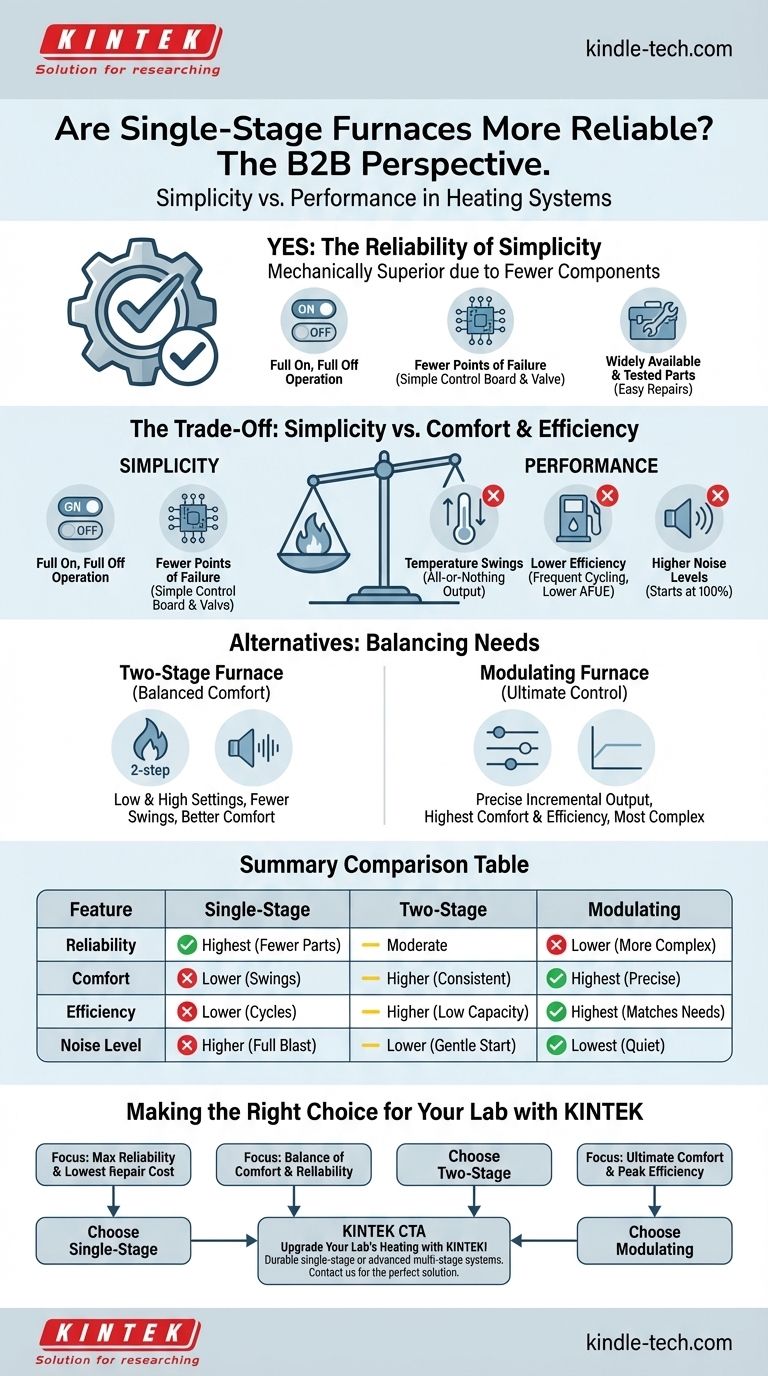
From a purely mechanical standpoint, yes, single-stage furnaces are generally more reliable. Their design simplicity means there are fewer components that can fail, and when a repair is needed, the parts are typically common and less expensive to replace.
The core decision is not just about reliability, but about balancing the straightforward dependability of a single-stage furnace against the superior comfort and efficiency offered by more complex multi-stage systems.

What Makes a Single-Stage Furnace Reliable?
The reliability of a single-stage furnace stems directly from its simple, no-frills design. It operates on a basic principle that has been tested and refined for decades.
A "Full On, Full Off" Design
A single-stage furnace has only one level of heat output: 100%. When your thermostat calls for heat, the furnace turns on at full blast and runs until the desired temperature is reached, then shuts off completely.
This binary operation requires the fewest moving parts and the simplest control logic, forming the foundation of its dependability.
Fewer Points of Failure
Compared to more advanced furnaces, a single-stage model has a less complex gas valve and a simpler control board. It lacks the sophisticated components needed to operate at multiple capacities.
Fewer components inherently mean there are fewer potential points of failure over the lifespan of the unit.
Widely Available and Tested Parts
Because single-stage technology is so established, its components are widely available and familiar to virtually every HVAC technician. This makes troubleshooting faster and repairs less expensive.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Reliability vs. Performance
Choosing the most reliable option comes with clear compromises in other areas. The simplicity of a single-stage furnace directly impacts comfort, efficiency, and noise.
The Cost of Simplicity: Temperature Swings
The "all or nothing" operation of a single-stage furnace can create noticeable temperature swings in your home. You may feel a blast of very hot air, followed by a period where the air cools down significantly before the furnace kicks on again.
More advanced furnaces run for longer periods at a lower output, providing a much more consistent and even temperature.
The Efficiency Question
While mechanically robust, single-stage furnaces can be less fuel-efficient. The constant cycling of on-at-full-blast and then off can use more energy than running a system at a lower, steadier rate.
Two-stage and modulating furnaces, which can match their output more closely to the home's heating needs, often carry a higher Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) rating.
Noise Levels
A single-stage furnace starting up at 100% capacity is audibly more disruptive than a multi-stage furnace that can start gently on a lower setting. The blower fan also operates at a single, high speed.
A Brief Look at Multi-Stage Alternatives
To understand the trade-off, it's helpful to know what the alternatives offer.
The Two-Stage Advantage: Balanced Comfort
A two-stage furnace has a low-fire setting (around 65-70% capacity) and a high-fire setting (100%). It will run on the low, quiet, and efficient setting for most of the time, only using the high-fire stage on the coldest days.
This results in fewer temperature swings and better overall comfort. While more complex than a single-stage unit, it is a very popular middle-ground option.
The Modulating Pinnacle: Ultimate Control
Modulating furnaces are the most advanced, capable of adjusting their heat output in tiny increments (e.g., from 40% to 100%). They run almost continuously at the precise level needed to maintain a perfect temperature.
This offers the highest level of comfort and efficiency but also represents the most complex design, with more specialized parts and sophisticated controls.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be based on what you value most for your home and budget.
- If your primary focus is maximum reliability and the lowest potential repair cost: A single-stage furnace is the most straightforward and dependable option.
- If your primary focus is a balance of enhanced comfort and solid reliability: A two-stage furnace offers a significant upgrade in comfort for a moderate increase in system complexity.
- If your primary focus is ultimate comfort and peak energy efficiency: A modulating furnace is the superior choice, with the understanding that its advanced technology is inherently more complex.
Understanding this fundamental trade-off between simplicity and performance is the key to selecting a furnace that truly meets your needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Single-Stage Furnace | Two-Stage Furnace | Modulating Furnace |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reliability | Highest (fewer parts) | Moderate | Lower (more complex) |
| Comfort | Lower (temperature swings) | Higher (consistent heat) | Highest (precise control) |
| Efficiency | Lower (cycles on/off) | Higher (runs at lower capacity) | Highest (matches needs) |
| Noise Level | Higher (starts at full blast) | Lower (gentle start) | Lowest (quiet operation) |
Upgrade your lab's heating efficiency with KINTEK's reliable equipment!
Whether you need durable single-stage furnaces for consistent performance or advanced multi-stage systems for precise temperature control, KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables to meet your exact needs. Contact us today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why do we use a muffle furnace? For Pure, Precise, and Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What does a lab muffle furnace do? Achieve Pure, Contamination-Free Heating for Your Lab
- How to use a muffle furnace in a laboratory? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe, Precise Thermal Processing
- What is the temperature accuracy of a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise and Uniform Heating
- What does a high ash content mean? A Guide to Material Quality & Contamination



















