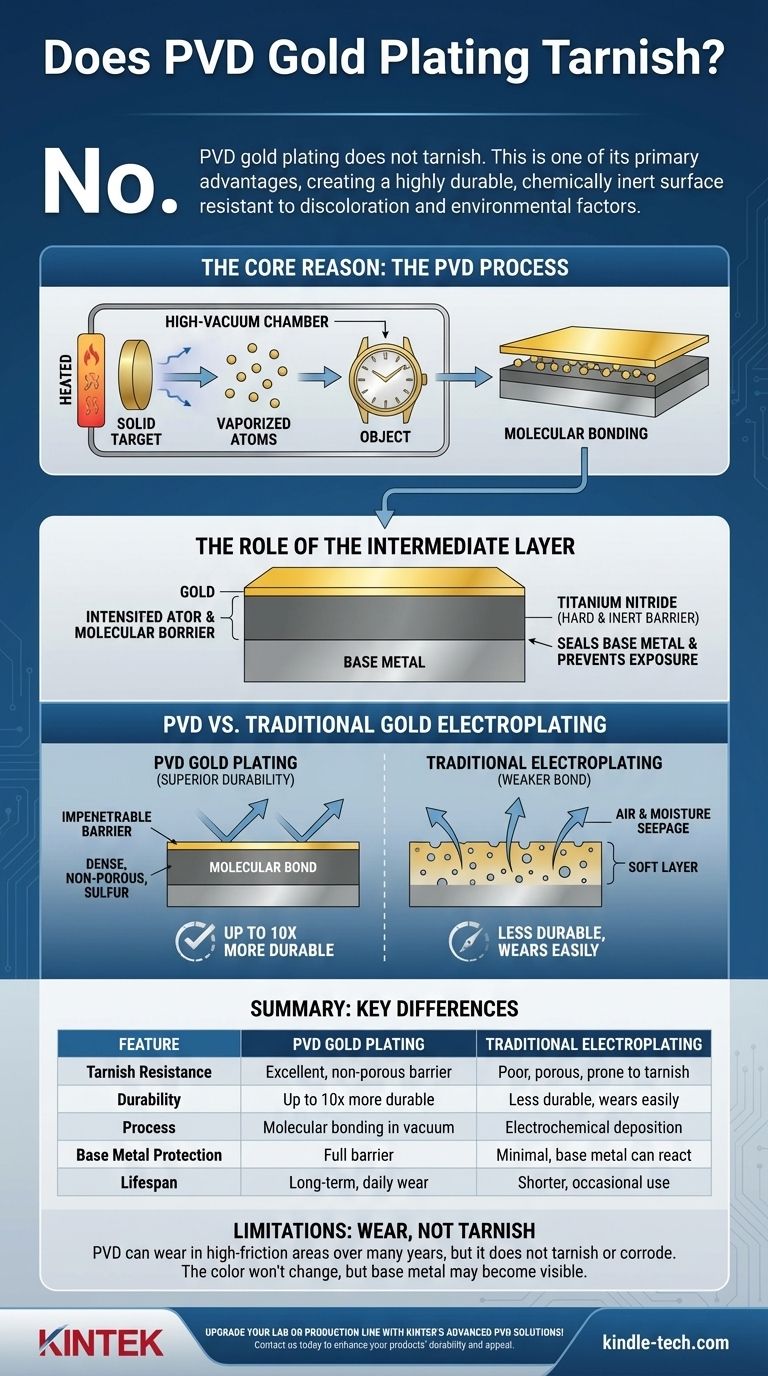
No, PVD gold plating does not tarnish. This is one of its primary advantages over traditional gold plating methods. The process creates a highly durable, chemically inert surface that is engineered to resist the environmental factors and chemical reactions that cause discoloration and tarnish.
The core reason PVD gold doesn't tarnish is the process itself. It molecularly bonds a hard, non-reactive material (like titanium nitride) to the base metal before applying the gold, creating an impenetrable barrier that protects both the base metal and the gold from corrosion and wear.
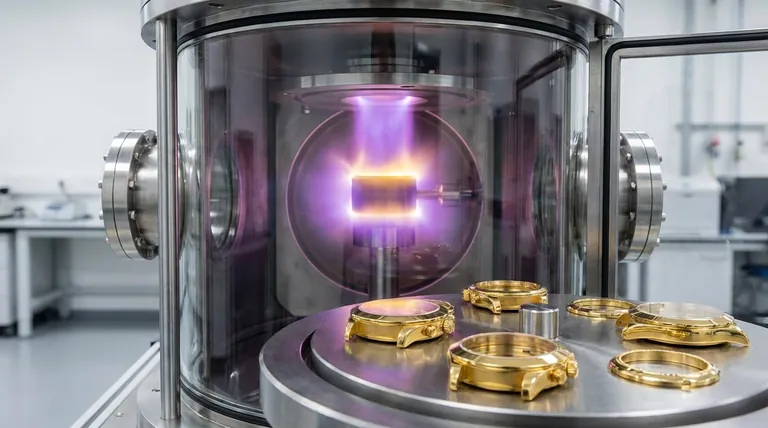
What is PVD and Why Doesn't It Tarnish?
To understand why PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) is so resistant, we need to look at how it differs from traditional methods. It's less of a "coating" and more of a "bonding."
The PVD Process in Brief
PVD is a high-tech vacuum deposition process. Inside a heated, high-vacuum chamber, a solid target material—often a durable ceramic like titanium nitride—is vaporized into a plasma of atoms.
This vapor is then molecularly bonded to the object being plated (such as a watch case or jewelry). Finally, a thin layer of real gold is bonded over this intermediate layer.
The Role of the Hard Intermediate Layer
The "secret sauce" of PVD is this intermediate layer. It is extremely hard, dense, and chemically inert.
This layer acts as the primary shield. It completely seals the base metal (like stainless steel), preventing it from ever being exposed to air, moisture, or skin oils.
How Tarnish Actually Happens
Tarnish is simply a chemical reaction on a metal's surface, most often oxidation. It occurs when a reactive metal is exposed to oxygen, sulfur compounds, and moisture in the air.
The classic example is silver turning black. In traditional gold plating, it's often the base metal underneath the gold (like copper or brass) that reacts and causes the discoloration you see.
PVD Creates an Impenetrable Barrier
Because the PVD process creates a dense, non-porous, and molecularly bonded layer, there is no path for corrosive elements to reach the base metal. The gold on top is also bonded strongly, protecting it from flaking or wearing away easily.
PVD vs. Traditional Gold Electroplating
The difference in tarnish resistance becomes clear when comparing PVD to its most common alternative, electroplating.
The Weakness of Electroplating
Traditional gold electroplating uses an electric current in a chemical bath to deposit a thin layer of gold onto a surface. This bond is purely surface-level and significantly weaker than PVD's molecular bond.
More importantly, electroplated layers can be porous, containing microscopic holes.
Why Electroplated Items Tarnish
Tarnish on electroplated items happens in two primary ways. First, the gold layer is soft and can easily rub off, exposing the reactive base metal beneath it.
Second, moisture and air can seep through the pores in the gold plating, reacting with the base metal and causing tarnish to form underneath the gold, which eventually discolors the entire piece.
Durability and Wear Resistance
PVD coatings are vastly superior in terms of wear and scratch resistance. The bonded ceramic layer is significantly harder than a layer of electroplated gold, making the entire finish up to 10 times more durable.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While PVD is a superior technology for durability, it's essential to have a complete picture.
PVD Can Still Wear Off
PVD coating is not indestructible. While it doesn't tarnish or corrode, the finish can eventually wear away in areas of extremely high friction over many years.
This might occur on the clasp of a watch bracelet or the bottom of a ring that is worn daily for a decade. The color won't change, but the base metal may eventually become visible.
Color and Thickness
The final color of PVD gold can be influenced by the underlying layer (e.g., titanium nitride, which is gold-toned itself). This can result in a slightly different hue compared to solid gold or thick electroplating.
The actual layer of gold used in PVD is often microscopically thin. Its longevity comes from the robust bonding process and the hard intermediate layer, not from the thickness of the gold itself.
Cost and Complexity
The PVD process requires specialized, expensive equipment and is more complex than electroplating. This means products with a genuine PVD finish are typically more expensive than their electroplated counterparts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this technology allows you to select the right product based on its intended use.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and tarnish resistance: PVD is the definitive choice for everyday items like watches, bracelets, and high-contact fixtures.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for occasional wear: Traditional, high-quality gold electroplating can be a suitable option for items that won't see constant friction.
- If your primary focus is the authentic heft and color of solid gold: No plating can truly replace solid gold, but PVD provides the most durable gold-colored finish currently available.
By choosing PVD, you are prioritizing modern engineering for a finish designed to deliver long-term color stability and superior resistance to wear.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD Gold Plating | Traditional Gold Electroplating |
|---|---|---|
| Tarnish Resistance | Excellent (non-porous barrier) | Poor (porous, prone to tarnish) |
| Durability | Up to 10x more durable | Less durable, wears easily |
| Process | Molecular bonding in a vacuum | Electrochemical deposition |
| Base Metal Protection | Full barrier (e.g., titanium nitride) | Minimal, base metal can react |
| Lifespan | Long-term, ideal for daily wear | Shorter, best for occasional use |
Upgrade your lab or production line with KINTEK's advanced PVD solutions! Whether you're developing durable jewelry, precision instruments, or high-performance components, our PVD coatings deliver unmatched tarnish resistance and longevity. Specializing in lab equipment and consumables, KINTEK ensures your projects benefit from cutting-edge technology and reliable performance. Contact us today to learn how our PVD services can enhance your products' durability and appeal!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- What is the process of coating deposition? A Step-by-Step Guide to Thin Film Engineering
- Is sputtering a PVD? Discover the Key Coating Technology for Your Lab
- What is direct current DC magnetron sputtering? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How do CVD diamonds grow? A Step-by-Step Guide to Lab-Grown Diamond Creation



















