In short, yes. Molybdenum is a good thermal conductor, a critical property that complements its primary role as a high-strength, high-temperature refractory metal. Its ability to conduct heat is essential for its use in demanding environments like vacuum furnaces, where uniform temperature is paramount.
Molybdenum's true value is not just its ability to conduct heat, but its unique combination of good thermal conductivity, excellent high-temperature strength, and a very high melting point. This profile makes it a specialized material for applications where common metals would fail.

Molybdenum's Thermal Properties in Context
To understand why molybdenum is chosen for specific jobs, we need to look at its thermal conductivity relative to other materials and how it behaves under extreme heat.
Quantifying Thermal Conductivity
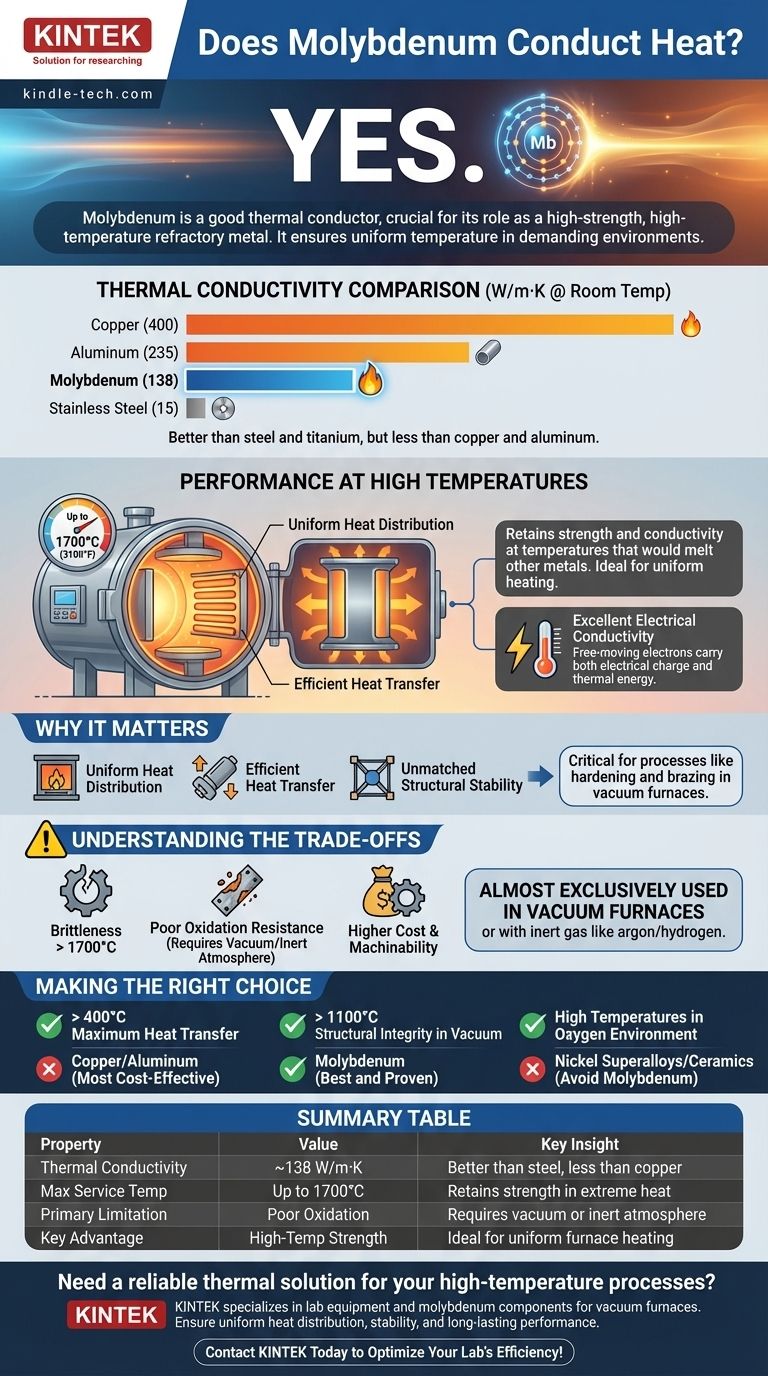
Molybdenum has a thermal conductivity of approximately 138 W/m·K (Watts per meter-Kelvin) at room temperature.
To put this in perspective, it is a significantly better heat conductor than stainless steel (~15 W/m·K) and titanium (~22 W/m·K). However, it is not as conductive as copper (~400 W/m·K) or aluminum (~235 W/m·K).
The Link to Electrical Conductivity
For most pure metals, good electrical conductivity strongly correlates with good thermal conductivity. The reference notes that molybdenum has excellent electrical conductivity.
This is because in metals, free-moving electrons are the primary carriers of both electrical charge and thermal energy. Molybdenum's atomic structure allows electrons to move easily, enabling efficient transfer of both electricity and heat.
Performance at High Temperatures
Molybdenum's key advantage is retaining its strength and conductivity at temperatures that would melt or severely weaken other metals. It is reliably used in processes up to 1700°C (3100°F).
While its thermal conductivity does decrease slightly at these extreme temperatures, it remains high enough to ensure effective heat distribution in furnace components and tooling.
Why This Matters for High-Temperature Applications
The combination of thermal conductivity and structural integrity makes molybdenum essential for specific industrial processes mentioned in the reference, such as hardening and brazing.
Uniform Heat Distribution
In a vacuum furnace, components made of molybdenum, such as heating elements and heat shields, ensure that heat is spread evenly throughout the chamber. This uniformity prevents hot spots and ensures the part being treated receives consistent heat, which is critical for quality.
Efficient Heat Transfer
As a heating element, molybdenum's electrical resistance generates immense heat. Its thermal conductivity then allows that heat to be efficiently radiated and conducted to the workpiece, enabling processes like brazing.
Unmatched Structural Stability
Unlike other metals that would warp, sag, or crack under intense thermal stress, molybdenum maintains its shape and strength. This mechanical stability is just as important as its thermal properties for building reliable, long-lasting furnace interiors.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every situation. Molybdenum has specific limitations that define where it can and cannot be used effectively.
Brittleness Above Operating Limits
As the reference notes, molybdenum becomes brittle beyond its maximum recommended service temperature of 1700°C. Pushing it past this limit can lead to catastrophic failure of the component.
Poor Oxidation Resistance
Molybdenum's most significant weakness is its susceptibility to oxidation at high temperatures. If heated in the presence of oxygen, it will rapidly form a volatile oxide and fail.
This is precisely why it is almost exclusively used in vacuum furnaces or environments with a protective, inert atmosphere like argon or hydrogen.
Cost and Machinability
As a refractory metal, molybdenum is more expensive and generally more difficult to machine than common alloys like steel. Its use is therefore justified only when its unique high-temperature properties are a strict requirement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a material requires balancing performance needs with environmental constraints and cost.
- If your primary focus is maximum heat transfer below 400°C: Copper or aluminum are far more conductive and cost-effective choices.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity and uniform heating above 1100°C in a vacuum: Molybdenum is one of the best and most proven materials for the job.
- If your application involves high temperatures in an open-air or oxygen-rich environment: You must avoid molybdenum and instead consider materials like nickel-based superalloys or ceramics.
Ultimately, choosing the right material means understanding the entire operating environment, not just a single physical property.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | ~138 W/m·K at room temperature | Better than steel, but less than copper |
| Maximum Service Temperature | Up to 1700°C (3100°F) | Retains strength and conductivity in extreme heat |
| Primary Limitation | Poor oxidation resistance | Requires vacuum or inert atmosphere for use |
| Key Advantage | Combines thermal conductivity with high-temperature strength | Ideal for uniform heating in furnace components |
Need a reliable thermal solution for your high-temperature processes? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, including molybdenum components for vacuum furnaces. Our expertise ensures you get materials that deliver uniform heat distribution, structural stability, and long-lasting performance in demanding environments. Contact us today to optimize your lab's efficiency with the right high-temperature solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- High Temperature Wear-Resistant Alumina Al2O3 Plate for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- At what temperature does molybdenum evaporate? Understanding Its High-Temperature Limits
- What are the problems with heat treatment? Avoid Distortion, Cracking, and Surface Defects
- Which factors are critical in heat treatment? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Cooling for Superior Results
- What are the most commonly used metals in a vacuum furnace's hot zone? Discover the Key to High-Purity Processing
- Can an arc happen in a vacuum? Yes, and here's how to prevent it in your high-voltage design.



















