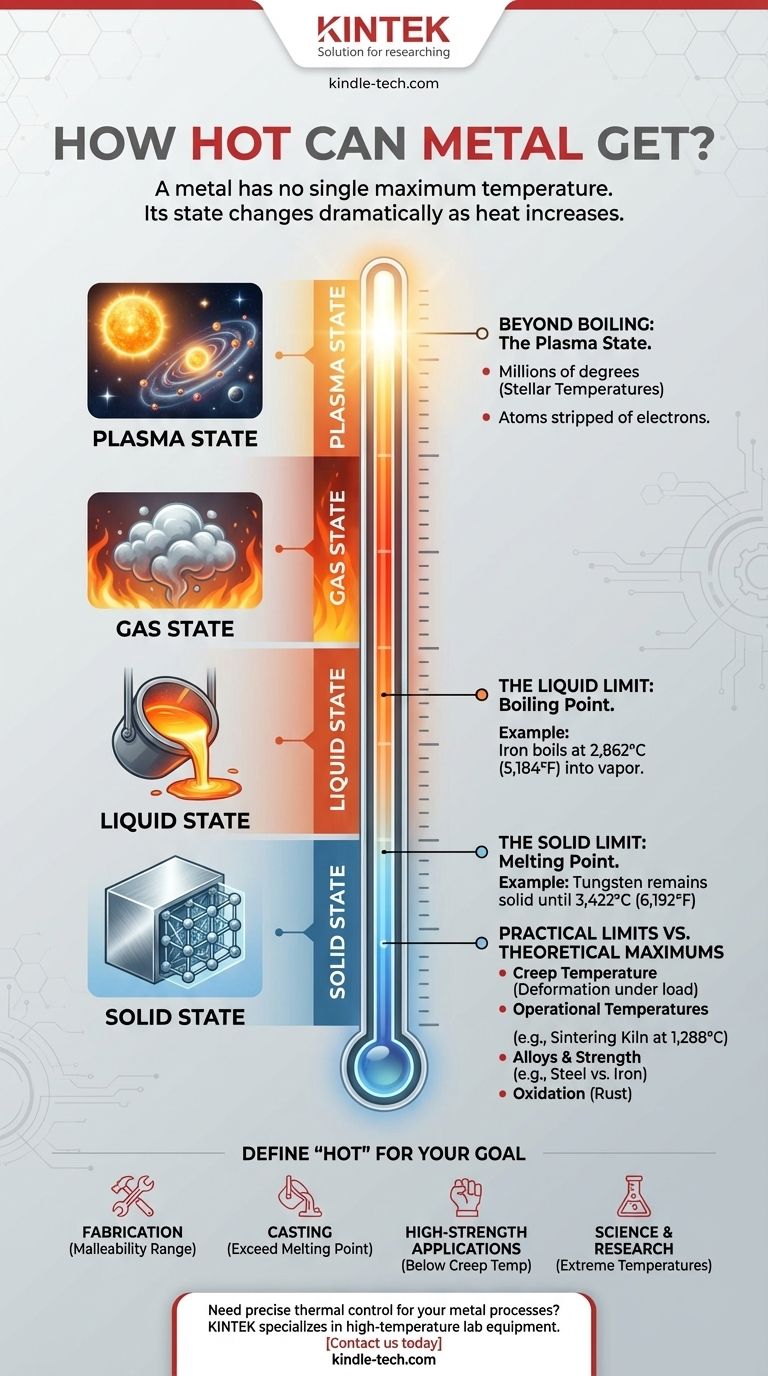
Fundamentally, a metal has no single maximum temperature. Instead, its state and integrity change dramatically as heat increases, progressing from a strong solid to a liquid, then a gas, and ultimately to a plasma at millions of degrees. The "limit" is therefore defined not by the metal itself, but by the physical state you require for your application.
A metal’s maximum temperature is not a single value but a series of critical thresholds. The most important limits are its melting point (when it turns to liquid) and boiling point (when it turns to gas), with practical engineering limits often being much lower.

The Journey Through Temperature: Solid, Liquid, Gas
Understanding how hot a metal can get requires looking at its phase transitions. Each metal has its own unique set of temperature thresholds.
The Solid Limit: The Melting Point
A metal's most commonly understood thermal limit is its melting point, the temperature at which it transitions from a solid to a liquid.
This temperature varies enormously between different metals. For example, Gallium melts in your hand at 30°C (86°F), while Tungsten, used in rocket nozzles and incandescent filaments, remains solid until 3,422°C (6,192°F).
The Liquid Limit: The Boiling Point
Just like water, metals can be heated further until they boil and turn into a gas. This is the boiling point.
This threshold is significantly higher than the melting point. For instance, while iron melts at 1,538°C (2,800°F), you would need to reach 2,862°C (5,184°F) to turn it into a metallic vapor.
Practical Limits vs. Theoretical Maximums
In engineering and industrial applications, theoretical limits like the boiling point are rarely the focus. The practical, usable temperature is often far lower.
Operational Temperatures in Industry
Many high-temperature processes operate well below a metal's melting point. For example, a sintering kiln used for powder metallurgy might operate at 1288°C (2350°F).
This temperature is high enough to fuse metal particles together without fully melting the material, demonstrating that a metal's "useful" hotness depends entirely on the goal.
The Impact of Alloys
Combining metals to create alloys is a primary way to manipulate thermal limits.
Steel, an alloy of iron and carbon, has a slightly lower melting point than pure iron but offers vastly superior strength. Superalloys used in jet engines are engineered to resist deformation and corrosion at extreme temperatures that would weaken their constituent metals.
Beyond Boiling: The Plasma State
If you continue to heat a metal vapor past its boiling point, you can reach the fourth state of matter.
What is Plasma?
Plasma is a superheated gas where atoms are stripped of their electrons, creating an ionized, electrically conductive substance. This is the most common state of matter in the universe.
Reaching Stellar Temperatures
Inside the sun and other stars, elements like iron exist as plasma at temperatures of millions of degrees Celsius. At this stage, the concept of a solid or liquid metal is meaningless. This represents the ultimate, though theoretical, answer to how hot a metal can get.
Key Considerations and Pitfalls
Defining a metal's heat limit requires avoiding common oversimplifications.
Usable Strength vs. Melting Point
A metal loses a significant amount of its structural strength long before it reaches its melting point. For engineers designing engines or structures, the creep temperature, where a material begins to deform under load, is a far more critical limit.
Ignoring Chemical Reactions
Heating metals in the presence of oxygen or other chemicals can cause reactions like oxidation (rust), which can degrade the material's integrity. The true operational limit must account for the chemical environment, not just the temperature.
How to Define "Hot" for Your Goal
The right temperature limit is the one that matches your objective.
- If your primary focus is fabrication (forging, bending): You care about the malleability range, which is well below the melting point.
- If your primary focus is casting: You must exceed the metal's melting point to ensure it flows into a mold properly.
- If your primary focus is a high-strength application (engines, tools): You are concerned with the maximum operating temperature where the metal retains its strength, which is significantly below its melting point.
- If your primary focus is science and research: You might be interested in the extreme temperatures required to create a metallic gas or plasma.
Ultimately, the temperature a metal can withstand is determined by the properties you need it to maintain.
Summary Table:
| Metal / State | Key Temperature Threshold | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Solid Metal | Melting Point (e.g., Tungsten: 3,422°C) | Determines fabrication and casting limits |
| Liquid Metal | Boiling Point (e.g., Iron: 2,862°C) | Transition to metallic vapor |
| Plasma State | Millions of Degrees (e.g., stellar conditions) | Atoms ionize; theoretical maximum |
| Practical Limit | Creep Temperature / Operational Range (e.g., sintering at 1,288°C) | Retains strength; avoids deformation |
Need precise thermal control for your metal processes? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature lab equipment, including furnaces and kilns designed for sintering, melting, and heat treatment applications. Our solutions help you achieve accurate temperature management—ensuring material integrity and process efficiency. Contact us today to discuss your specific metal heating requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the burning temperature of a furnace? From 200°C to 3000°C, It Depends on Your Needs
- What is the maximum temperature of a muffle furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Application
- How to maintain a muffle furnace? Ensure Long-Term Reliability and Safety
- What is the use of muffle furnace in soil? Analyze Soil Composition with High-Temperature Precision
- What is the temperature accuracy of a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise and Uniform Heating



















