At a fundamental level, quartz is a natural or synthetic crystalline material of high purity, while glass is an amorphous solid made from a mixture of ingredients. The primary differences lie in their molecular structure, chemical composition, thermal resistance, and electrical properties. Quartz is an ordered, pure, and highly resilient material, whereas glass is a disordered, impure, and more easily workable substance.
The core distinction is order versus disorder. Quartz possesses a perfectly ordered, crystalline atomic structure, granting it superior strength and unique properties. Glass has a random, amorphous structure like a frozen liquid, which makes it less resilient but far easier to manufacture and shape.

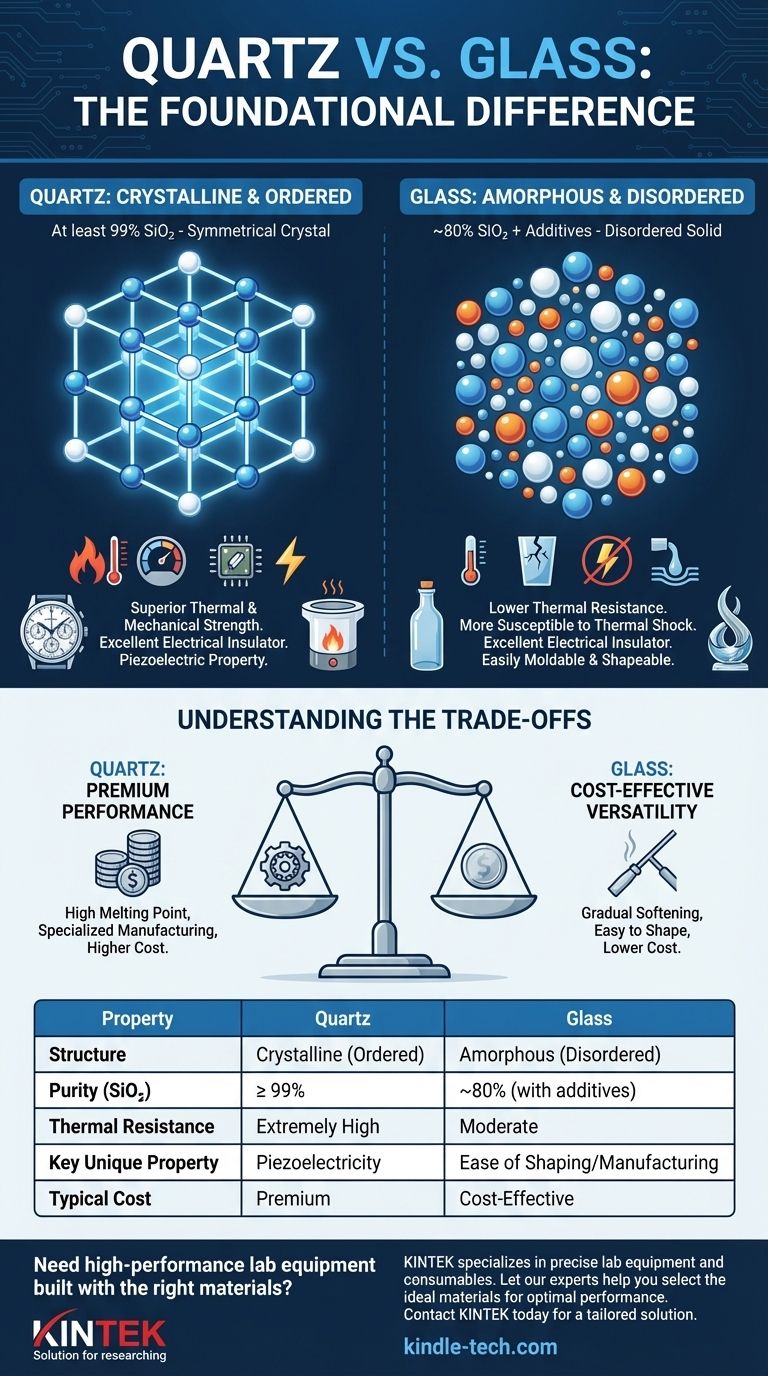
The Foundational Difference: Crystalline vs. Amorphous
The most significant distinction between quartz and glass is invisible to the naked eye. It lies in the arrangement of their molecules, which dictates nearly all of their other properties.
The Structure of Quartz: A Symmetrical Crystal
Quartz is a crystalline solid. This means its silicon and oxygen atoms are arranged in a precise, repeating, and symmetrical three-dimensional pattern.
This highly ordered lattice gives the material inherent strength and stability. Natural quartz crystals form this way, though they may require cutting and polishing to reveal their perfect internal symmetry.
The Structure of Glass: A Disordered Solid
Glass is an amorphous solid. Its molecules have no long-range order and are arranged randomly, much like in a liquid that has been frozen in place before it had a chance to crystallize.
This random structure is a direct result of its manufacturing process, where ingredients are melted and then cooled rapidly.
How Structure Dictates Purity
The ordered crystal lattice of quartz is composed of at least 99% silicon dioxide (SiO₂). Its structure naturally rejects impurities.
Because glass is amorphous, its random structure can easily accommodate other elements. Standard glass contains only about 80% silicon dioxide, with additives like lead oxide (up to 32%) often included to increase its refractive index and make it sparkle.
Practical Implications of Their Differences
The structural and chemical distinctions give rise to vastly different performance characteristics, making each material suitable for very different applications.
Thermal and Mechanical Strength
The strong, ordered bonds in the quartz crystal lattice allow it to withstand extremely high temperatures and pressure without losing its integrity.
Glass, with its weaker and disordered structure, has a much lower melting point and is more susceptible to cracking from thermal shock or physical stress. This makes quartz essential for high-temperature industrial processes and scientific labware.
Electrical Behavior
Both glass and quartz are excellent electrical insulators. They do not conduct electricity in the way a metal does.
However, quartz possesses a unique property called piezoelectricity. When subjected to mechanical pressure, its crystalline structure generates a small, precise electrical voltage. This effect is the reason quartz is critical for timekeeping in watches and for frequency control in electronics. Glass does not have this property.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost and Workability
While quartz has superior performance, glass remains far more common for a reason. The choice between them often comes down to balancing performance requirements with practical constraints.
The Challenge of Workability
The amorphous structure of glass causes it to soften gradually over a wide temperature range. This makes it easy to mold, blow, and shape into complex forms, from bottles to artistic sculptures.
Quartz has a very high and precise melting point. It is significantly more difficult and energy-intensive to melt and form, making the manufacturing of quartz components a specialized and costly process.
The Impact on Cost
The abundance of raw materials and the ease of manufacturing make glass an inexpensive and versatile material for countless everyday applications.
The purity requirements and difficult processing make quartz a premium material reserved for applications where its specific high-performance properties are non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires a clear understanding of your project's primary goal.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and design flexibility: Glass is the ideal choice for applications like windows, containers, and decorative items.
- If your primary focus is performance in harsh environments: Quartz is necessary for its superior resistance to high temperatures and thermal shock, as seen in lab equipment or industrial lenses.
- If your primary focus is precision electronics or optics: Quartz is the only option due to its unique piezoelectric properties and purity, which is critical for UV transparency and frequency standards.
By understanding these fundamental differences, you can select the right material based on performance needs rather than appearance alone.
Summary Table:
| Property | Quartz | Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Crystalline (Ordered) | Amorphous (Disordered) |
| Purity (SiO₂) | ≥ 99% | ~80% (with additives) |
| Thermal Resistance | Extremely High | Moderate |
| Key Unique Property | Piezoelectricity | Ease of Shaping/Manufacturing |
| Typical Cost | Premium | Cost-Effective |
Need high-performance lab equipment built with the right materials?
The choice between quartz and glass is critical for the success and safety of your laboratory processes. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables your facility needs. Our experts can help you select the ideal materials—whether you require the superior thermal resistance of quartz or the cost-effective versatility of glass—to ensure optimal performance, durability, and results.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application and get a tailored solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Resistant Optical Quartz Glass Sheet
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Single Double Sided Coated K9 Quartz Sheet
- Optical Ultra-Clear Glass Sheet for Laboratory K9 B270 BK7
- Zinc Selenide ZnSe Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer and Lens
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
People Also Ask
- Does quartz have a high melting point? Discover Its Superior High-Temperature Performance
- What is the high temperature of quartz? Key Thresholds for Crystalline vs. Fused Silica
- What is the temperature range of quartz glass? Master Its Thermal Limits for Demanding Applications
- What is the working temperature of quartz glass? Master Its High-Temp Limits & Applications
- What is optical quartz? The Ultimate Material for UV and High-Temp Optics


















