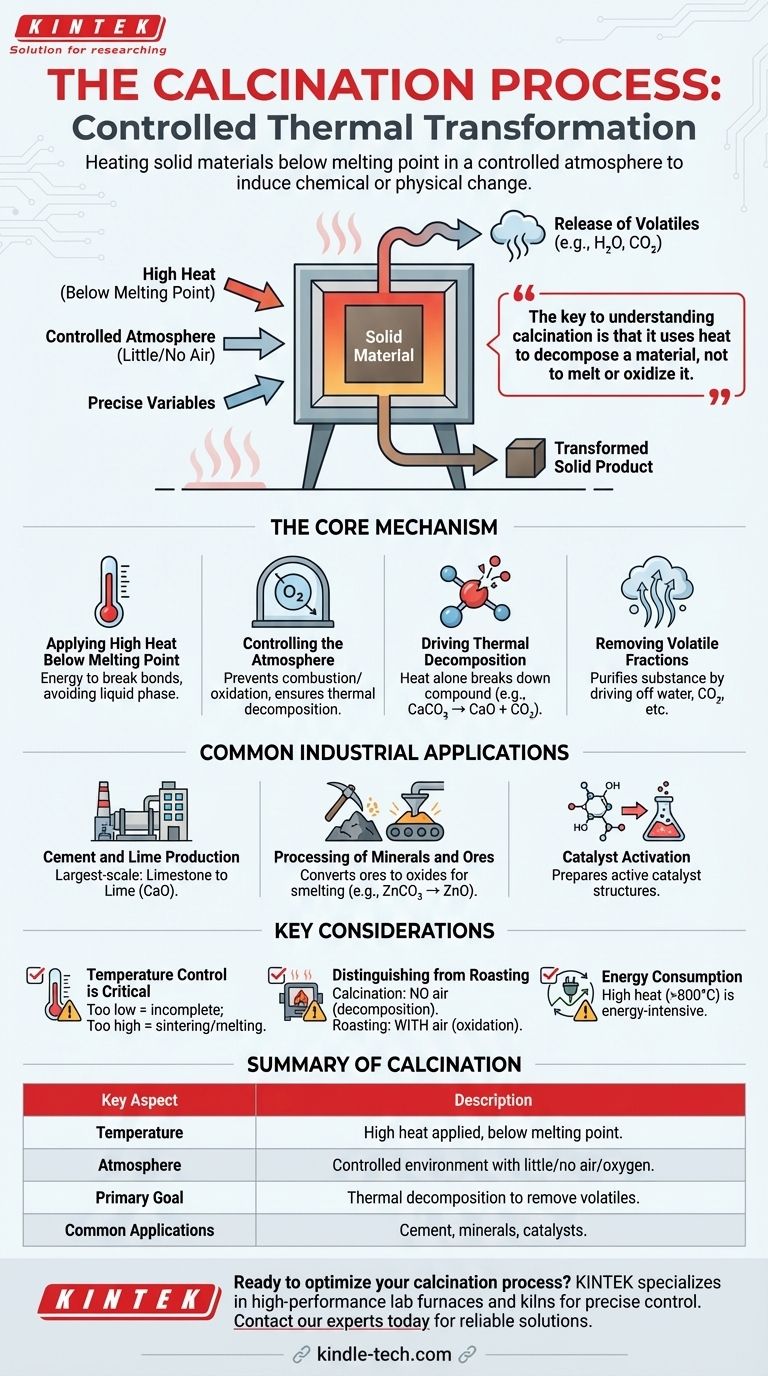
At its core, calcination is a thermal treatment process performed by heating a solid material to a high temperature, but below its melting point, in an environment with little to no air. This controlled heating is not meant to burn the material, but rather to induce a chemical or physical change, such as driving off volatile substances like water and carbon dioxide or altering its crystalline structure.
The key to understanding calcination is that it uses heat to decompose a material, not to melt or oxidize it. The controlled atmosphere—specifically the absence of air—is what distinguishes it from other heat-based processes and enables targeted chemical transformations.

The Core Mechanism of Calcination
Calcination is a precise and widely used industrial process. Its effectiveness hinges on the careful control of two primary factors: temperature and atmosphere.
Applying High Heat Below Melting Point
The material is placed inside a specialized furnace, such as a rotary kiln or shaft furnace. The temperature is raised significantly to provide the energy needed to break chemical bonds.
Crucially, this temperature remains below the material's melting point. The goal is a solid-state transformation, not a change into a liquid phase.
Controlling the Atmosphere
Calcination is defined by its execution in the absence or a very limited supply of air (oxygen). This is critical because it prevents combustion or oxidation.
Instead of burning, the material undergoes thermal decomposition. This controlled atmosphere ensures that heat is the sole agent of change.
Driving Thermal Decomposition
Heat alone acts as a catalyst to break down the compound into simpler substances. The most common example is the decomposition of carbonates.
When limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) is calcined, the heat breaks it down into lime (calcium oxide, CaO) and carbon dioxide (CO₂), which is released as a gas.
Removing Volatile Fractions
The primary purpose of calcination is often to "purify" a substance by removing a volatile component. This can be water from hydrated minerals, carbon dioxide from carbonates, or other volatile organic compounds.
The result is a more concentrated, and often more reactive, solid product. For example, calcining bauxite ore removes water, preparing it for aluminum production.
Common Industrial Applications
Calcination is not an obscure laboratory technique; it is a foundational process in several major global industries.
Production of Cement and Lime
This is the largest-scale application of calcination. Millions of tons of limestone are calcined annually to produce lime, a fundamental ingredient in cement, mortar, and plaster.
Processing of Minerals and Ores
Calcination is a key step in metallurgy. It is used to convert metal ores into their oxide forms, which are easier to reduce to pure metal in a subsequent smelting process. For example, zinc carbonate (ZnCO₃) is calcined to produce zinc oxide (ZnO).
Catalyst Activation
In the chemical industry, many catalysts are prepared as precursor materials. Calcination is used to heat these precursors, driving off unwanted components and creating the final, highly porous, and active catalyst structure.
Understanding the Key Considerations
While the principle is straightforward, successful industrial calcination requires careful management of several variables.
Temperature Control is Critical
If the temperature is too low, the decomposition reaction will be incomplete, resulting in a low-quality product. If the temperature is too high, the material may sinter (fuse into a solid mass) or melt, reducing its reactivity and surface area.
Distinguishing from Roasting
Calcination is often confused with roasting, another thermal process. The key difference is the atmosphere: calcination occurs without air, while roasting is done with an excess of air specifically to promote oxidation.
Energy Consumption
Heating materials to the high temperatures required for calcination (often >800°C or 1500°F) is extremely energy-intensive. This makes energy efficiency a primary concern in the design and operation of kilns.
Matching the Process to Your Goal
The specific parameters of calcination are always tailored to the starting material and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is producing cement or lime: You will perform calcination on limestone (CaCO₃) to thermally decompose it into lime (CaO) by driving off CO₂.
- If your primary focus is preparing a metal ore for smelting: You will use calcination to convert a carbonate or hydrate ore into its oxide form, making it easier to process later.
- If your primary focus is creating a high-purity material: You will use calcination to drive off volatile impurities like water, leaving behind a more concentrated and often more reactive solid.
Ultimately, calcination is a precise thermal tool used to chemically transform solid materials by carefully applying heat in a controlled atmosphere.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Temperature | High heat applied, but below the material's melting point. |
| Atmosphere | Controlled environment with little to no air/oxygen. |
| Primary Goal | Thermal decomposition to remove volatile substances (e.g., water, CO₂). |
| Common Applications | Cement production, mineral processing, catalyst activation. |
Ready to optimize your calcination process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and kilns that deliver the precise temperature control and atmosphere management required for effective thermal decomposition. Whether you're in research, metallurgy, or chemical production, our equipment ensures reliable results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect calcination solution for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker



















