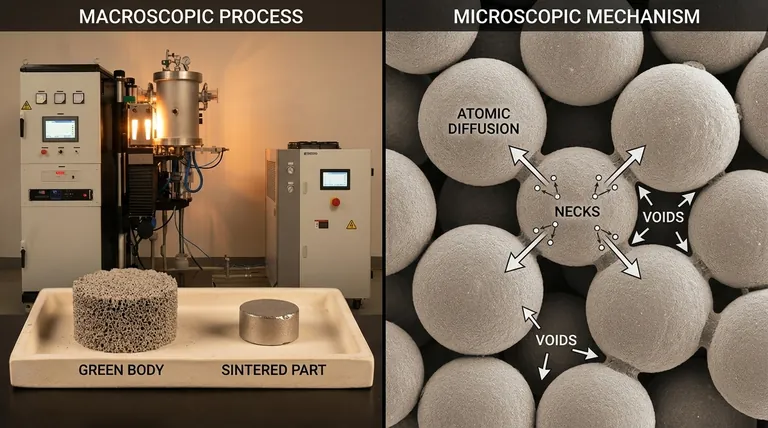
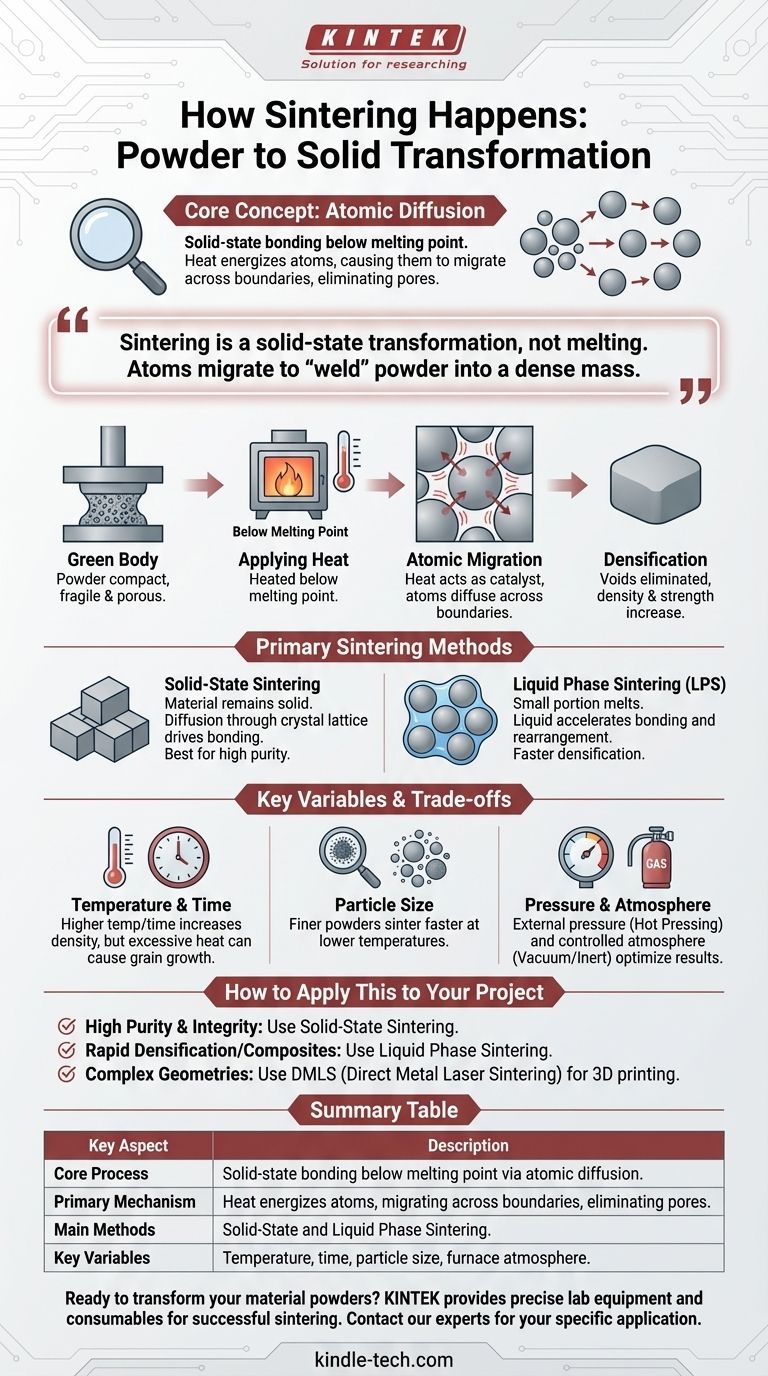
At its core, sintering transforms a collection of powder into a solid object. This is achieved by applying heat to a compacted powder, causing its individual particles to bond and fuse together without ever melting into a liquid state. The entire process is driven by a phenomenon called atomic diffusion.
Sintering is not a melting process; it's a solid-state transformation. By heating a material below its melting point, you give its atoms enough energy to migrate across particle boundaries, effectively "welding" the powder into a dense, solid mass.
The Fundamental Mechanism: Atomic Diffusion in Action
To understand how sintering works, we must look at the process on a microscopic level. It's a sequence of physical changes that methodically reduces the space between particles.
Starting with a Powder Compact
The process begins with a "green body," which is a mass of powder that has been pressed or molded into a desired shape. At this stage, it is fragile and porous, with individual particles only loosely touching one another.
Applying Heat (But Not Enough to Melt)
The green body is heated in a furnace to a high temperature, but one that is critically kept below the material's melting point. This is why sintering is essential for manufacturing parts from materials with extremely high melting points, such as ceramics and certain metals.
The Role of Atomic Migration
This applied heat acts as a catalyst. It energizes the atoms within the particles, causing them to vibrate and move. Atoms begin to diffuse or migrate across the boundaries where individual particles make contact.
Eliminating Voids and Increasing Density
As atoms move to fill the gaps, the points of contact between particles grow larger. This atomic movement pulls the centers of the particles closer together, systematically eliminating the pores (voids) between them. The result is a component that shrinks, becomes significantly denser, and gains immense strength.
The Primary Sintering Methods
While the underlying principle of atomic diffusion is constant, the process can be categorized into two main types based on the state of the material during heating.
Solid-State Sintering
This is the most common form of the process. The material remains entirely in a solid state from beginning to end. The diffusion of atoms through the solid crystal lattice is what drives the densification and bonding of the powder compact.
Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS)
In this method, the powder is a mixture of materials, or it contains additives. When heated, a small portion of the material melts and forms a liquid phase that wets the remaining solid particles. This liquid accelerates the bonding and rearrangement of particles, often resulting in faster and more complete densification.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Variables
Controlling the sintering process is critical to achieving the desired material properties. The outcome is a balance of several key factors.
Temperature and Time
Higher sintering temperatures and longer processing times generally lead to greater density. However, excessive heat or time can cause grain growth, where smaller grains merge into larger ones, which can sometimes negatively impact the material's final mechanical properties.
Particle Size and Shape
Finer powders with a larger surface area tend to sinter more easily and at lower temperatures. The initial packing density of the green body also plays a significant role in how efficiently the final part consolidates.
Pressure and Atmosphere
Some advanced techniques, such as hot pressing, apply external pressure during heating to accelerate densification. The atmosphere inside the furnace (e.g., vacuum or inert gas) is also controlled to prevent oxidation or other unwanted chemical reactions.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Understanding the different methods allows you to align the process with your specific manufacturing or material goal.
- If your primary focus is high purity and material integrity: Solid-state sintering is the ideal choice, as it bonds a single material without introducing a secondary liquid phase.
- If your primary focus is rapid densification or creating composite materials: Liquid phase sintering is highly effective, as the liquid acts as a transport medium to accelerate the process.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing complex geometries: Advanced techniques like Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) apply these principles on a micro-scale, using a laser to sinter powder layer by layer in 3D printing.
By mastering these principles, you can effectively transform simple powders into robust, high-performance components.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Core Process | Solid-state bonding of powder particles below the melting point via atomic diffusion. |
| Primary Mechanism | Heat energizes atoms, causing them to migrate across particle boundaries, eliminating pores. |
| Main Methods | Solid-State Sintering (pure materials) and Liquid Phase Sintering (faster densification with a liquid phase). |
| Key Variables | Temperature, time, particle size, and furnace atmosphere critically control the final part's properties. |
Ready to transform your material powders into high-performance components? KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for successful sintering processes. Whether you're working with advanced ceramics or metal powders, our expertise ensures you achieve the density, strength, and material integrity your project demands. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific sintering application and how we can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace facilitate the post-treatment of Zirconia coatings?
- Why is a high vacuum environment necessary in sintering equipment for TiAl alloys? Ensure High-Purity Metal Bonding
- Why is a high vacuum required for sintering Ti-43Al-4Nb-1Mo-0.1B? Ensure Purity & Fracture Toughness
- How does precise temperature control affect FeCoCrNiMnTiC high-entropy alloys? Master Microstructural Evolution
- Does sintering use diffusion? The Atomic Mechanism for Building Stronger Materials



















