At its core, a coating chamber uses a high-tech process called vacuum deposition to transform a solid material into a vapor. This vapor then travels through a vacuum and bonds with a product's surface on an atomic level. The result is not just a layer of paint, but a new, integrated surface layer that is exceptionally durable and protective.
The critical takeaway is that coating chambers don't just apply a layer onto a surface; they create a controlled vacuum environment where a vaporized material can atomically bond with the surface, forming a fundamentally new, high-performance layer.
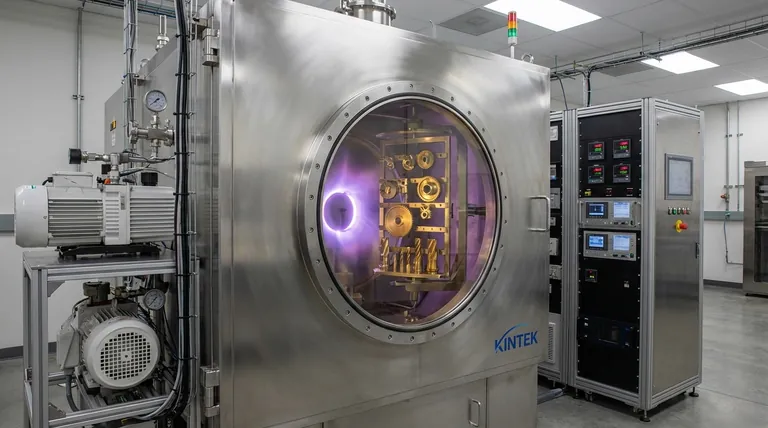

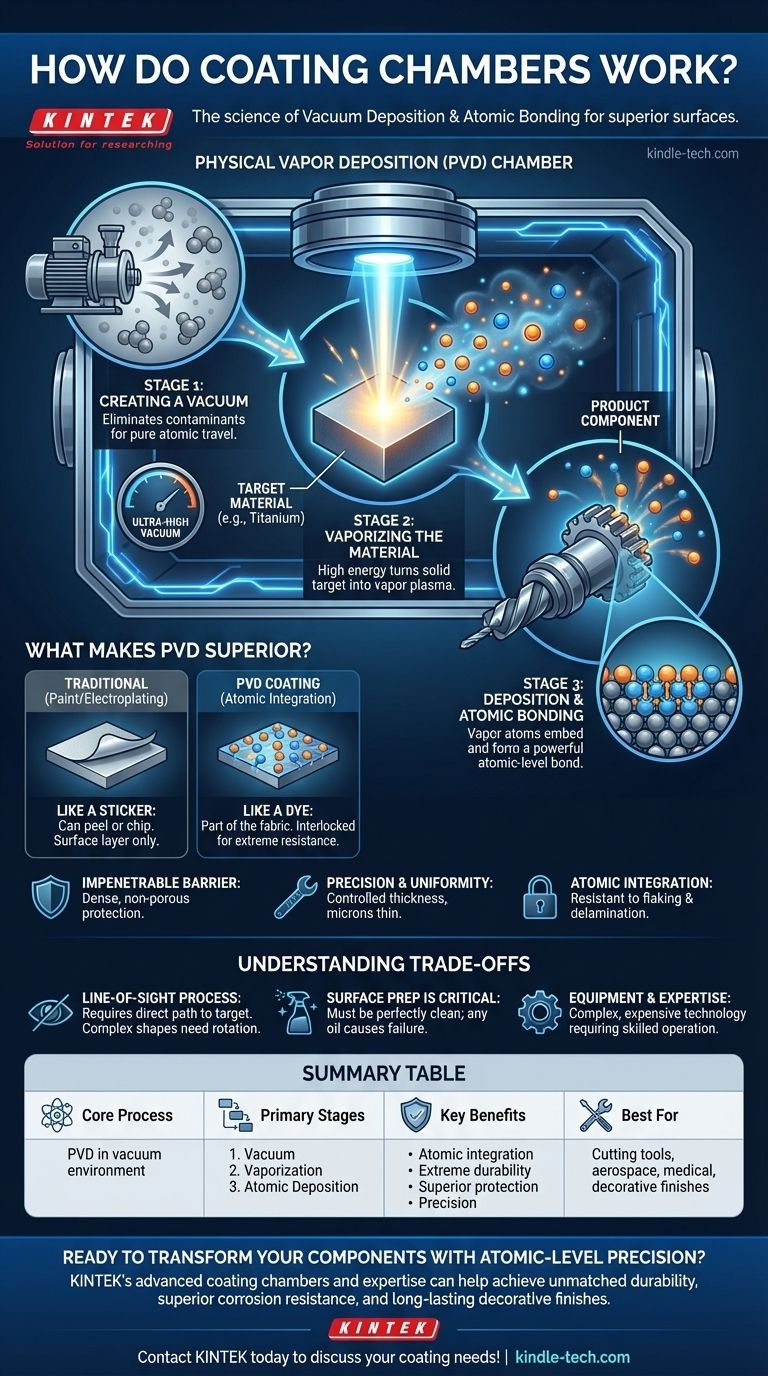
The Fundamental Principle: Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
The process that occurs inside a coating chamber is known as Physical Vapor Deposition, or PVD. It's a method of re-engineering a material's surface by depositing atoms one by one. The entire process hinges on three critical stages.
Stage 1: Creating a Vacuum
Before anything else happens, nearly all the air and other gases are pumped out of the chamber. This vacuum is non-negotiable because it eliminates contaminants like oxygen, nitrogen, and water vapor that would otherwise interfere with the process and compromise the coating's quality.
A clean vacuum ensures that the vaporized coating material can travel unimpeded from its source to the product surface, creating the purest possible bond.
Stage 2: Vaporizing the Coating Material
A solid block of the coating material, often a metal like titanium, chromium, or aluminum, is placed inside the chamber. This material is known as the "target."
High energy is then introduced to bombard this target, causing its atoms to be ejected and converted into a vapor or plasma. This is the "physical vapor" in PVD.
Stage 3: Deposition and Atomic Bonding
The vaporized atoms travel across the vacuum chamber and strike the surface of the product being coated. Because these atoms are highly energized, they don't just settle on the surface.
Instead, they embed themselves slightly and form a powerful, atomic-level bond. This process builds, atom by atom, to form a thin, dense, and perfectly uniform coating that becomes an integral part of the original component.
What Makes This Coating Superior?
PVD coatings are fundamentally different from traditional methods like painting or electroplating. The difference lies in the quality and nature of the bond to the surface.
It's an Integration, Not a Layer
Think of paint as a sticker placed on a surface—it can be peeled or chipped off. A PVD coating is more like a dye that becomes part of the fabric itself. The coating is atomically interlocked with the substrate, making it incredibly resistant to flaking or delamination.
Creating an Impenetrable Barrier
Because the coating is built atom by atom in a vacuum, it is extremely dense and non-porous. This creates a highly effective barrier that protects the underlying component from wear, corrosion, friction, and chemical attack.
Precision and Uniformity
The vacuum deposition process allows for extremely fine control over the coating's thickness. This means a uniform layer, often only a few microns thick, can be applied evenly over the entire surface, which is critical for high-precision parts where tolerances matter.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the PVD process has specific requirements and limitations that are important to understand.
Line-of-Sight Process
The vaporized atoms travel in a straight line from the target to the substrate. This means that any surface that doesn't have a direct "line of sight" to the target may not get coated properly. Coating complex, internal geometries often requires sophisticated rotating mechanisms for the parts.
Surface Preparation is Critical
The quality of the atomic bond depends entirely on the cleanliness of the product's surface. The parts must be impeccably cleaned before entering the chamber. Any trace of oil, dirt, or oxidation will cause the coating to fail.
Equipment and Expertise
Coating chambers are complex and expensive pieces of industrial equipment. Operating them correctly requires significant technical expertise to manage the vacuum, energy sources, and deposition parameters for different materials and applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding if vacuum deposition coating is the right solution depends entirely on your performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability and wear resistance: This process is ideal for creating ultra-hard surfaces on items like cutting tools, engine components, and industrial molds.
- If your primary focus is superior corrosion protection: The dense, non-porous layer provides an exceptional barrier against oxidation, making it perfect for aerospace parts, marine hardware, and medical devices.
- If your primary focus is a decorative finish that lasts: PVD is used to create durable, brilliant finishes on consumer products like watches, faucets, and high-end electronics, offering colors that won't easily scratch or fade.
Ultimately, a coating chamber transforms a standard component into a high-performance material by fundamentally re-engineering its surface at the atomic level.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Process | Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) in a vacuum environment |
| Primary Stages | 1. Vacuum creation 2. Material vaporization 3. Atomic deposition & bonding |
| Key Benefits | • Atomic-level integration with substrate • Extreme durability & wear resistance • Superior corrosion protection • Precise, uniform thin-film coatings |
| Best For | Cutting tools, aerospace components, medical devices, and decorative finishes requiring longevity |
Ready to transform your components with atomic-level precision?
KINTEK's advanced coating chambers and expertise in PVD technology can help you achieve: • Unmatched durability for your cutting tools and industrial components • Superior corrosion resistance for aerospace and medical applications • Long-lasting decorative finishes that won't scratch or fade
Our team specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables for surface engineering applications. Let us help you select the right coating solution for your specific needs.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our coating technologies can enhance your product performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between DC and RF magnetron sputtering? Choose the Right Method for Your Materials
- What is the primary purpose of an oven in geopolymer pretreatment? Ensuring Moisture Stability and Process Precision
- What are the disadvantages of DC sputtering? Key Limitations for Thin Film Deposition
- What are the principles of physical vapor deposition of thin films? Master the 3-Step Process for High-Purity Coatings
- What role does a laboratory homogenizer play in radioactive cesium detection? Ensure Accuracy in Wildlife Sampling
- How does a laboratory drying oven contribute to TiO2 synthesis? Unlock Advanced Material Stability & Chemical Bonding
- How does heat treatment affect microstructure? Mastering the Balance Between Hardness and Toughness
- What is the composition of plastic pyrolysis product? A Breakdown of Oil, Gas, and Char Outputs
















