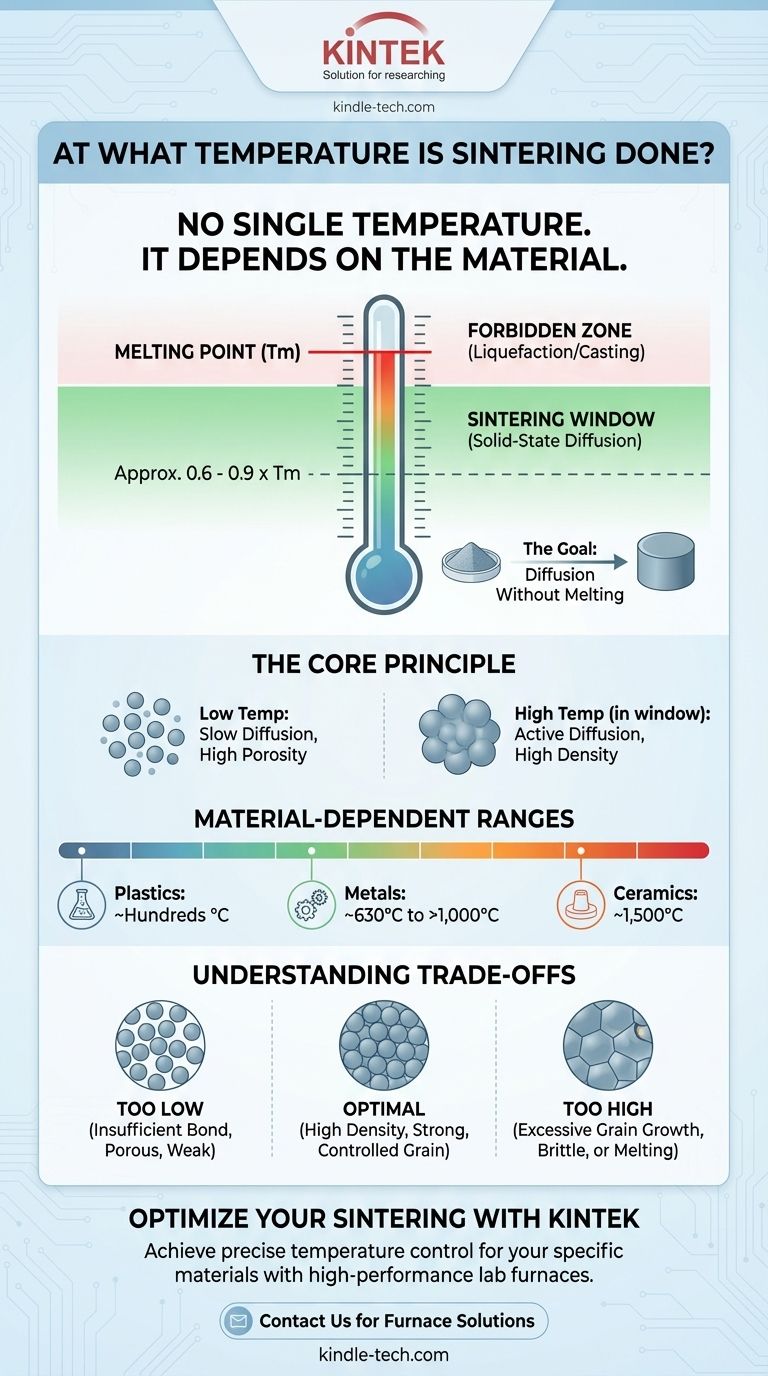
There is no single temperature for sintering; it is fundamentally dependent on the specific material being processed. The temperature must be high enough to enable atomic bonding but remain below the material's melting point. As a general rule, sintering occurs at a temperature greater than 60% of the material's absolute melting temperature, which can range from a few hundred to well over 1,500°C.
The core challenge of sintering is finding the precise thermal sweet spot. The temperature must be high enough to activate atomic diffusion, causing solid particles to fuse together, but low enough to avoid liquefying the material entirely.

The Core Principle: Diffusion Without Melting
Sintering is a thermal process that converts a powder compact into a dense, solid object. Temperature is the primary driver of this transformation, governing the speed and effectiveness of the process.
Activating Atomic Diffusion
For sintering to occur, atoms on the surfaces of adjacent powder particles must have enough energy to move and form new bonds. High temperature provides this kinetic energy, promoting atomic diffusion across particle boundaries.
This process naturally reduces the total surface area of the particles, pulling them together, shrinking the part, and eliminating the pores between them.
Staying Below the Melting Point
Crucially, sintering is a solid-state process. The goal is to make the particles fuse together without ever becoming a liquid.
If the temperature reaches the material's melting point (Tm), the process is no longer sintering; it is casting. This would destroy the controlled microstructure that sintering is designed to create.
The "Rule of Thumb" Temperature
The most reliable guideline is that sintering temperature is a function of the material's melting point. The process typically requires a temperature of approximately 0.6 to 0.9 times the absolute melting temperature of the material.
For example, a material that melts at 2000°C would likely be sintered somewhere between 1200°C and 1800°C.
Why Temperature Varies So Widely
The vast temperature range seen in sintering processes—from 600°C to over 1500°C—is a direct result of the diverse materials being used and the desired final properties.
Material Type is the Primary Factor
Different materials have vastly different melting points. This is the main reason for the wide range of sintering temperatures.
- Ceramics like Zirconia, with a very high melting point, are often sintered at temperatures around 1,500°C to achieve maximum density.
- Metals have a wide range, with some alloys being sintered around 630°C and others well over 1000°C.
- Plastics have much lower melting points and are therefore sintered at correspondingly lower temperatures, often only a few hundred degrees Celsius.
The Goal: Controlling Density
Temperature is a direct lever for controlling the final density of the part. Higher temperatures (within the appropriate range) generally lead to faster diffusion and higher final density.
For many high-performance applications, the goal is to get as close to 100% theoretical density as possible, as this maximizes strength and other mechanical properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sintering temperature is not just about hitting a minimum threshold; it is a balancing act with significant consequences for the final product.
Insufficient Temperature
If the temperature is too low, diffusion will be slow and incomplete. This results in a part with high porosity, low density, and poor mechanical strength. The particles have not been sufficiently bonded together.
Excessive Temperature
Even if the temperature stays below the melting point, setting it too high can be detrimental. It can cause excessive grain growth, where the microscopic crystalline structures within the material become too large. This can sometimes make the material more brittle.
The Risk of Over-Sintering
The most obvious failure is exceeding the melting point. This causes the part to lose its shape and results in a cast or semi-molten mass rather than a precisely formed sintered component.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct sintering temperature is determined by the material and the desired outcome. Use these principles to guide your thinking.
- If your primary focus is understanding the concept: Remember that sintering operates in a window above 60% of the material's melting point but strictly below the point of liquefaction.
- If your primary focus is processing a specific material: Do not rely on general rules. Look up the established sintering cycle for that exact material, as it has been optimized for specific results.
- If your primary focus is optimizing performance: Treat temperature as a tool to control density and grain size, which are the primary drivers of the final part's mechanical properties.
Ultimately, temperature is the fundamental control that transforms loose powder into a coherent, high-performance solid.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Typical Sintering Temperature Range | Key Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramics (e.g., Zirconia) | ~1,500°C | Very High Melting Point |
| Metals | ~630°C to >1,000°C | Alloy Composition |
| Plastics | A few hundred °C | Low Melting Point |
| General Rule | 0.6 - 0.9 x Absolute Melting Point (Tm) | Atomic Diffusion |
Optimize Your Sintering Process with KINTEK
Achieving the perfect balance of density and strength in your sintered parts requires precise temperature control. The right lab furnace is critical for success.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and equipment designed for reliable sintering processes. We provide the tools you need to hit the thermal sweet spot for your specific materials, from metals and ceramics to plastics.
Let us help you:
- Select the ideal furnace for your temperature range and material requirements.
- Ensure consistent results with equipment built for accuracy and durability.
- Enhance your lab's capabilities with solutions tailored to your research or production goals.
Contact us today to discuss your sintering application and find the perfect solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the main purpose of a furnace? A Guide to Heating, Comfort, and Material Transformation
- What is the construction of a muffle furnace? Discover the Precision Engineering for Pure, Controlled Heating
- What is the difference between a retort and a muffle furnace? Uncover the Truth About Indirect Heating
- What is the difference between muffle furnace and induction furnace? Choosing the Right Heat Source for Your Lab
- What construction features contribute to the practicality and reliability of a muffle furnace? Key Design Elements for Lab Success



















