Introduction to Essential Oil Extraction
Nature of Essential Oils in Plants
Essential oils are a remarkable biochemical product of plants, synthesized due to their unique physiological and biochemical characteristics. These oils are not uniformly distributed throughout the plant but are concentrated in specific parts such as epidermal cells, glandular hairs, and specialized structures like resin ducts and secretory cavities. The presence of these oils in such localized areas serves multiple functions, including defense against herbivores, attraction of pollinators, and protection against environmental stresses.
The production of essential oils is a complex process involving a series of biochemical pathways. These pathways are often regulated by environmental factors such as light, temperature, and soil composition, as well as by genetic factors. The resulting oils are highly diverse in their chemical compositions, with each plant species typically producing a unique blend of terpenes, phenols, esters, and other compounds. This diversity is crucial for the ecological roles these oils play and is also the basis for their varied uses in human applications, from aromatherapy to medicinal treatments.
In addition to their functional roles within the plant, the unique storage locations of essential oils, such as in glandular trichomes on the leaves or in the secretory cavities of flowers, highlight the specialized nature of these compounds. These storage mechanisms not only protect the oils from degradation but also facilitate their release when needed, whether for attracting beneficial insects or repelling pests. Understanding the nature and distribution of essential oils in plants is therefore key to optimizing their extraction processes and maximizing their potential benefits.

Challenges in Extraction Methods
Traditional extraction methods, such as distillation, present significant challenges in maintaining the integrity of essential oils. These methods often involve high temperatures and evaporation processes, which can lead to the alteration of the chemical composition of the oils. This alteration can result in the degradation of valuable compounds, reducing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the extraction process.
For instance, the heat applied during distillation can cause thermal decomposition of certain sensitive compounds, leading to a loss of their therapeutic properties. Additionally, the evaporation process can result in the loss of volatile oils, which are critical for the desired aroma and medicinal effects. These drawbacks highlight the need for more advanced and precise extraction techniques that can preserve the natural composition and potency of essential oils.
To address these challenges, modern extraction technologies, such as supercritical CO2 extraction, supramolecular extraction, and targeted extraction, have been developed. These methods offer more controlled environments and selective extraction capabilities, minimizing the risk of chemical alteration and loss of valuable compounds.
Cutting-Edge Extraction Technologies
Supercritical CO2 Extraction
Supercritical CO2 extraction harnesses the power of supercritical fluid technology, employing carbon dioxide (CO2) as the solvent. This method involves pressurizing CO2 to achieve a supercritical state, where it exhibits properties of both a gas and a liquid. The CO2 stream is then passed through a chamber containing the cannabis material, effectively extracting the active compounds.
One of the primary advantages of this technique is its simplicity and the low operating temperatures, which help preserve the integrity of the extracted compounds. However, the process is not without its drawbacks. The initial setup and operational costs are high, and the method is primarily suited for non-polar molecules.
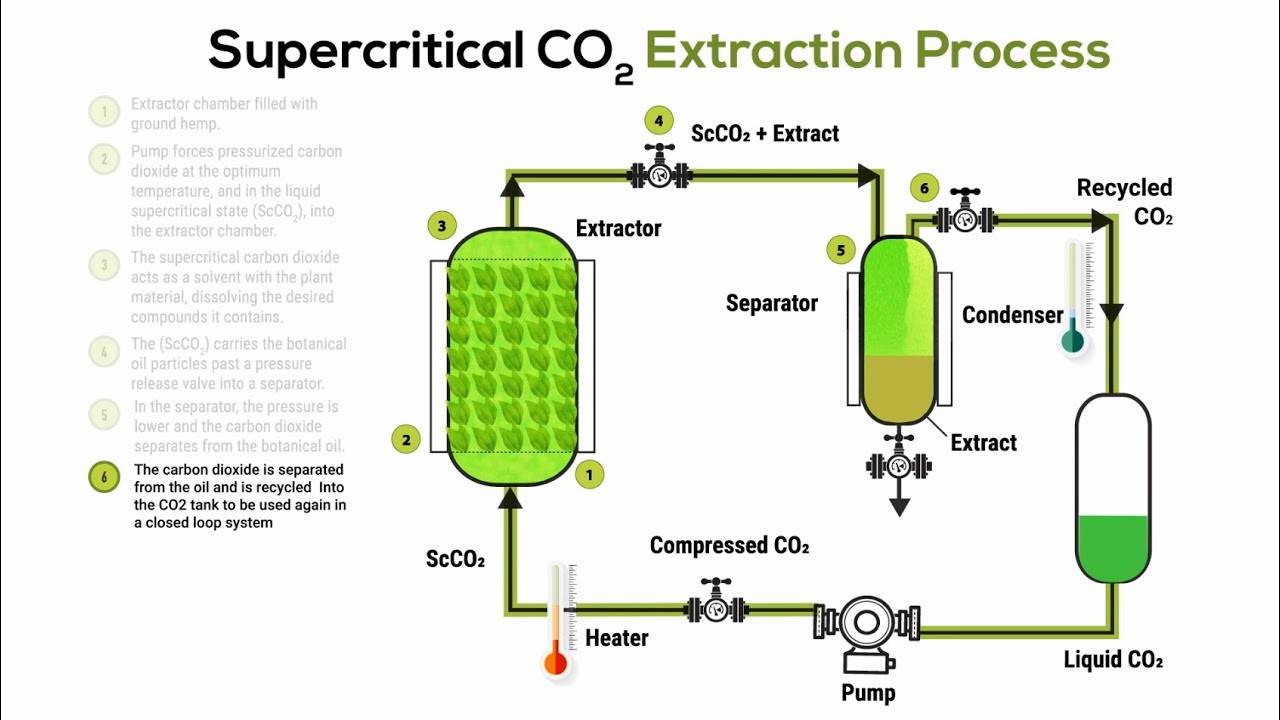
To optimize the extraction, the temperature and pressure can be finely tuned, allowing for the preservation of a complete terpene profile. Advanced systems may incorporate fractionation, enabling the isolation of specific components. Additionally, refrigerated chillers and recirculating heaters are integrated to facilitate the recycling of CO2, ensuring efficient and controlled operation.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simple process | High costs |
| Low operating temperature | Limited to non-polar molecules |
| Preserves terpene profile | Requires sophisticated equipment |
| Efficient CO2 recycling |
In summary, while supercritical CO2 extraction offers significant benefits in terms of process simplicity and compound preservation, it is constrained by its high costs and limited applicability to non-polar molecules. Nevertheless, its ability to yield high-quality extracts makes it a valuable tool in the field of plant extraction science.
Supramolecular Extraction
Supramolecular extraction represents a sophisticated method that harnesses the power of supramolecular systems to selectively isolate target substances. This technique stands out for its rapidity and efficiency, making it a promising alternative in the realm of aromatic plant extraction. Unlike traditional methods that often involve high temperatures and potentially damaging solvents, supramolecular extraction operates under milder conditions, thereby preserving the integrity of the extracted compounds.
The environmental friendliness of supramolecular extraction is another noteworthy feature. By minimizing the use of harsh chemicals and reducing waste, this method aligns with contemporary sustainability goals. Despite these advantages, the application of supramolecular extraction in aromatic plant extraction remains relatively rare, primarily due to the complexity and cost associated with setting up the necessary supramolecular systems.

In summary, while supramolecular extraction offers a fast, efficient, and eco-friendly approach to substance isolation, its broader adoption in the field of aromatic plant extraction is still in its nascent stages. Future research and development could potentially bridge this gap, making this advanced technique more accessible and prevalent in the industry.
Targeted Extraction
Targeted extraction represents a sophisticated approach to isolating specific active ingredients within plant materials, driven by advanced target modeling techniques. This method is instrumental in adhering to the stringent requirements of emerging cosmetic regulations, ensuring that products meet the highest standards of safety and efficacy. Despite its significant advantages, targeted extraction remains a costly endeavor, primarily confined to the pharmaceutical sector due to the high precision and specialized equipment required.
In the context of cosmetic manufacturing, the ability to precisely extract and quantify active ingredients is paramount. New regulatory frameworks demand not only the presence of effective components but also their accurate measurement and documentation. Targeted extraction excels in this regard, offering a solution that can precisely identify and isolate the desired compounds, thereby facilitating compliance with these rigorous standards.
However, the financial and technical barriers associated with targeted extraction limit its widespread adoption outside of the pharmaceutical industry. The process necessitates state-of-the-art technology and highly skilled personnel, both of which contribute to its elevated cost structure. As a result, while the cosmetic industry recognizes the potential of this method, its application remains restricted, awaiting advancements that could democratize its use and make it more accessible to broader sectors.
Modern extraction techniques, such as short path distillation, are gaining traction due to their efficiency and precision. Additionally, equipment like the water chiller circulator plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal temperatures during extraction processes, ensuring the preservation of sensitive compounds.
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
Related Articles
- The Real Reason Your Sintered Parts Crack (And It’s Not the Furnace)
- How Vacuum Induction Melting Prevents Catastrophic Material Failures in Critical Components
- Inconsistent Melts? The Problem Isn't Your Furnace, It's the Physics.
- Understanding Hot Isostatic Pressing in PVD Sputtering Targets
- Application of Liquid Nitrogen in Food Freezing




















