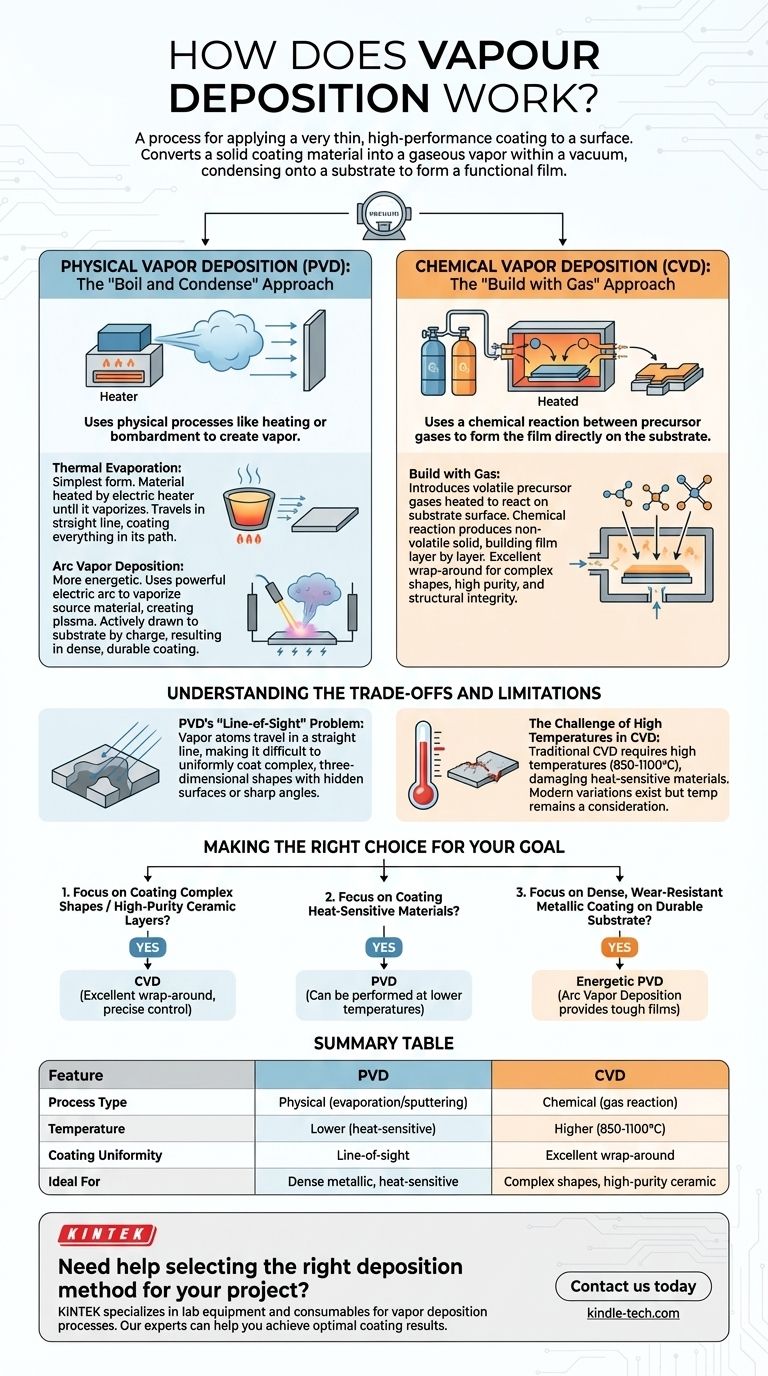
Vapor deposition is a process for applying a very thin, high-performance coating to a surface. The core principle involves converting a solid coating material into a gaseous vapor within a vacuum, which then condenses onto a target object—the substrate—to form a solid, functional film.
The critical distinction to understand is that vapor deposition techniques are divided into two main families. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) uses physical processes like heating or bombardment to create the vapor, while Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) uses a chemical reaction between precursor gases to form the film directly on the substrate.

The Two Pillars of Vapor Deposition
To truly grasp how these processes work, we must examine the fundamental differences between the physical and chemical approaches. Each has a distinct method for creating the vapor and depositing the film, leading to different strengths and applications.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): The "Boil and Condense" Approach
PVD is best understood as a highly controlled version of how water vapor condenses on a cold surface. A solid source material is physically converted into a gas, which then travels through a vacuum chamber and solidifies on the substrate.
Thermal Evaporation is the simplest form of PVD. The source material is heated by an electric heater until it vaporizes. This vapor then travels in a straight line and coats anything in its path, forming a thin film as it cools and condenses.
Arc Vapor Deposition is a more energetic and complex PVD method. Instead of just heat, it uses a powerful electric arc to vaporize the source material. This creates a highly ionized vapor, or plasma, which is then actively drawn to the substrate by an electrical charge, resulting in a very dense and durable coating.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): The "Build with Gas" Approach
CVD does not start with a solid block of coating material. Instead, it introduces specific, volatile precursor gases into a reaction chamber containing the substrate.
These gases are heated and react with each other on the surface of the substrate. This chemical reaction produces a new, non-volatile solid material that is "built" directly onto the surface, one layer of atoms at a time.
Because the film is formed by a gas that can envelop the entire object, CVD provides excellent "wrap-around" properties. This makes it ideal for coating complex shapes evenly, producing films of high purity, density, and structural integrity.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Choosing between PVD and CVD requires understanding their inherent limitations. The ideal process depends entirely on the substrate material and the desired characteristics of the final coating.
The Challenge of High Temperatures in CVD
Traditional CVD requires very high reaction temperatures, often between 850-1100°C. This extreme heat is necessary to drive the chemical reactions but means many substrate materials, such as plastics or certain metals, simply cannot withstand the process without being damaged or destroyed.
Modern variations using plasma or lasers can lower this temperature, but it remains a primary consideration.
PVD's "Line-of-Sight" Problem
In most PVD processes, the vaporized atoms travel in a straight line from the source to the substrate. This "line-of-sight" transfer makes it difficult to achieve a uniform coating on complex, three-dimensional shapes with hidden surfaces or sharp angles.
The Question of Purity and Control
CVD offers exceptional control over the final film's properties. By precisely adjusting the precursor gases and deposition parameters, operators can control the chemical composition, grain size, and crystal structure of the coating. This makes it superior for creating highly engineered, multi-component, or ceramic layers.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use PVD or CVD is a function of your material, the geometry of your part, and the performance you require.
- If your primary focus is coating complex shapes or creating high-purity ceramic layers: CVD is often the superior choice due to its excellent wrap-around capability and precise chemical control.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-sensitive materials: PVD is generally more suitable, as many of its methods can be performed at much lower temperatures than traditional CVD.
- If your primary focus is a dense, wear-resistant metallic coating on a durable substrate: Energetic PVD methods like Arc Vapor Deposition provide an excellent solution for creating tough, resilient films.
Understanding the fundamental difference between the physical and chemical pathways is the key to selecting the right technology for your application.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical (evaporation/sputtering) | Chemical (gas reaction) |
| Temperature | Lower (suitable for heat-sensitive materials) | Higher (often 850-1100°C) |
| Coating Uniformity | Line-of-sight (may miss complex shapes) | Excellent wrap-around coverage |
| Ideal For | Dense metallic coatings, heat-sensitive substrates | Complex shapes, high-purity ceramic layers |
Need help selecting the right deposition method for your project? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for vapor deposition processes, serving diverse laboratory needs. Whether you require PVD for heat-sensitive materials or CVD for complex geometries, our experts can help you achieve optimal coating results. Contact us today to discuss your specific application requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What is MOCVD used for? Precision Manufacturing for LEDs, Lasers, and RF Semiconductors
- What is atomic layer deposition of a gas? Achieve Perfectly Uniform Thin Films with Atomic Precision
- What are the primary advantages of utilizing a horizontal hot-wall CVD reactor? Gain Industrial Alumina Coating Quality
- Why is vacuum important in thin film coating? Achieve Purity and Control for Superior Film Quality
- What is the difference between sputtering and deposition? Understanding the Core Hierarchy of Thin-Film Coating
- What gases are used in chemical vapor deposition? Choosing the Right Precursors for Your Thin Film
- How do you identify a CVD diamond? The Definitive Guide to Lab-Grown Diamond Verification
- What do you mean by sputtering process? A Guide to Atomic-Level Thin Film Deposition



















