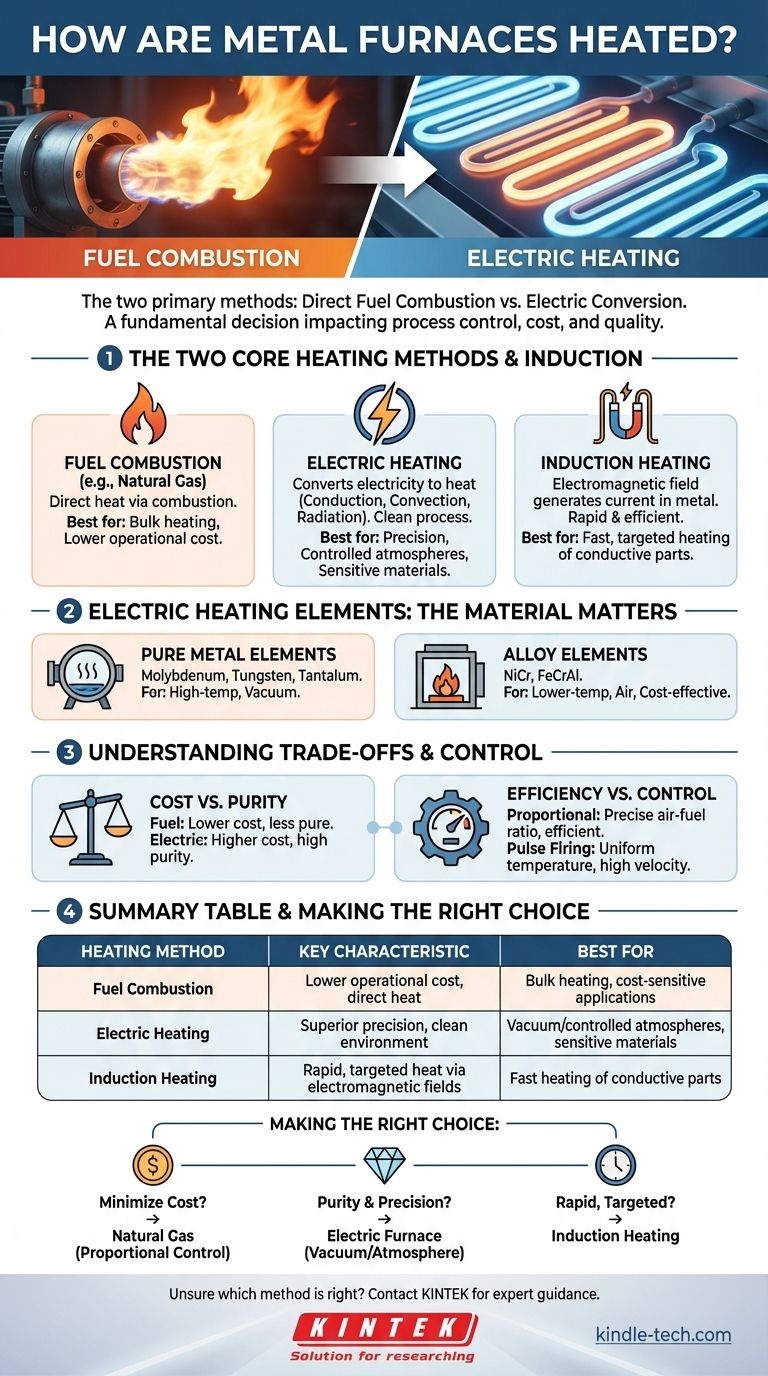
At their core, metal furnaces are heated using one of two primary methods: the direct combustion of fuel or the conversion of electricity into heat. Fuel-based systems, such as those using natural gas, are common due to lower fuel costs, while electric systems offer superior precision and environmental purity for more specialized metallurgical processes.
The choice between a fuel-fired or electric furnace is not merely about generating heat. It is a fundamental decision that dictates process control, operational cost, and the final quality of the metal being treated.

The Two Core Heating Methods
The method used to generate heat is the most fundamental design characteristic of any furnace, directly influencing its capabilities and ideal applications.
Fuel Combustion: The Industrial Workhorse
Furnaces powered by fuel, most commonly natural gas, generate heat through direct combustion. In this process, a burner mixes fuel with air and ignites it within the furnace chamber, transferring heat directly to the metal workload.
This method is widely used for bulk heating applications where its lower operational cost provides a significant economic advantage.
Electric Heating: The Precision Instrument
Electric furnaces convert electrical energy into thermal energy. This is achieved through several mechanisms, including conduction, convection, and blackbody radiation, all of which occur without creating combustion by-products.
This inherent cleanliness makes electric heating ideal for processes requiring a controlled atmosphere, such as in a vacuum, or for treating metals that are sensitive to contamination.
Induction Heating: A Specialized Approach
A distinct form of electric heating, induction heating, uses an electromagnetic field to generate an electric current directly within the metal part itself. The metal's own electrical resistance causes it to heat up rapidly and efficiently.
This method is exceptionally fast and energy-efficient but is typically limited to conductive materials and specific part geometries.
A Deeper Look at Electric Heating Elements
Not all electric furnaces are the same. The material used for the heating element is a critical factor that determines the furnace's operating temperature and atmospheric capabilities.
Pure Metal Elements for High Temperatures
For high-temperature vacuum furnaces, elements made from pure refractory metals like molybdenum, tungsten, and tantalum are required. These materials can withstand extreme heat and maintain their integrity under vacuum.
Alloy Elements for General Use
For lower-temperature applications or those operating in air, alloy elements are more common. Materials like nickel-chromium (NiCr) and iron-chromium-aluminum (FeCrAl) offer excellent performance at a lower cost than pure refractory metals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a heating method involves balancing competing priorities. An expert understands these compromises to choose the right tool for the job.
Cost vs. Purity
The primary trade-off is often between the lower ongoing cost of fuel and the process purity of electricity. Fuel combustion is cheaper to run but introduces by-products like water vapor and carbon dioxide into the furnace atmosphere.
Electric heating has a higher energy cost but provides an impeccably clean environment, which is non-negotiable for aerospace, medical, and high-purity alloy applications.
Efficiency vs. Control
The level of control directly impacts fuel efficiency. The simplest systems only control the flow of fuel, which is inexpensive to implement but inefficient.
More advanced proportional systems that manage both the fuel and air supply significantly improve fuel efficiency and lower operating costs by ensuring a more complete and controlled burn.
The Critical Role of Temperature Control
Generating heat is only half the battle; controlling it with precision is what ensures a successful metallurgical process.
Proportional Air-Fuel Control
Most modern fuel-fired furnaces use proportional control systems. These systems maintain a precise ratio of air to fuel throughout the heating cycle, maximizing combustion efficiency and ensuring consistent heat delivery.
Advanced Pulse Firing Systems
For the highest level of temperature uniformity, pulse control systems are used. This technique maintains a fixed air-fuel ratio while firing the burner at full power in short pulses.
This high-velocity firing creates significant turbulence in the furnace atmosphere, mixing it thoroughly and eliminating hot or cold spots. This ensures the entire workload experiences the exact same temperature profile.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal determines the optimal heating technology.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational cost for bulk heating: A natural gas furnace with proportional air-fuel control offers the best economic performance.
- If your primary focus is process purity and precision for sensitive materials: An electric furnace is the superior choice, especially when a vacuum or controlled atmosphere is needed.
- If your primary focus is extremely rapid and targeted heating of individual parts: Induction heating provides unmatched speed and efficiency for compatible materials.
Understanding these core heating principles empowers you to select the right furnace not just for the temperature required, but for the specific metallurgical outcome you need to achieve.
Summary Table:
| Heating Method | Key Characteristic | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Combustion | Lower operational cost, direct heat | Bulk heating, cost-sensitive applications |
| Electric Heating | Superior precision, clean environment | Vacuum/controlled atmospheres, sensitive materials |
| Induction Heating | Rapid, targeted heat via electromagnetic fields | Fast heating of conductive parts |
Still unsure which heating method is right for your lab's metallurgical processes? The choice between fuel and electric heating directly impacts your costs, control, and final product quality. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering expert guidance to help you select the perfect furnace for your specific needs—whether you prioritize cost-efficiency, process purity, or rapid heating. Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to discuss your application and discover the KINTEK solution that will enhance your lab's efficiency and outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between upflow and horizontal furnace? Find the Perfect Fit for Your Home's Layout
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results



















