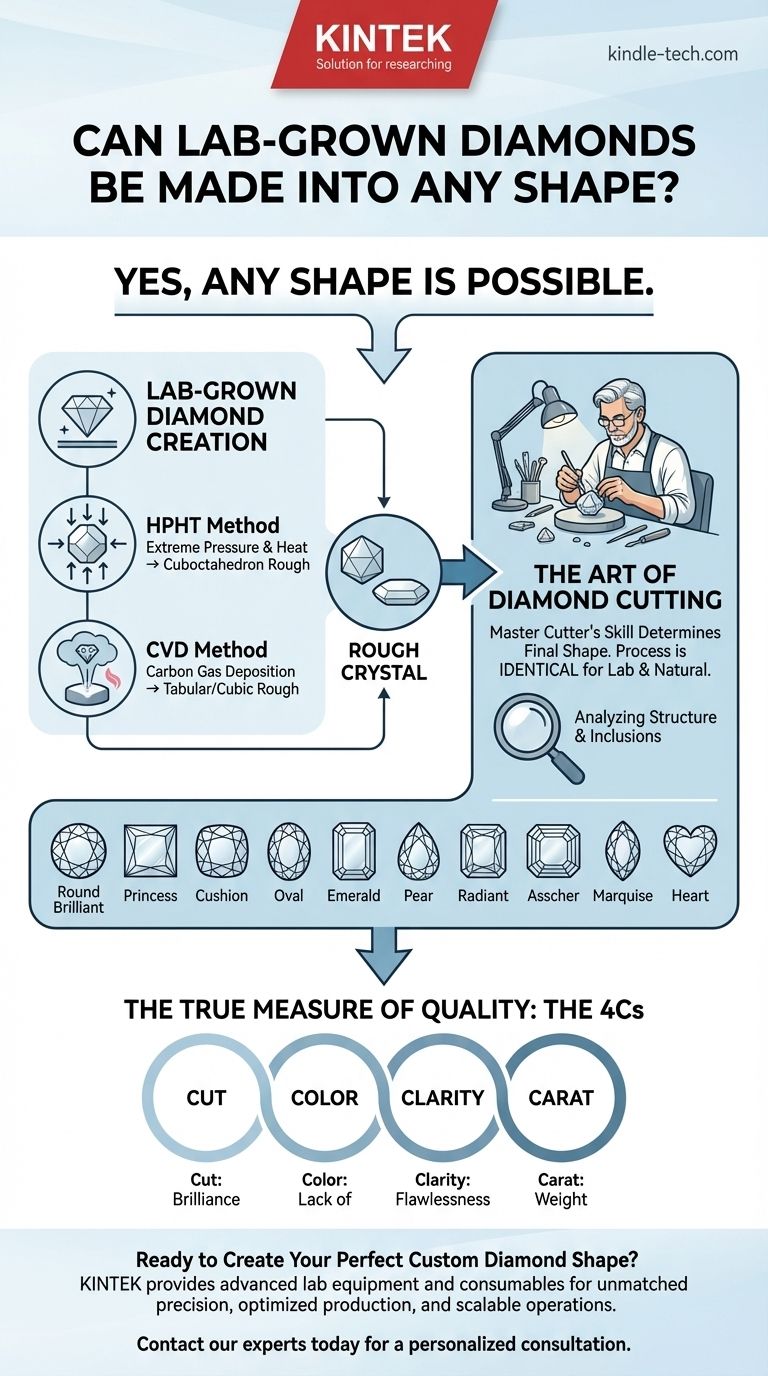
Yes, a lab-grown diamond can be fashioned into any shape. Just like a mined diamond, a lab-grown diamond begins as a rough crystal. It is the skill of the diamond cutter, not the origin of the stone, that determines its final, polished shape—whether that be a classic round brilliant, an elegant pear, or a modern emerald cut.
The final shape of a lab-grown diamond is not a limitation of the creation process. The process produces a rough crystal, which is then cut and polished into any desired form, identical to the methods used for natural diamonds.

The Journey from Crystal to Gem
To understand why shape is not a constraint, you must first distinguish between how a diamond is grown and how it is cut. The growth process creates the raw material; the cutting process creates the final product.
How Lab Diamonds Are Grown
Labs primarily use two methods to create diamonds, both starting from a tiny diamond "seed."
The HPHT Method (High Pressure/High Temperature) This process mimics the intense conditions deep within the Earth's mantle where natural diamonds form. A diamond seed is placed in a chamber with pure carbon and subjected to extreme pressure and heat, causing the carbon to melt and crystallize onto the seed, growing a larger diamond.
The CVD Method (Chemical Vapor Deposition) In this method, a diamond seed is placed in a vacuum chamber filled with carbon-rich gases. These gases are superheated into a plasma, which causes carbon atoms to detach and deposit onto the seed, building up a diamond crystal layer by layer.
From Rough Crystal to Polished Shape
The growth method determines the shape of the rough crystal, which is the starting point for the cutter. This initial form influences the cutting plan but does not limit the final outcome.
The Shape of the Rough Diamond
A key difference a gemologist can spot is in the raw, uncut crystal form:
- Natural Diamonds typically grow in an eight-sided octahedral shape.
- HPHT Lab Diamonds tend to form a cuboctahedron shape with 14 growth directions.
- CVD Lab Diamonds usually grow in a flatter, cubic or tabular shape.
The Art of the Diamond Cutter
A master cutter receives this rough crystal—whether it's natural, HPHT, or CVD. Their job is to analyze its unique structure, including its shape and any internal inclusions.
They then map out a cutting plan to achieve the best possible combination of carat weight, brilliance, and clarity. This highly skilled process is identical for both lab-grown and mined diamonds.
The Result: A Full Spectrum of Shapes
Because the cutting process is universal, any shape achievable with a mined diamond is also achievable with a lab-grown one. The talent of the cutter is the deciding factor in the stone's final beauty and fire, not its origin.
Understanding the Practical Implications
While any shape is possible, the shape of the rough crystal can have subtle effects on the manufacturing process. This does not limit your choices but is a factor for the cutter.
Rough Shape Can Influence Yield
The flatter, tabular shape of a rough CVD diamond is often well-suited for creating "fancy" shapes like emerald, princess, or radiant cuts. This can sometimes result in a higher yield, meaning less of the rough crystal is wasted during cutting.
The True Measure of Quality
Ultimately, the growth method (HPHT vs. CVD) or origin (lab vs. mined) is secondary. The quality of the final gem comes down to the famous 4Cs: Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat. A well-cut diamond will be brilliant and beautiful, regardless of how the rough crystal was formed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When selecting a diamond, your focus should be on the qualities of the finished stone, not on perceived limitations of its origin.
- If your primary focus is a specific shape: Be assured that lab-grown diamonds offer the complete range of shapes, so your desired style is fully available.
- If your primary focus is value and carat size: The efficiency of cutting certain shapes from tabular CVD rough might offer advantages, but always prioritize the final cut quality.
- If your primary focus is identical properties: Remember that lab-grown diamonds are chemically, physically, and optically identical to natural diamonds, differing only in their origin.
Your choice of diamond shape should be guided by your personal style, not by any restriction related to its creation.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Lab-Grown Diamonds | Natural Diamonds |
|---|---|---|
| Shape Availability | Any shape (round, pear, emerald, etc.) | Any shape (round, pear, emerald, etc.) |
| Cutting Process | Identical process by master cutters | Identical process by master cutters |
| Rough Crystal Shape | HPHT: Cuboctahedron CVD: Tabular/Cubic |
Typically Octahedral |
| Final Quality Determinant | The 4Cs (Cut, Color, Clarity, Carat) | The 4Cs (Cut, Color, Clarity, Carat) |
Ready to Create Your Perfect Custom Diamond Shape?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced laboratory equipment and consumables that power the creation of stunning lab-grown diamonds. Whether you are a jewelry designer, a gemologist, or a manufacturer, our high-precision tools are essential for every step of the process—from growing the initial crystal to achieving the perfect cut.
We help you:
- Achieve Unmatched Precision: Our equipment supports the exacting standards required for cutting any diamond shape, ensuring maximum brilliance and yield.
- Optimize Your Production: Leverage our technology to efficiently transform rough lab-grown crystals into high-value finished gems, reducing waste and increasing profitability.
- Scale Your Operations: From small bespoke projects to large-scale manufacturing, KINTEK provides reliable, consistent solutions tailored to your laboratory's needs.
Let's discuss how our lab equipment can enhance your diamond creation process. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation and discover the KINTEK difference in quality and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What is the difference between PECVD and CVD? Unlock the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method



















