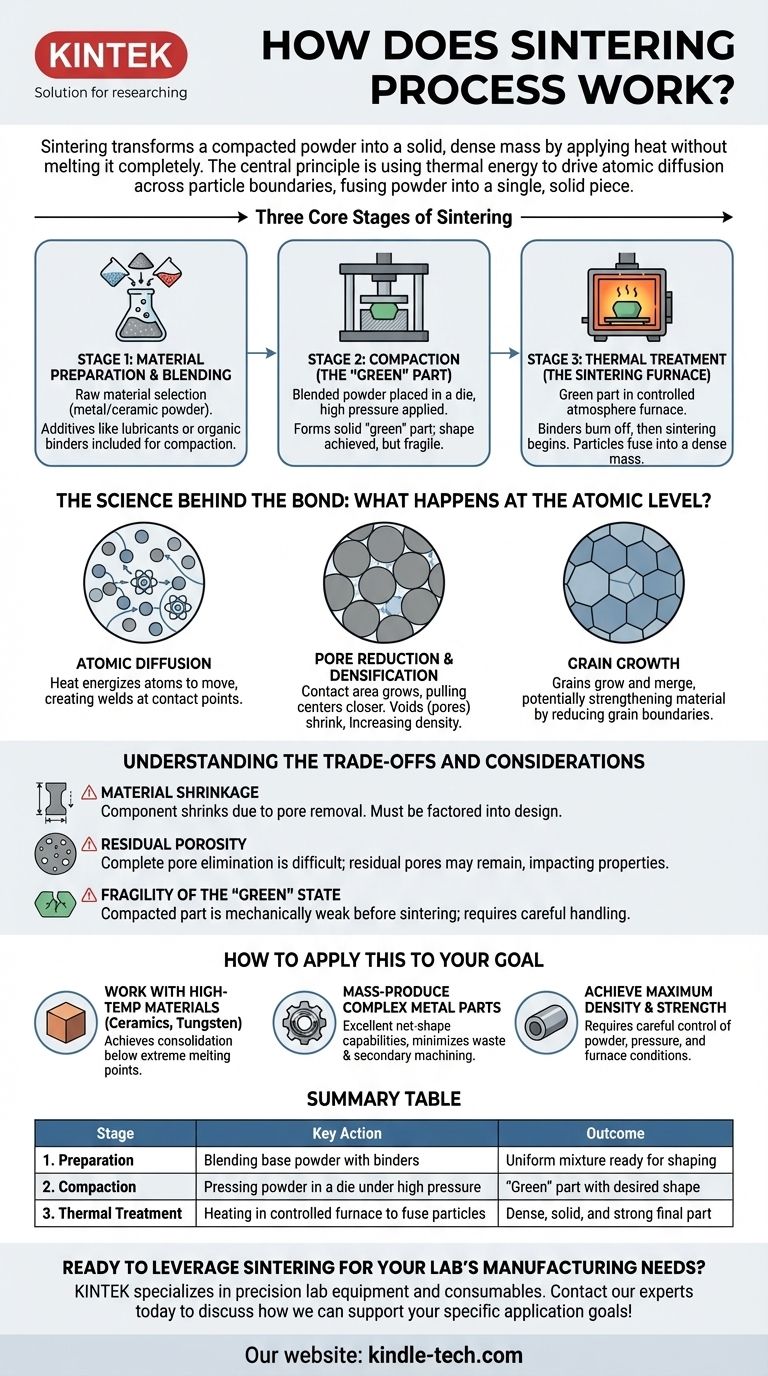
At its core, the sintering process transforms a compacted powder into a solid, dense mass by applying heat without melting it completely. The process typically involves three fundamental stages: preparing and mixing the powdered material, compressing it into a desired shape (known as a "green" part), and then heating it in a controlled furnace where the individual particles fuse together.
The central principle of sintering is using thermal energy to drive atomic diffusion across particle boundaries. This fuses the powder into a single, solid piece, a technique essential for manufacturing components from materials with extremely high melting points or for creating complex net-shape parts efficiently.

The Three Core Stages of Sintering
Sintering is not a single action but a carefully controlled sequence of events. Each stage plays a critical role in determining the final properties of the component.
Stage 1: Material Preparation and Blending
Before any heating occurs, the raw material must be prepared. This involves selecting a primary metal or ceramic powder and often mixing it with other elements.
Additives like lubricants or organic binders (coupling agents) are included to improve the compaction process and provide initial strength to the pressed part.
Stage 2: Compaction (The "Green" Part)
The blended powder is placed into a die or mold. Extremely high pressure is then applied to press the powder together, forcing the particles into tight contact.
This process forms a solid object with the desired shape, often called a "green" part. This part is solid enough to be handled but is still fragile and has not yet achieved its final strength or density.
Stage 3: Thermal Treatment (The Sintering Furnace)
The green part is placed into a sintering furnace with a controlled atmosphere. The heating process occurs in distinct phases.
First, at lower temperatures, any residual organic binders are burned off. Then, as the temperature rises to just below the material's melting point, the actual sintering begins. The particles bond and fuse, creating a dense, unified mass.
The Science Behind the Bond: What Happens at the Atomic Level?
The true power of sintering happens at a microscopic scale. The applied heat energizes the atoms within the powder particles, causing several transformative effects.
Atomic Diffusion
Sintering works because heat gives atoms enough energy to move, or diffuse, across the boundaries where particles touch.
This atomic movement effectively creates welds at countless points of contact throughout the part, fusing the individual grains of powder into a single, solid piece.
Pore Reduction and Densification
As particles begin to fuse, the contact area between them grows. This process pulls the centers of the particles closer together.
The result is that the voids, or pores, between the particles shrink and are gradually eliminated. This reduction in porosity is what causes the part to densify and become stronger.
Grain Growth
During the thermal process, the individual crystalline structures, or grains, of the material can grow and merge.
This phenomenon can further strengthen the material by reducing the number of grain boundaries, which can sometimes be points of weakness.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, the sintering process has specific characteristics that engineers and designers must account for to achieve success.
Material Shrinkage
The process of densification and pore elimination is not without consequence. As the pores are removed, the entire component shrinks in size.
This shrinkage is predictable and must be factored into the initial design of the mold and the green part to ensure the final component meets dimensional specifications.
Residual Porosity
In most cases, it is very difficult to eliminate 100% of the porosity. Some small, residual pores may remain within the final part.
This can impact the material's ultimate mechanical properties, such as its strength and hardness, when compared to a component made from fully molten metal.
Fragility of the "Green" State
The compacted part is mechanically weak before it enters the furnace. This "green" state requires careful handling to prevent cracks, chips, or other defects that would be locked in during the final sintering stage.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Your specific objective will determine which aspects of the sintering process are most critical to control.
- If your primary focus is working with high-temperature materials (like ceramics or tungsten): Sintering is a primary method because it achieves consolidation well below the material's extreme melting point.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing complex metal parts: Sintering offers excellent net-shape capabilities, minimizing material waste and the need for costly secondary machining operations.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum theoretical density and strength: You must carefully control powder characteristics, compaction pressure, and furnace conditions to minimize residual porosity.
Ultimately, mastering the sintering process is about precisely controlling heat and pressure to transform loose powder into a dense, unified, and high-performance component.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Blending base powder with binders | Uniform mixture ready for shaping |
| 2. Compaction | Pressing powder in a die under high pressure | "Green" part with desired shape |
| 3. Thermal Treatment | Heating in controlled furnace to fuse particles | Dense, solid, and strong final part |
Ready to leverage sintering for your lab's manufacturing needs? KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for advanced material processing. Whether you are developing complex net-shape parts or working with high-temperature materials, our sintering solutions can help you achieve superior density and performance. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific application goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
People Also Ask
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results
- What is one of the newest applications for dental ceramics? Monolithic Zirconia for Full-Arch Bridges
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs



















