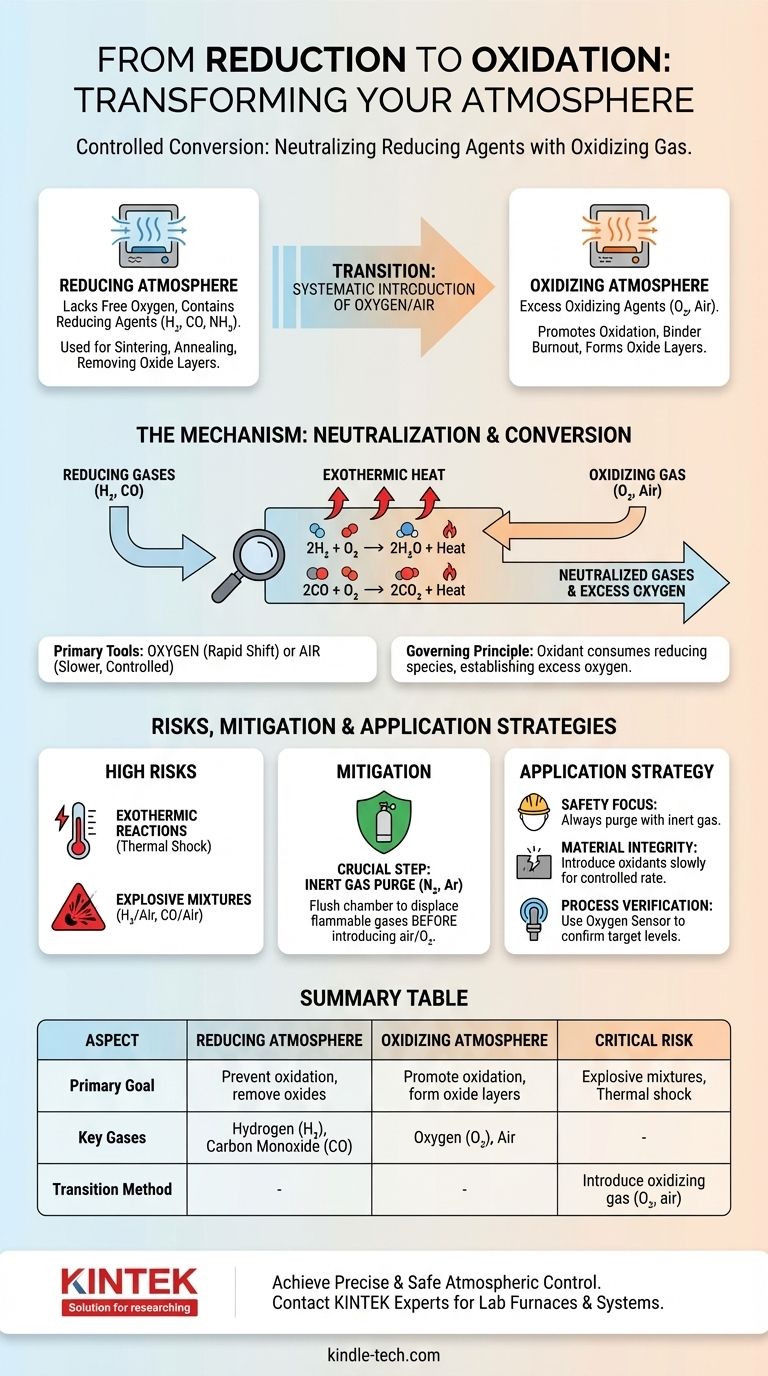
Transforming a reducing atmosphere to an oxidizing one is achieved by systematically introducing an oxidizing gas, most commonly oxygen or air. This process neutralizes the active reducing agents present, such as hydrogen or carbon monoxide, by reacting with them to form more stable molecules like water and carbon dioxide, fundamentally shifting the chemical potential of the environment.
The change from a reducing to an oxidizing atmosphere is a controlled chemical conversion. It's not merely about dilution; it's about deliberately supplying an oxidant to consume the reducing species and create an excess of oxygen.
Understanding the Core Concepts: Reducing vs. Oxidizing
What Defines a Reducing Atmosphere?
A reducing atmosphere is an environment that lacks free oxygen and contains active reducing agents. These agents, like hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), or dissociated ammonia (NH₃), readily donate electrons or strip oxygen atoms from materials they contact.
Such atmospheres are used to prevent oxidation or to actively remove oxide layers from metals and ceramics during high-temperature processing, such as sintering or annealing.
What Defines an Oxidizing Atmosphere?
An oxidizing atmosphere, by contrast, has an excess of an oxidizing agent, most ubiquitously oxygen (O₂). This environment promotes oxidation, a reaction where a material loses electrons or combines with oxygen.
Air, which is approximately 21% oxygen, is the most common oxidizing atmosphere. These environments are essential for processes like binder burnout in ceramics or creating specific oxide layers on a material's surface.
The Mechanism of Transition: From Reduction to Oxidation
The Principle: Neutralization via Reaction
The transition hinges on a simple principle: an oxidizing agent will react with and neutralize a reducing agent. To change the atmosphere, you must introduce enough oxidant to consume all the reducing gases present and then establish an excess.
Oxygen and Air: The Primary Tools
Oxygen or air are the standard gases used for this conversion. The choice between them depends on the required speed of the reaction and the level of control needed.
Pure oxygen provides a more potent and rapid shift, while air allows for a slower, more diluted, and often more controllable transition.
The Governing Chemical Reactions
When oxygen is introduced into a typical hot reducing atmosphere, it immediately reacts with the reducing agents. The primary reactions are highly favorable and spontaneous at processing temperatures.
For a hydrogen atmosphere:
2H₂ (gas) + O₂ (gas) → 2H₂O (gas) + Heat
For a carbon monoxide atmosphere:
2CO (gas) + O₂ (gas) → 2CO₂ (gas) + Heat
The atmosphere only becomes truly oxidizing once all the H₂ or CO has been converted into H₂O or CO₂ and a surplus of O₂ is established.
Understanding the Risks and Trade-offs
High Risk of Exothermic Reactions
The reactions that neutralize reducing agents are highly exothermic, meaning they release a significant amount of heat. A rapid introduction of oxygen can cause a sudden temperature spike inside a furnace, potentially damaging the equipment or the product.
This thermal shock can crack sensitive materials like ceramics or cause unwanted phase transformations in metals.
Potential for Explosive Mixtures
The most critical risk is the creation of an explosive atmosphere. Mixtures of hydrogen and air (between 4% and 75% H₂) or carbon monoxide and air (between 12% and 75% CO) are explosive.
If an ignition source is present—such as a hot element or static discharge—a rapid, uncontrolled introduction of air or oxygen can cause a violent explosion. Safety protocols are non-negotiable.
Purging with an Inert Gas
To mitigate these risks, a crucial intermediate step is often employed: purging with an inert gas. Before introducing air, the furnace chamber is flushed with a gas like nitrogen (N₂) or argon (Ar).
This purge displaces the flammable reducing gas, preventing the formation of an explosive mixture when oxygen is finally introduced.
How to Apply This to Your Process
A controlled transition is paramount for safety and achieving the desired material properties. The correct strategy depends entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is safety: Always purge the reducing gas with an inert gas like nitrogen before introducing any amount of air or oxygen.
- If your primary focus is material integrity: Introduce the oxidizing gas slowly and at a controlled rate to prevent thermal shock from the exothermic reaction.
- If your primary focus is process verification: Use an oxygen sensor or gas analyzer on the furnace exhaust to confirm that all reducing agents have been consumed and you have achieved the target oxygen level.
Mastering this atmospheric transition gives you precise control over your material's final chemical state and physical properties.

Summary Table:
| Aspect | Reducing Atmosphere | Oxidizing Atmosphere |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Prevent oxidation, remove oxides | Promote oxidation, form oxide layers |
| Key Gases | Hydrogen (H₂), Carbon Monoxide (CO) | Oxygen (O₂), Air |
| Transition Method | Introduce oxidizing gas (O₂, air) to consume reducing agents | Achieved after reducing agents are neutralized |
| Critical Risk | Formation of explosive mixtures during transition | Thermal shock from exothermic reactions |
Achieve precise and safe atmospheric control in your lab.
Mastering the transition from a reducing to an oxidizing atmosphere is critical for material integrity and operator safety. Whether you are sintering metals, annealing ceramics, or developing new materials, the right equipment and expertise are essential.
KINTEK specializes in lab furnaces and atmosphere control systems designed for precise, reliable, and safe operation. Our solutions help you:
- Prevent explosive mixtures with integrated safety features.
- Control thermal profiles to avoid damaging your samples.
- Verify process outcomes with compatible monitoring equipment.
Let KINTEK be your partner in laboratory excellence. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific furnace and atmosphere control needs. We provide the equipment and consumables to ensure your processes are both successful and safe.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can nitrogen gas be heated? Leverage Inert Heat for Precision and Safety
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2
- How we can develop inert atmosphere for a chemical reaction? Master Precise Atmospheric Control for Your Lab
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process



















