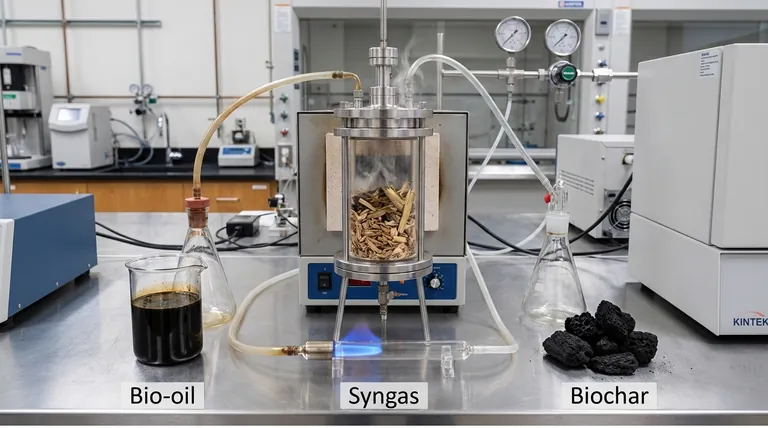
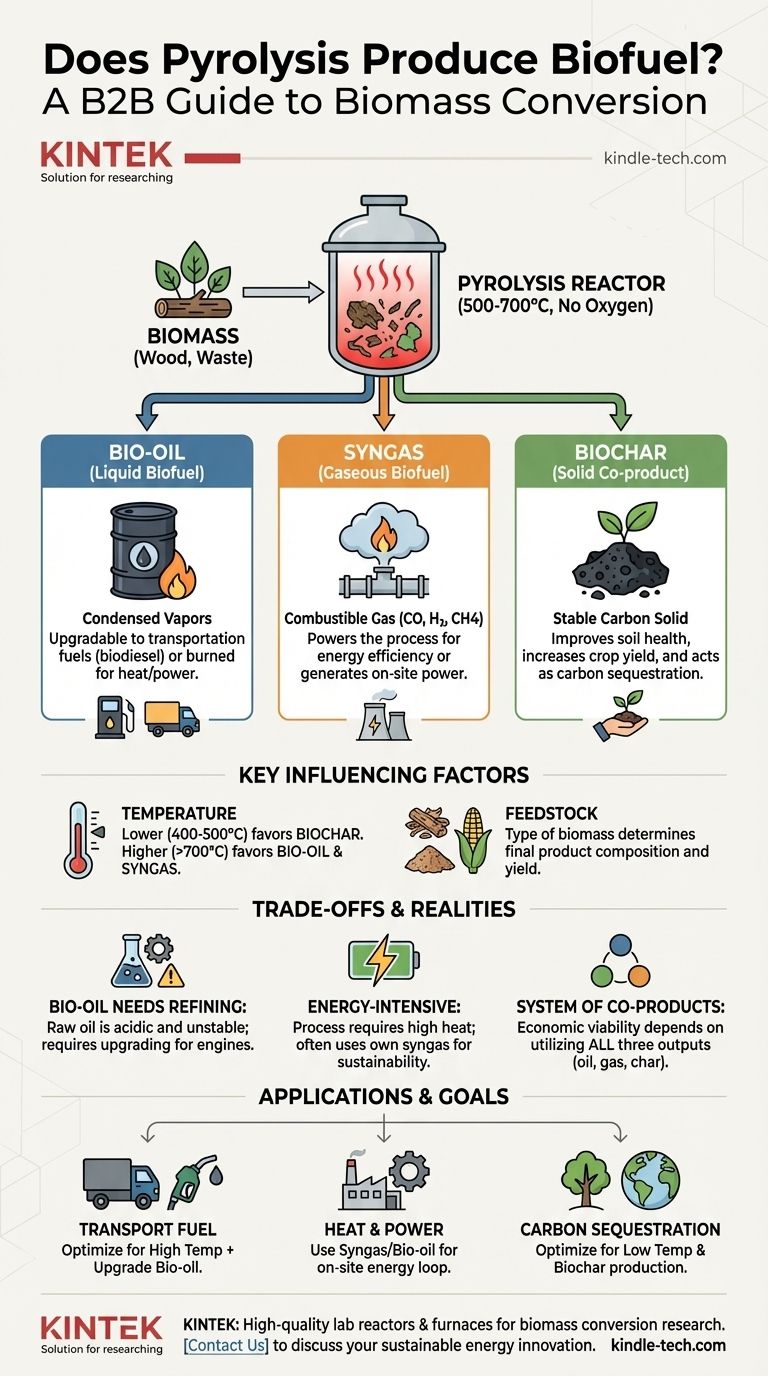
Yes, pyrolysis is a foundational process for producing biofuels. It works by heating organic materials like wood, agricultural waste, or other forms of biomass to high temperatures in an oxygen-free environment. This process breaks the material down, yielding a combustible gas (syngas), a liquid (bio-oil), and a solid (biochar), with the gas and oil being direct forms of biofuel.
Pyrolysis should not be seen as a machine that produces a single biofuel. Instead, it is a versatile thermochemical process that converts biomass into a portfolio of valuable products: a solid, a liquid, and a gas. The primary biofuels it creates are the liquid bio-oil and the combustible syngas.

How Pyrolysis Creates Fuel from Biomass
Pyrolysis is fundamentally a process of thermal decomposition. By heating organic material without oxygen, you prevent it from burning and instead cause it to break apart into smaller molecules.
The Core Process: Heat Without Oxygen
The feedstock, typically some form of biomass, is heated rapidly in a reactor to temperatures between 500°C and 700°C. The absence of oxygen is critical, as it ensures the material decomposes into valuable components rather than simply combusting into ash and smoke.
The Liquid Product: Bio-Oil
The heat turns the biomass into a mix of vapors and gases. Once separated from the solid char, these vapors are rapidly cooled and condensed into a dark liquid known as pyrolysis oil or bio-oil. This bio-crude can be burned directly for heat or power, or it can be upgraded and refined into more advanced liquid fuels like biodiesel for transportation.
The Gaseous Product: Syngas
Not all of the output condenses into a liquid. A significant portion remains as a non-condensable gas, commonly called syngas. This gas is rich in combustible components and is often used to provide the heat needed to run the pyrolysis plant itself, making the process more energy-efficient and self-sustaining.
The Solid Product: Biochar
The stable, carbon-rich solid left over from the process is called biochar. While not a fuel in the same way as oil or gas, biochar is a valuable co-product. It is widely used in agriculture to improve soil health and acts as an effective method of carbon sequestration.
Key Factors That Define the Output
You don't just get one fixed ratio of products. The output of a pyrolysis system is highly dependent on the conditions under which it is run.
The Role of Temperature
Temperature is the primary lever for controlling the outcome. Lower temperatures (around 400–500 °C) tend to favor the production of solid biochar. Conversely, higher temperatures (above 700 °C) maximize the yield of liquid bio-oil and gaseous syngas.
The Importance of Feedstock
The type of organic material used as feedstock also influences the final product mix. Wood chips, crop residues, and even methane gas can be pyrolyzed, but the chemical composition of each will result in different proportions and properties of the final oil, gas, and solid outputs.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Realities
While pyrolysis is a powerful technology, it's essential to understand its practical limitations. It is not a perfect or simple solution for creating fuel.
Bio-oil Is Not a Drop-in Fuel
Raw pyrolysis oil is acidic, unstable, and has a lower energy density than conventional petroleum fuels. It cannot be used directly in standard engines and requires significant upgrading or refining to become a stable, usable transportation fuel.
The Process is Energy-Intensive
Reaching and maintaining the high temperatures required for pyrolysis demands a substantial energy input. The overall efficiency and sustainability of a pyrolysis operation often depend on its ability to use its own gaseous product (syngas) to power the process.
It's a System of Co-products
The economic viability of a pyrolysis facility rarely depends on the biofuel alone. A successful operation must find markets or uses for all three output streams—the bio-oil, the syngas, and the biochar. Treating any of them as waste drastically undermines the model.
Applying This to Your Goal
The right way to view pyrolysis depends entirely on what you want to achieve. The process can be optimized for different outcomes.
- If your primary focus is liquid transport fuel: Your system must be designed for higher temperatures and include a plan for the secondary step of upgrading the raw bio-oil into a stable fuel.
- If your primary focus is renewable heat and power: The most direct path is using the produced syngas and bio-oil to generate energy on-site, potentially creating a self-sufficient energy loop.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration and agriculture: You should optimize the process for biochar production by using lower temperatures, treating the resulting liquid and gas as valuable energy co-products.
Understanding that pyrolysis yields a portfolio of outputs—not just a single biofuel—is the key to leveraging this powerful technology effectively.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Product | Primary Use as Biofuel | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Bio-oil (Liquid) | Can be upgraded to transportation fuels or burned for heat/power. | Raw form is acidic and unstable; requires refining. |
| Syngas (Gas) | Combusted directly for heat and power, often to run the pyrolysis process itself. | A mixture of combustible gases; enables energy self-sufficiency. |
| Biochar (Solid) | Not a direct fuel; used for soil amendment and carbon sequestration. | A stable, carbon-rich solid that improves soil health. |
Ready to harness the power of pyrolysis for your renewable energy or research goals? The right lab equipment is critical for developing and optimizing this process. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab reactors, furnaces, and pyrolysis systems designed for biomass conversion research. Our experts can help you select the perfect equipment to efficiently produce and analyze biofuels and co-products. Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your sustainable energy innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
People Also Ask
- What role does an autoclave play in the acid treatment for microalgae disruption? Unlock High-Yield Cell Pretreatment
- What critical environmental conditions does a laboratory autoclave provide for evaluating wear resistance? - KINTEK
- What is the primary function and principle of autoclaving? Master Lab Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What are the advantages of using an autoclave equipped with a stirring device for molten salt testing? Dynamic Accuracy
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization



















