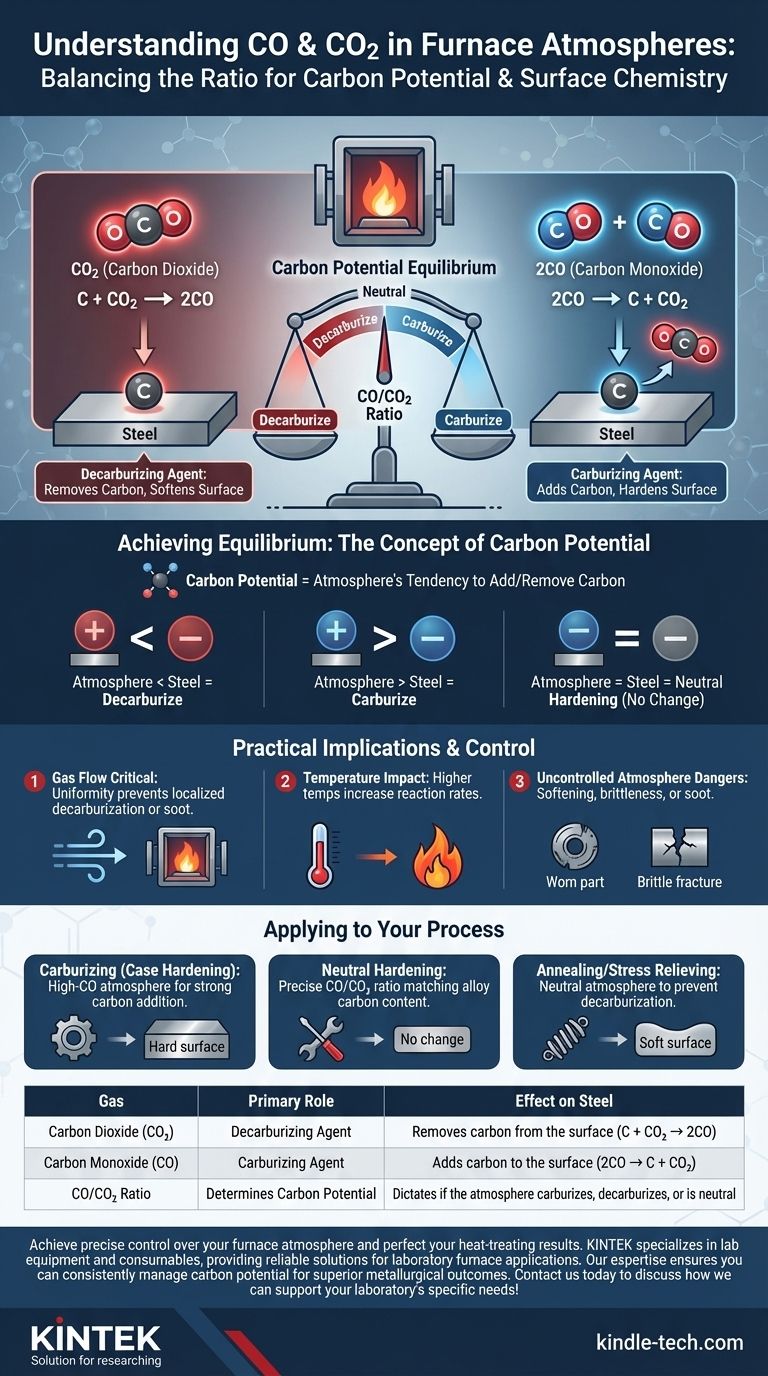
In furnace atmospheres, carbon dioxide (CO2) and carbon monoxide (CO) exist in a critical, reversible chemical reaction that dictates the surface chemistry of the material being processed. CO2 acts as a decarburizing agent, reacting with and removing carbon from a part's surface, while CO can act as a carburizing agent, depositing carbon onto it.
The core function to understand is not the presence of CO2 or CO, but their ratio. This ratio determines the atmosphere's "carbon potential"—its tendency to either add carbon to, remove carbon from, or remain neutral to the steel being heat-treated.

The Core Chemical Reaction: A Balancing Act
The interaction between CO, CO2, and the carbon (C) in steel is a dynamic equilibrium. The direction of the reaction dictates the final properties of the component.
The Role of Carbon Dioxide (CO2): The Decarburizing Agent
Carbon dioxide is an oxidizing gas in this context. It actively seeks to react with the carbon present on the surface of the steel.
This reaction, C + CO2 → 2CO, effectively strips carbon atoms from the material, forming two molecules of carbon monoxide. If uncontrolled, this process is known as decarburization, which can leave the surface of a part soft and unable to meet hardness specifications.
The Role of Carbon Monoxide (CO): The Carburizing Agent
Carbon monoxide is the product of the decarburizing reaction, but it can also be the source of carbon.
Under the right conditions of temperature and pressure, the reaction can reverse: 2CO → C + CO2. In this process, CO breaks down, depositing a carbon atom onto the steel's surface and releasing a molecule of carbon dioxide. This is carburizing, a process used to create a hard, wear-resistant surface layer (case hardening).
Achieving Equilibrium: The Concept of Carbon Potential
The furnace atmosphere is constantly trying to reach a state of equilibrium based on the concentration of these gases and the temperature. This equilibrium point is the carbon potential.
If the carbon potential of the atmosphere is higher than the carbon content of the steel, the atmosphere will attempt to carburize the part.
Conversely, if the atmosphere's carbon potential is lower than the steel's, it will decarburize the part. For neutral hardening, the goal is to match the atmosphere's potential precisely to the steel's carbon content, so no change occurs.
Understanding the Practical Implications
Controlling the CO/CO2 ratio is one of the most critical aspects of modern heat treating. Failure to manage this balance can lead to scrapped parts and inconsistent quality.
Why Gas Flow is Critical
As stated in the references, controlling the flow of gas is essential. A consistent and uniform flow ensures that the CO/CO2 ratio remains stable throughout the entire furnace chamber.
Without proper flow, localized areas can form where CO2 becomes depleted or CO becomes concentrated. This leads to non-uniform case depth or patches of decarburization on the same part.
The Impact of Temperature
Temperature is the catalyst for these reactions. Higher temperatures dramatically increase the rate at which carbon can be transferred.
This is why precise control of both furnace temperature and gas composition is required. A slight change in one variable can completely alter the effect of the other.
The Danger of an Uncontrolled Atmosphere
An atmosphere that is accidentally decarburizing will soften the surface of components, leading to premature failure from wear or fatigue.
An atmosphere that is uncontrollably carburizing can make parts too brittle, leading to fracture under stress. It can also lead to the formation of surface soot if the carbon potential is excessively high.
How to Apply This to Your Process
Your goal dictates how you must manage the balance between carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide in your furnace.
- If your primary focus is Carburizing (Case Hardening): You must generate a high-CO atmosphere to create a strong driving force for adding carbon to the steel.
- If your primary focus is Neutral Hardening: You must precisely control the CO/CO2 ratio to match the specific carbon content of the alloy being treated, preventing any net gain or loss of carbon.
- If your primary focus is Annealing or Stress Relieving: You must ensure the atmosphere is at least neutral to the material to prevent unintended and detrimental surface decarburization during the thermal cycle.
Mastering this chemical balance is fundamental to achieving precise and repeatable metallurgical properties in your components.
Summary Table:
| Gas | Primary Role in Furnace | Effect on Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Dioxide (CO2) | Decarburizing Agent | Removes carbon from the surface (C + CO2 → 2CO) |
| Carbon Monoxide (CO) | Carburizing Agent | Adds carbon to the surface (2CO → C + CO2) |
| CO/CO2 Ratio | Determines Carbon Potential | Dictates if the atmosphere carburizes, decarburizes, or is neutral |
Achieve precise control over your furnace atmosphere and perfect your heat-treating results. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable solutions for laboratory furnace applications. Our expertise ensures you can consistently manage carbon potential for superior metallurgical outcomes. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2
- How we can develop inert atmosphere for a chemical reaction? Master Precise Atmospheric Control for Your Lab
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- What is the role of an atmosphere-controlled tube furnace in Cu-Mo sintering? Achieve High-Purity Densification
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes



















