysis deconstructs biomass into gas, liquid, and solid products, offering versatility. Torrefaction upgrades biomass into a single, high-quality solid fuel, prioritizing energy density and compatibility with existing infrastructure.

What is Pyrolysis? The Decomposition Pathway
Pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that breaks down organic materials at high temperatures in the complete absence of oxygen. Think of it as high-temperature decomposition, designed to fracture complex molecules into simpler, more valuable components.
High-Temperature, Oxygen-Free Process
Pyrolysis operates at temperatures typically ranging from 400 to 600°C (750 to 1100°F). The lack of oxygen is critical, as it prevents the biomass from combusting and instead forces it to thermally decompose.
The Three Key Products: Bio-oil, Biochar, and Syngas
This decomposition yields three distinct product streams:
- Bio-oil: A dark, viscous liquid that can be upgraded into transportation fuels or used as a source for renewable chemicals. This is a primary advantage of pyrolysis.
- Biochar: A stable, carbon-rich solid that is excellent for soil amendment, improving water retention and sequestering carbon.
- Syngas: A mixture of flammable gases (like hydrogen and carbon monoxide) that can be used to generate heat and power for the pyrolysis process itself, making it more self-sustaining.
Maximizing Desired Outputs
The process can be tuned. Fast pyrolysis, with rapid heating, maximizes the yield of bio-oil. Slow pyrolysis, with longer residence times, is optimized to produce the highest possible yield of biochar.
What is Torrefaction? The Upgrading Pathway
Torrefaction is a milder form of pyrolysis, often described as "roasting" biomass. Its purpose is not to break the material down into separate products, but to improve its quality as a solid fuel.
Lower-Temperature "Roasting"
Torrefaction occurs at lower temperatures, typically 200 to 300°C (400 to 570°F), in a low-oxygen environment. This process drives off moisture and volatile compounds without significantly decomposing the biomass structure.
The Primary Product: Torrefied Biomass (Bio-coal)
The end product is a dry, brittle, energy-dense solid often called bio-coal. It is hydrophobic (repels water), making it far easier to store and transport than raw biomass.
The Goal is Solid Fuel Improvement
The primary application for torrefied biomass is as a direct substitute for coal in power plants. Its improved properties allow it to be pulverized and co-fired with coal using existing equipment, a major logistical and economic advantage.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The "better" process depends entirely on the technical and economic goals of the project. Each has distinct advantages and disadvantages.
Product Versatility vs. Singularity
Pyrolysis offers a portfolio of valuable products. The ability to produce liquid fuels and high-value biochar creates multiple potential revenue streams from a single feedstock.
Torrefaction is designed to do one thing well: create a superior solid fuel. It does not produce any significant amount of liquid bio-oil.
Process Complexity and Cost
Pyrolysis is a more complex and capital-intensive process. It requires higher temperatures and sophisticated equipment to condense, collect, and handle the corrosive bio-oil and flammable syngas streams.
Torrefaction is simpler, operates at lower temperatures, and requires less downstream processing. This generally results in lower capital and operational costs.
Energy Retention
Torrefaction is highly efficient at preserving the energy of the original biomass in the solid product, retaining up to 90% of the initial energy.
Pyrolysis distributes the initial energy among the three products. While the total energy is conserved, only a portion of it ends up in the desired bio-oil or biochar, with the rest in the syngas.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine the superior process, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid biofuels or chemical feedstocks: Pyrolysis is the correct and only choice, as it is specifically designed to create bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is creating a high-quality, solid coal replacement for co-firing: Torrefaction is the more direct, energy-efficient, and cost-effective process.
- If your primary focus is maximizing soil amendment production: Slow pyrolysis is the technology specifically optimized to generate the highest yield and quality of biochar.
By aligning the conversion technology with your specific end-goal, you move from asking which is "better" to choosing which is "right."
Summary Table:
| Feature | Pyrolysis | Torrefaction |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Produce multiple products (bio-oil, biochar, syngas) | Upgrade biomass into a superior solid fuel (bio-coal) |
| Process Temperature | 400-600°C (750-1100°F) | 200-300°C (400-570°F) |
| Key Product(s) | Bio-oil (liquid fuel), Biochar, Syngas | Torrefied Biomass (Bio-coal) |
| Best For | Liquid biofuels, chemical feedstocks, soil amendment | Direct coal replacement for power generation |
| Complexity & Cost | Higher | Lower |
Ready to choose the right biomass conversion technology for your lab or project?
The choice between pyrolysis and torrefaction is critical for achieving your specific research or production goals. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for advanced biomass conversion processes.
Whether you're developing new biofuels, analyzing biochar for soil science, or testing torrefied biomass for energy applications, our reliable pyrolysis and torrefaction systems are designed to deliver precise, reproducible results.
Let KINTEK empower your research and development:
- Accelerate Innovation: Access equipment tailored for both pyrolysis and torrefaction studies.
- Ensure Data Accuracy: Rely on our robust systems for consistent, high-quality output.
- Optimize Your Process: Get expert support to select and utilize the right technology for your specific feedstock and objectives.
Don't leave your project's success to chance. Contact our experts today to discuss your needs and find the perfect laboratory solution from KINTEK.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions



















