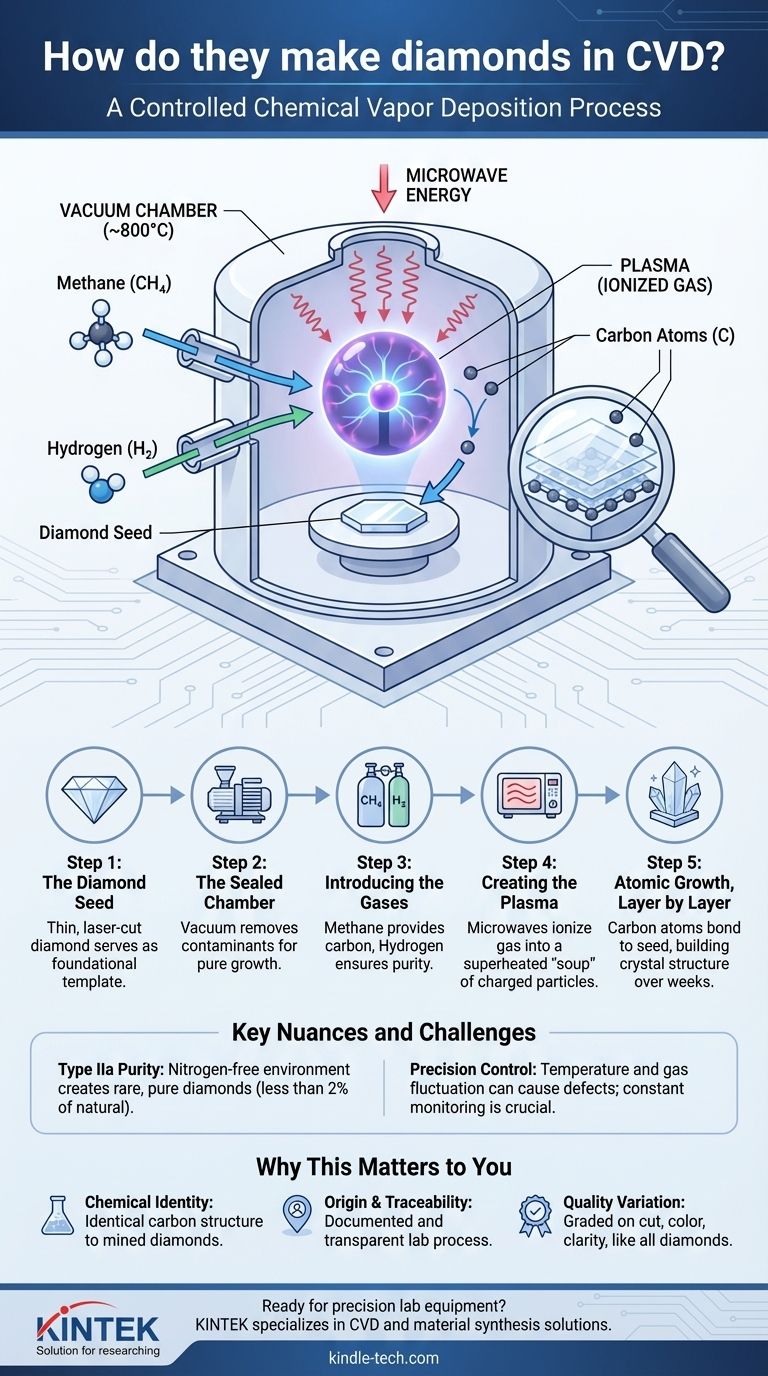
To make a CVD diamond, a small, thin diamond "seed" is placed inside a vacuum chamber. The chamber is heated to around 800°C (1500°F) and filled with a carbon-rich gas mixture, typically methane and hydrogen. This gas is then ionized into a plasma, which breaks the gas molecules apart and frees the carbon atoms. These carbon atoms then attach themselves to the diamond seed, building upon its crystal structure layer by layer until a new, larger diamond has formed.
The core principle of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is not melting carbon, but building a diamond atom by atom. It uses a controlled gas environment to deposit carbon onto a diamond template, essentially continuing the growth of a pre-existing diamond crystal.

Deconstructing the CVD Process
The name "Chemical Vapor Deposition" perfectly describes how these diamonds are made. A chemical reaction involving a vapor (gas) results in the deposition of solid material (carbon) onto a substrate (the diamond seed).
Step 1: The Diamond Seed
The entire process begins with a "seed," which is a very thin, laser-cut slice of a pre-existing diamond. This seed acts as the foundational template. The quality of the final diamond is highly dependent on the quality and orientation of this initial seed.
Step 2: The Sealed Chamber
The seed is placed inside a highly controlled vacuum chamber. This vacuum environment is critical because it removes any contaminants and allows for precise control over the pressure and atmosphere, which are essential for growing a pure diamond crystal.
Step 3: Introducing the Gases
A specific mixture of gases is pumped into the chamber. This is almost always a combination of a carbon-source gas, like methane (CH₄), and a much larger volume of hydrogen (H₂) gas.
Step 4: Creating the Plasma
The chamber is heated to approximately 800°C. Then, an energy source, typically microwaves, is introduced. This energy ionizes the gas, stripping electrons from the atoms and creating a glowing ball of plasma—a superheated "soup" of charged particles.
Step 5: Atomic Growth, Layer by Layer
Within the plasma, the methane and hydrogen molecules are broken apart. This releases individual carbon atoms. These carbon atoms are then drawn to the slightly cooler surface of the diamond seed.
Crucially, they bond to the seed's crystal lattice, extending it and growing the diamond one atomic layer at a time. The hydrogen gas plays a vital role by selectively etching away any carbon that tries to form weaker, non-diamond bonds (like graphite), ensuring the growing crystal remains pure diamond. This process continues for several weeks to grow a single gem-quality crystal.
Understanding the Nuances and Challenges
While the process is straightforward in principle, its execution is a sophisticated technological challenge. The final quality of the diamond depends entirely on mastering several key variables.
The Critical Role of Purity
The CVD process creates Type IIa diamonds, a category that is very rare in nature (less than 2% of all mined diamonds). This is because the controlled environment is free of nitrogen, the element that causes the common yellowish tint in most natural diamonds.
Controlling Growth Conditions
The slightest fluctuation in temperature, pressure, or the gas mixture ratio can introduce defects or stop the growth process altogether. Technicians must constantly monitor and adjust these conditions to produce clear, well-formed crystals.
Post-Growth Treatments
Sometimes, as-grown CVD diamonds have a brownish tint due to minor structural distortions. These diamonds can undergo a post-growth treatment process, such as High-Pressure/High-Temperature (HPHT) annealing, to correct these distortions and improve their color. This is a permanent enhancement.
Why This Process Matters to You
Understanding the science behind CVD diamonds allows you to evaluate them based on their fundamental properties, not just their origin.
- If your primary focus is chemical identity and quality: CVD technology produces a product that is chemically, physically, and optically identical to a mined diamond, composed of the same carbon atoms in the same crystal structure.
- If your primary focus is origin and traceability: The CVD process is a documented and controlled manufacturing process, offering a clear and transparent history for every stone produced.
- If your primary focus is understanding the final product: Know that the "CVD" label describes the growth method, and the resulting diamond can still vary in quality (color, clarity) just like any other diamond, which is then graded accordingly.
This knowledge empowers you to see that a lab-grown diamond is not an imitation, but rather the result of recreating the diamond-growing process in a highly advanced technological setting.
Summary Table:
| CVD Diamond Growth Step | Key Element | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Seed Preparation | Diamond Seed | Acts as a template for atomic growth |
| Chamber Setup | Vacuum Chamber | Provides a pure, contaminant-free environment |
| Gas Introduction | Methane (CH₄) & Hydrogen (H₂) | Supplies carbon source and ensures diamond purity |
| Plasma Creation | Microwaves & Heat (~800°C) | Ionizes gas to free carbon atoms |
| Crystal Growth | Atomic Deposition | Builds diamond layer by layer over several weeks |
Ready to explore precision lab equipment for your own advanced material synthesis? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratories with reliable solutions for CVD, thermal processing, and more. Whether you're growing diamonds or developing new materials, our expertise ensures your processes run efficiently and accurately. Contact us today via our Contact Form to discuss how we can support your laboratory's unique needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- What is the floating catalyst method? A Guide to High-Yield CNT Production
- What are the advantages of industrial CVD for solid boriding? Superior Process Control and Material Integrity
- What role does Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) equipment play in the preparation of C/C composites? Expert Analysis
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition



















