Yes, you can absolutely melt steel using induction heating. This method is not only possible but is a widely used industrial process for creating high-purity alloys and casting steel parts. Unlike a traditional furnace that uses external flames or heating elements, induction generates intense heat directly inside the steel itself by leveraging powerful, rapidly changing magnetic fields.
Induction melting is a non-contact process that effectively turns the steel into its own heating element. Its success relies on a precisely engineered system that delivers immense electrical power at a specific frequency to overcome steel's high melting point in a clean, controlled manner.

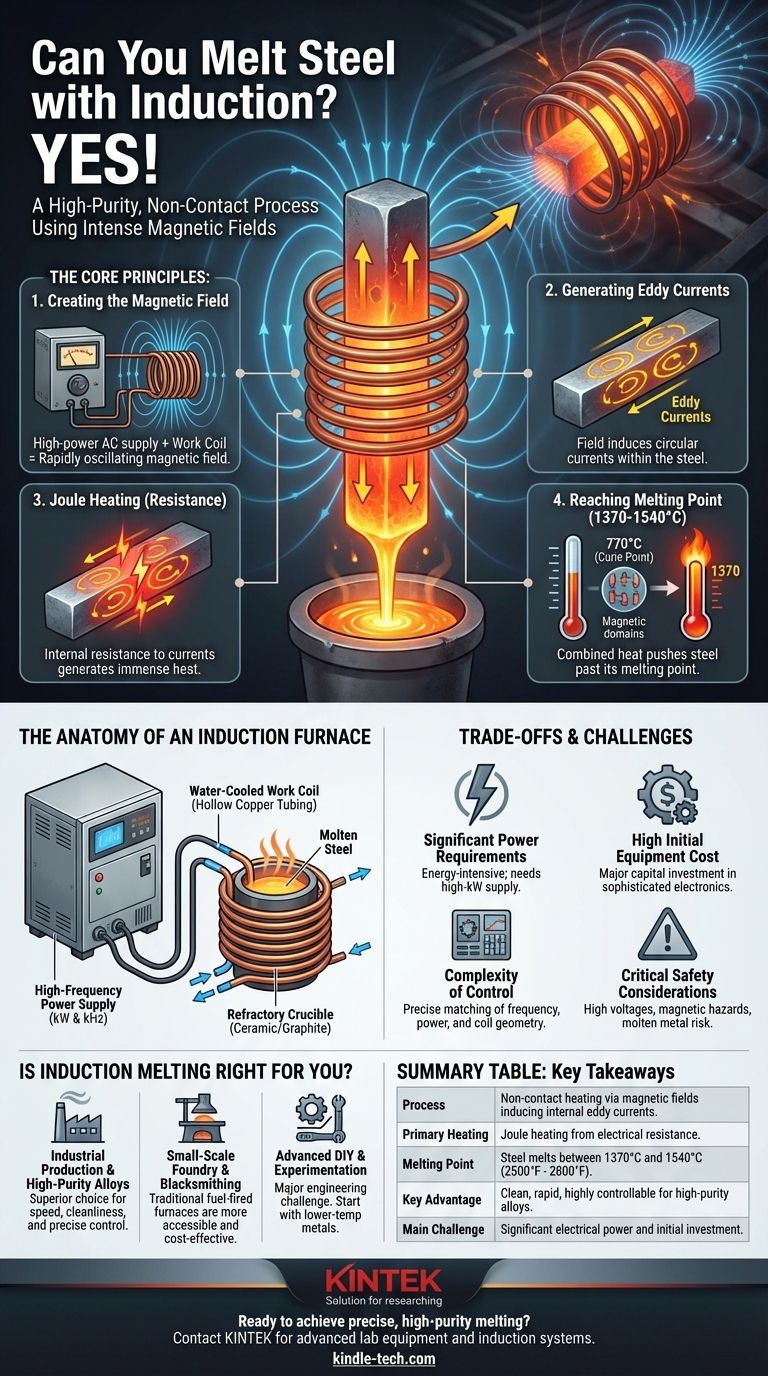
The Core Principles: How Induction Turns Steel to Liquid
To understand induction melting, you must first understand that it is fundamentally an electrical process, not a thermal one in the conventional sense. The heat is a byproduct of electrical currents induced within the metal.
Creating the Magnetic Field
The process begins with a high-power AC power supply connected to a copper coil, known as the work coil. When high-frequency alternating current flows through this coil, it generates a powerful and rapidly oscillating magnetic field in the space within and around the coil.
Generating Heat Through Eddy Currents
When a conductive material like steel is placed within this magnetic field, the field induces small, circular electric currents within the metal. These are called eddy currents. As these currents swirl through the steel, they encounter electrical resistance, which generates immense heat—a phenomenon known as Joule heating.
The Role of Magnetic Hysteresis
For magnetic materials like steel, there is a secondary heating effect. The rapidly reversing magnetic field forces the magnetic domains within the steel to flip back and forth billions of times per second. This internal friction also generates significant heat. However, this effect ceases once the steel reaches its Curie temperature (around 770°C / 1420°F) and loses its magnetic properties.
Reaching the Melting Point
The combination of intense Joule heating from eddy currents and initial heating from hysteresis rapidly raises the steel's temperature. By supplying enough power, the system can quickly push the steel past its melting point (ranging from 1370 to 1540°C / 2500 to 2800°F) until it becomes fully molten.
The Anatomy of an Induction Furnace
A system capable of melting steel is more than just a simple coil. It's a carefully balanced set of industrial components, each with a critical function.
The High-Frequency Power Supply
This is the heart of the system. It takes standard utility power and converts it into the high-current, high-frequency output needed to drive the work coil. The power (measured in kilowatts, kW) determines the heating rate, while the frequency (measured in kilohertz, kHz) influences the heating depth.
The Water-Cooled Work Coil
The work coil itself is almost always made from hollow copper tubing. The immense currents flowing through it generate their own heat, requiring a constant flow of cooling water to prevent the coil from melting long before the steel does. The coil's shape is engineered to maximize the magnetic field's coupling with the steel for best efficiency.
The Refractory Crucible
The molten steel must be held in a container. This container, or crucible, must be made from a refractory material like ceramic or graphite. It needs to be able to withstand extreme temperatures and thermal shock while also being "transparent" to the magnetic field, allowing the energy to pass through it and heat the steel directly.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While powerful, induction melting is not a universal solution. It comes with specific requirements and limitations that are important to understand.
Significant Power Requirements
Melting steel is an incredibly energy-intensive process. A small, hobbyist-scale induction heater capable of melting a few grams of aluminum is orders of magnitude less powerful than an industrial furnace needed to melt several kilograms of steel. These systems require high-kilowatt power supplies and robust electrical infrastructure.
High Initial Equipment Cost
Professional induction furnaces are a major capital investment. The sophisticated power electronics, precisely wound and cooled coils, and durable crucibles represent significant upfront costs compared to simpler fuel-fired forges or furnaces.
The Complexity of Control
Effective induction melting is a science. The system's frequency, power level, and coil geometry must be carefully matched to the mass, shape, and type of steel being melted. An improper setup leads to poor efficiency or can even damage the equipment.
Critical Safety Considerations
The dangers are significant and must be respected. The system operates at high voltages and currents, the magnetic fields can heat metallic objects (like jewelry or tools) unexpectedly, and a failure could result in the catastrophic release of molten metal.
Is Induction Melting Right for Your Goal?
Deciding whether to use induction depends entirely on your objective, budget, and scale.
- If your primary focus is industrial production or high-purity casting: Induction is a superior choice, offering unparalleled speed, cleanliness, and precise control over the final alloy.
- If your primary focus is small-scale foundry work or blacksmithing: A traditional gas or coke-fired furnace is far more accessible and cost-effective for heating and melting smaller quantities of metal.
- If your primary focus is advanced DIY or electronics experimentation: Be aware that melting steel is a major engineering challenge. Start with lower-temperature metals like tin or aluminum to understand the principles safely before considering the immense power needed for steel.
Ultimately, mastering induction melting is about controlling electromagnetism to precisely deliver vast amounts of energy exactly where it is needed.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Process | Non-contact heating via magnetic fields induces internal eddy currents in the steel. |
| Primary Heating | Joule heating from electrical resistance to induced currents. |
| Melting Point | Steel melts between 1370°C and 1540°C (2500°F - 2800°F). |
| Key Advantage | Clean, rapid, and highly controllable process ideal for high-purity alloys. |
| Main Challenge | Requires significant electrical power and a substantial initial investment in equipment. |
Ready to achieve precise, high-purity melting in your lab or production facility? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including induction melting systems. Our experts can help you select the right solution for your specific steel or alloy requirements, ensuring efficiency, safety, and superior results. Contact our team today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can empower your innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting



















