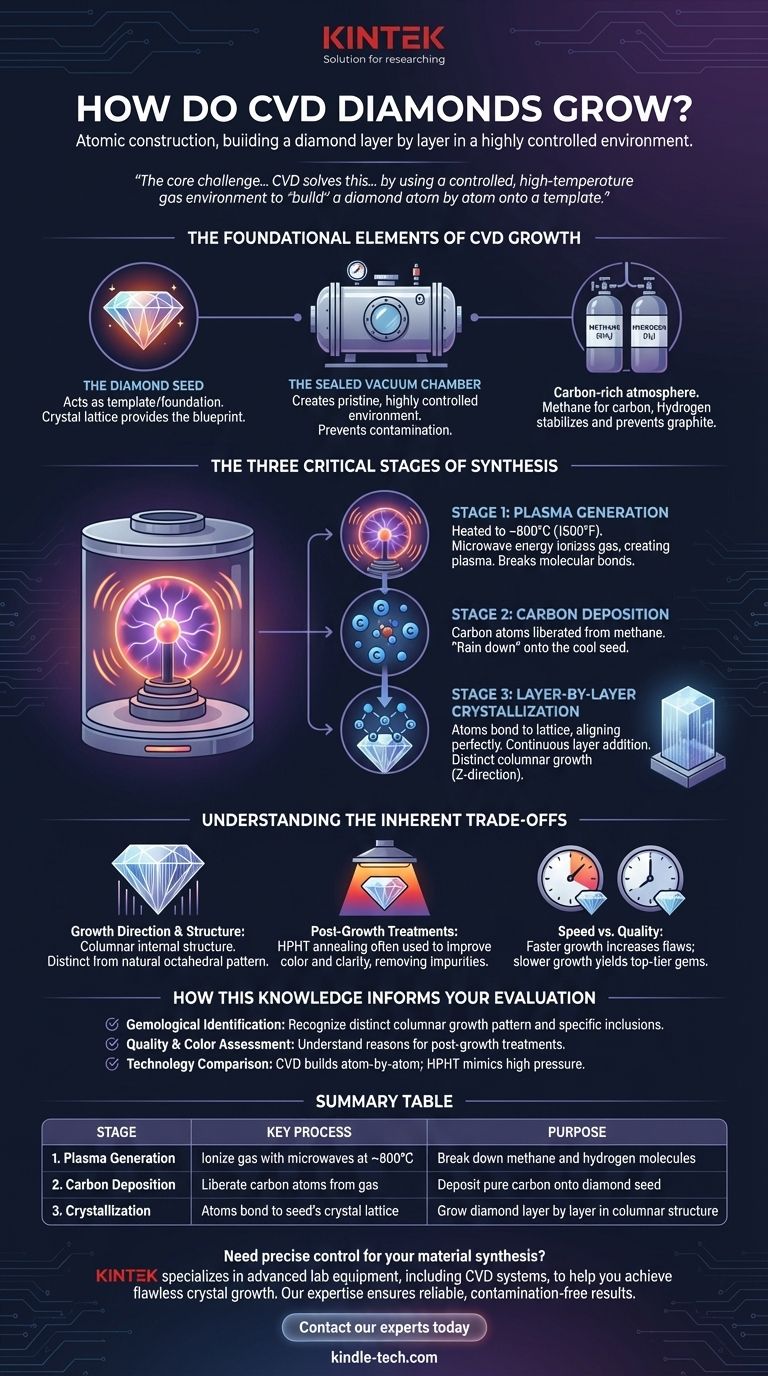
CVD diamond growth is a process of atomic construction, where a diamond is built layer by layer in a highly controlled environment. It begins by placing a thin diamond "seed" into a vacuum chamber, which is then filled with carbon-rich gases and heated. A plasma is generated, breaking the gas molecules apart and allowing pure carbon atoms to deposit onto the seed, meticulously replicating its crystal structure.
The core challenge in creating a lab-grown diamond is replicating a process that takes billions of years and immense geological pressure. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) solves this not by mimicking nature's force, but by using a controlled, high-temperature gas environment to "build" a diamond atom by atom onto a template.

The Foundational Elements of CVD Growth
To understand the process, you must first understand its three core components. Each plays a critical and specific role in the successful synthesis of a diamond crystal.
The Diamond Seed
The entire process begins with a diamond seed. This is a very thin, flat slice of a pre-existing diamond, which can be either a natural or previously grown lab diamond.
This seed acts as the template or foundation for the new diamond. Its crystal lattice provides the blueprint that the new carbon atoms will follow, ensuring the final product grows as a single, coherent diamond crystal.
The Sealed Vacuum Chamber
The diamond seed is placed inside a sealed vacuum chamber. This chamber's primary function is to create a pristine, highly controlled environment.
By removing all other atmospheric gases, scientists can ensure that only the desired elements are present, preventing contamination and allowing the chemical reactions to proceed with precision.
The Carbon-Rich Atmosphere
Once a vacuum is established, the chamber is filled with a specific mixture of gases, typically methane (CH₄) and hydrogen (H₂).
Methane serves as the source of carbon, the building block of the diamond. Hydrogen plays a crucial role in stabilizing the process and preventing the formation of non-diamond carbon, such as graphite.
The Three Critical Stages of Synthesis
With the environment set, the growth process unfolds in three distinct stages, transforming simple gas into one of the hardest materials known.
Stage 1: Plasma Generation
The chamber is heated to a high temperature, typically around 800°C (1500°F). Then, energy—often in the form of microwaves—is introduced into the chamber.
This energy ionizes the gas, stripping electrons from the atoms and creating a glowing ball of plasma, the fourth state of matter. This intense energy breaks the molecular bonds in the methane and hydrogen gases.
Stage 2: Carbon Deposition
Within the plasma, individual carbon atoms are liberated from the methane molecules.
These free carbon atoms then "rain down" and deposit onto the surface of the much cooler diamond seed crystal placed at the bottom of the chamber.
Stage 3: Layer-by-Layer Crystallization
As the carbon atoms land on the diamond seed, they form strong atomic bonds, aligning perfectly with the seed's underlying crystal lattice.
This process repeats continuously, adding layer upon layer of carbon. The growth occurs in a distinct vertical, columnar fashion (known as the Z-direction), resulting in a larger, rough diamond that often has a cubic or tabular shape. The entire process can take several weeks to produce a sizeable gem-quality diamond.
Understanding the Inherent Trade-offs
The CVD method is a feat of engineering, but it is not without its unique characteristics and limitations. Understanding these is key to evaluating the final product.
Growth Direction and Internal Structure
Because CVD diamonds grow in a single, upward direction, they exhibit a layered or columnar internal structure. This is a fundamental characteristic that distinguishes them from the octahedral growth pattern of most natural diamonds.
The Role of Post-Growth Treatments
During the rapid growth process, certain crystallographic imperfections or color impurities (often a brownish tint) can develop.
For this reason, many CVD diamonds undergo post-growth treatments, such as high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) annealing, to improve their color and clarity. This is a standard and accepted enhancement step in the production pipeline.
Speed vs. Quality
There is a direct trade-off between the speed of growth and the quality of the resulting crystal. While the process can be accelerated, doing so increases the likelihood of inclusions and structural flaws, making a slower, more patient growth cycle essential for top-tier gems.
How This Knowledge Informs Your Evaluation
Understanding the CVD growth process moves you beyond marketing claims and empowers you to assess these diamonds with technical insight.
- If your primary focus is gemological identification: The distinct columnar growth pattern and specific types of inclusions are key identifiers that gemologists use to distinguish CVD from natural or HPHT diamonds.
- If your primary focus is quality and color: Knowing the process helps you understand why post-growth treatments are common and why asking about them is a valid part of a quality assessment.
- If your primary focus is the technology itself: The core difference to remember is that CVD "builds" a diamond atom-by-atom from a gas, whereas the HPHT method "squeezes" solid carbon under immense pressure, more closely mimicking Earth's geological forces.
By grasping how a CVD diamond is constructed, you are equipped to evaluate the technology and its final product with confidence and clarity.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Plasma Generation | Ionize gas with microwaves at ~800°C | Break down methane and hydrogen molecules |
| 2. Carbon Deposition | Liberate carbon atoms from gas | Deposit pure carbon onto diamond seed |
| 3. Crystallization | Atoms bond to seed's crystal lattice | Grow diamond layer by layer in columnar structure |
Need precise control for your material synthesis? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including CVD systems, to help you achieve flawless crystal growth. Our expertise in vacuum technology and plasma generation ensures reliable, contamination-free results for your laboratory. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your research and production processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of microwave plasma? From Diamond Synthesis to Semiconductor Fabrication
- How do lab-grown diamonds compare to natural diamonds? Uncover the Truth About Origin, Price, and Value
- What are the limitations of diamonds? Beyond the Myth of Perfection
- What is the difference between MPCVD and HFCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- What is a microwave plasma reactor? Unlock Precision Synthesis of High-Performance Materials



















