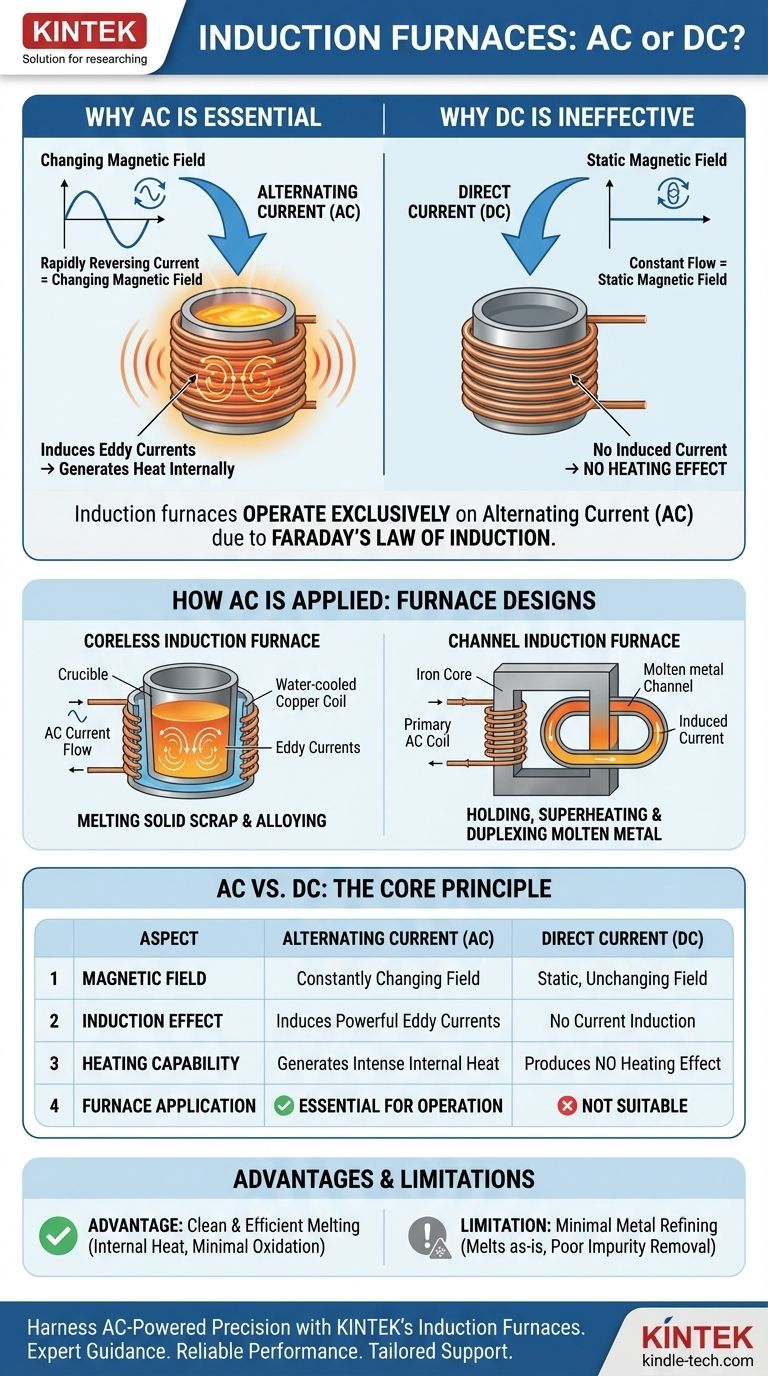
At their core, induction furnaces operate exclusively on Alternating Current (AC). Their entire heating principle is fundamentally dependent on the continuously changing magnetic fields that only AC can produce. A Direct Current (DC) supply, which creates a static magnetic field, would be entirely ineffective for this purpose.
An induction furnace does not use electricity as a direct heat source like a simple resistor. Instead, it leverages the laws of electromagnetism. The rapid, constant reversal of an AC flow in a primary coil creates a powerful, changing magnetic field that induces secondary electrical currents directly within the metal itself, generating intense heat from the inside out.

The Core Principle: Why AC is Essential
The operation of an induction furnace is a direct application of Faraday's Law of Induction. Understanding this principle makes it clear why AC is not just a choice, but a physical necessity for the technology to function.
Faraday's Law of Induction
This fundamental law of physics states that a changing magnetic field will induce an electromotive force, or voltage, in any conductor placed within it. This induced voltage, in turn, drives an electrical current.
The Role of Alternating Current
Alternating Current is the engine of this process. Because AC rapidly and continuously changes its direction and magnitude, the magnetic field it generates in the furnace's primary coil is also constantly changing and collapsing.
A Direct Current, by contrast, flows in one steady direction. It would create a strong but static, unchanging magnetic field. This static field would not induce any current in the metal charge, producing no heating effect whatsoever.
Generating Heat with "Eddy Currents"
The currents induced within the metal charge are known as eddy currents. As these powerful currents swirl through the metal, they encounter the material's natural electrical resistance. This resistance converts the electrical energy of the eddy currents directly into thermal energy, or heat, causing the metal to melt efficiently.
How This Principle is Applied in Practice
While the AC-driven principle is the same, it is applied in two primary furnace designs mentioned in your references: the coreless furnace and the channel furnace. Each is optimized for different industrial applications.
The Coreless Induction Furnace
In a coreless design, the metal charge is placed inside a refractory crucible. This crucible is surrounded by a water-cooled coil of heavy copper tubing, through which a powerful alternating current flows.
The coil acts as the primary winding of a transformer. The metal charge itself becomes the secondary winding—a single, short-circuited turn. The intense eddy currents induced in the charge lead to rapid and direct heating.
The Channel Induction Furnace
A channel furnace functions more like a conventional transformer. It has an iron core with a primary AC coil, which induces a current in a secondary loop of molten metal contained within a channel.
This design is extremely efficient for holding, superheating, and alloying already-molten metal. However, it is less suited for melting solid scrap from a cold start compared to the coreless type.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The direct, internal heating method of induction furnaces provides distinct advantages but also comes with a key limitation that dictates their use.
Advantage: Clean and Efficient Melting
Because the heat is generated within the metal, the process is incredibly efficient and fast. It also allows for a clean melt with minimal loss of valuable alloys to oxidation, as there are no direct products of combustion.
Limitation: Minimal Metal Refining
Unlike an arc furnace, an induction furnace provides very little metallurgical refining. It essentially melts what is put into it. The process does not effectively remove impurities like sulfur or phosphorus, meaning the quality of the raw material scrap directly determines the quality of the final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The choice between the two main furnace types depends entirely on the operational goal, as both are built on the same non-negotiable principle of AC-powered induction.
- If your primary focus is melting solid scrap and alloying various metals: The coreless furnace is the standard, offering versatility and powerful direct-melting capabilities.
- If your primary focus is holding, superheating, or duplexing already molten metal: The channel furnace provides superior thermal efficiency for maintaining the temperature of a liquid bath.
Ultimately, understanding that induction heating is an AC-dependent electromagnetic process is the key to mastering its application in any metallurgical operation.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Alternating Current (AC) | Direct Current (DC) |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Field | Creates a constantly changing field | Creates a static, unchanging field |
| Induction Effect | Induces powerful eddy currents in metal | No current induction occurs |
| Heating Capability | Generates intense internal heat | Produces no heating effect |
| Furnace Application | Essential for all induction furnace operation | Not suitable for induction heating |
Ready to harness the precision of AC-powered induction heating for your lab or foundry?
At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment, including induction furnaces designed for efficient and clean melting. Whether you're processing metals, alloys, or advanced materials, our solutions deliver rapid, controlled heating with minimal oxidation.
Let us help you achieve superior results:
- Expert Guidance: Choose the right furnace type (coreless or channel) for your specific application.
- Reliable Performance: Benefit from equipment built for durability and precision.
- Tailored Support: Get solutions optimized for your laboratory or production needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's induction furnaces can enhance your metallurgical processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the effects of hydrogen (H2) in a controlled furnace environment? Mastering Reduction and Risk
- What is hydrogen atmosphere heat treatment? Achieve Superior Surface Purity & Brightness
- Why must a hydrogen-reducing atmosphere be maintained for tungsten annealing? Ensure Purity in High-Temp Processing
- What is hydrogen annealing? Achieve Superior Material Properties with Bright Annealing
- When would you need to use a controlled atmosphere? Prevent Contamination and Control Reactions



















