In short, the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) process grows a real diamond by placing a small diamond "seed" into a vacuum chamber and introducing a specific mixture of gases. These gases are heated until they break down, allowing carbon atoms to "rain" down and attach to the seed crystal, building a new, larger diamond layer by atomic layer. This method is a feat of material science, creating a diamond that is chemically and physically identical to one from the earth.
The core insight is that CVD is a process of chemical finesse, not brute force. It uses low pressure and high temperature in combination with specific gases—primarily hydrogen and a carbon source like methane—to create an environment where carbon atoms are chemically compelled to arrange themselves into the diamond crystal structure.

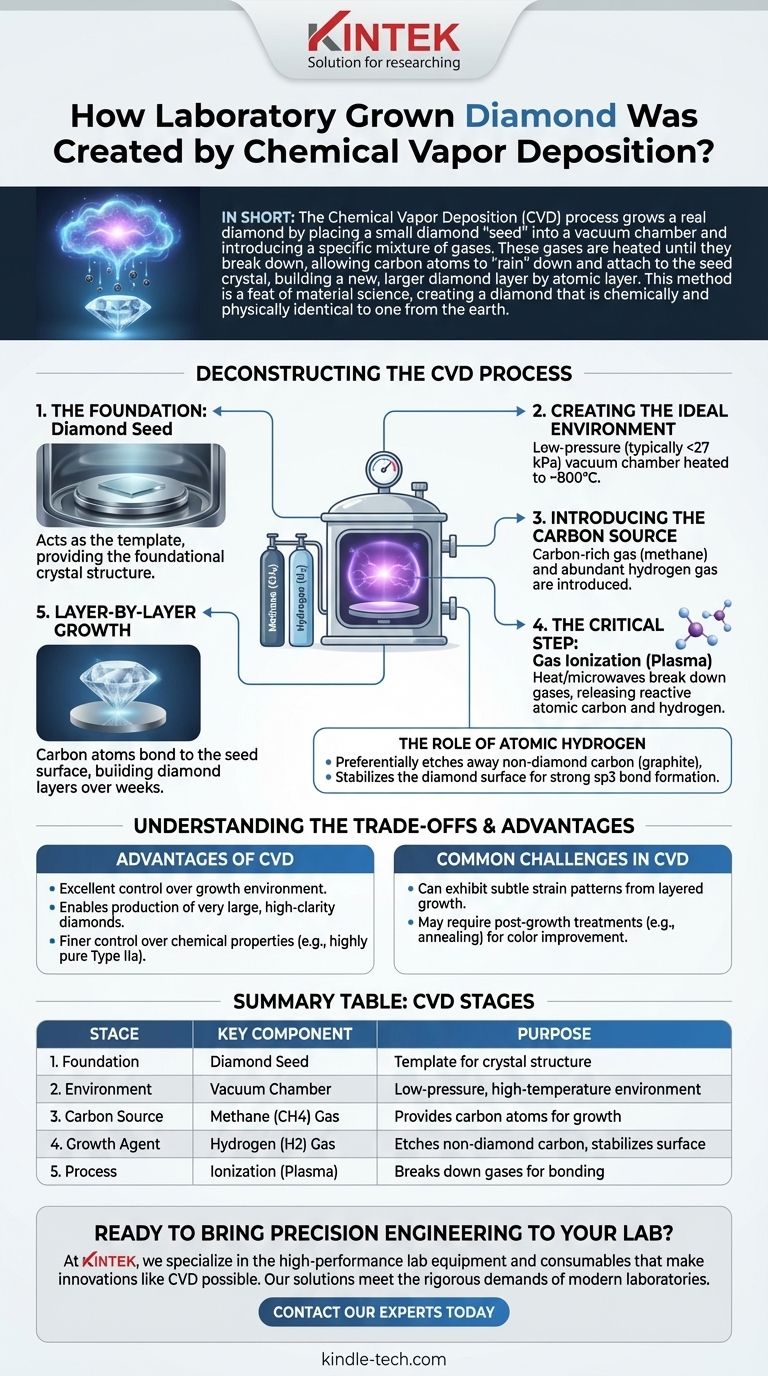
Deconstructing the CVD Process
To truly understand how a CVD diamond is grown, it's best to break the process down into its fundamental stages. Each step is precisely controlled to ensure the final product is a pure, high-quality diamond.
The Foundation: The Diamond Seed
The entire process begins with a substrate, which is a very thin, flat slice of a pre-existing diamond. This can be from either a natural diamond or a previously grown lab diamond. This "seed" acts as the template, providing the foundational crystal structure for the new carbon atoms to bond to.
Creating the Ideal Environment
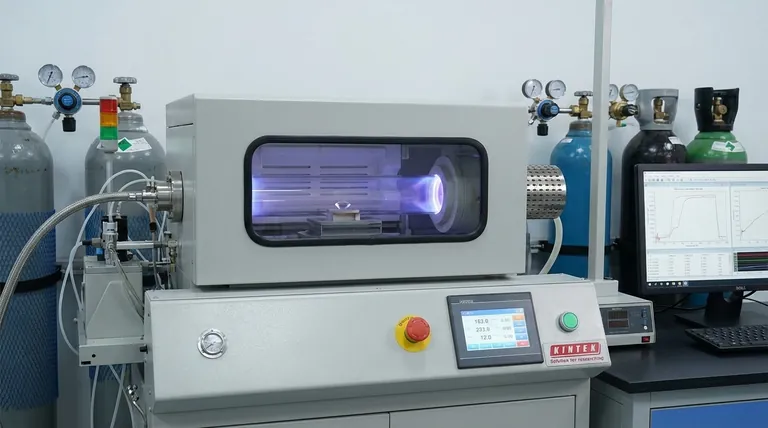
The diamond seed is placed inside a sealed, low-pressure vacuum chamber. The pressure is reduced to well below one atmosphere—typically under 27 kPa. This low pressure is a key differentiator from the alternative High-Pressure/High-Temperature (HPHT) method, which mimics the crushing force deep within the Earth.
Introducing the Carbon Source
A carefully measured mixture of gases is then introduced into the chamber. The primary ingredients are a carbon-rich gas, almost always methane (CH4), and an abundance of hydrogen (H2).
The Critical Step: Gas Ionization
The chamber is heated to a high temperature, often around 800°C. This heat, frequently supplemented by another energy source like microwaves, breaks the molecular bonds of the gases. This process, called ionization, creates a plasma of reactive elements. Methane molecules break apart, releasing pure carbon atoms, while hydrogen molecules (H2) split into highly reactive atomic hydrogen (H).
The Role of Atomic Hydrogen
The presence of atomic hydrogen is the secret to growing high-quality diamond instead of graphite (the form of carbon in a pencil lead). It serves two critical functions:
- It preferentially etches away any non-diamond carbon (graphite) that tries to form on the crystal's surface.
- It stabilizes the diamond surface, preparing it for new carbon atoms to land and form strong, stable diamond bonds (known as sp3 bonds).
Layer-by-Layer Growth
The freed carbon atoms are drawn down to the slightly cooler diamond seed. Guided by the seed's crystal lattice, they bond to the surface one by one. The diamond grows vertically, adding atomic layer upon atomic layer, over a period of several weeks. The result is a rough, newly formed diamond crystal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
CVD is one of two primary methods for growing lab diamonds. Understanding its unique characteristics compared to the HPHT method is key to appreciating its place in the market.
Advantages of the CVD Method
CVD allows for excellent control over the growth environment. This enables the production of very large, high-clarity diamonds. It also provides finer control over the diamond's chemical properties, making it easier to produce certain types of diamonds, including highly pure Type IIa stones, which are rare in nature.
Common Challenges in CVD
While highly controlled, the process isn't perfect. CVD diamonds can sometimes exhibit subtle strain patterns from the layered growth process. Some may also require post-growth treatments, such as annealing, to improve their color. The technology is constantly advancing to minimize these factors.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The science behind lab-grown diamonds has matured, making the origin a matter of technological preference rather than quality.
- If your primary focus is understanding the technology: The key is that CVD uses low pressure and precise gas chemistry to favor diamond growth, unlike the brute-force simulation of geological pressure in the HPHT method.
- If your primary focus is on the final product: A CVD-grown diamond is chemically, physically, and optically identical to a mined diamond and is only distinguishable by its origin using specialized laboratory equipment.
- If your primary focus is market implications: The CVD method allows for scalable production of high-quality diamonds, offering consumers a verifiable and often more affordable alternative to mined stones.
Ultimately, CVD technology represents a mastery of materials science, allowing us to create one of nature's hardest and most brilliant materials from simple gas.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Component | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Foundation | Diamond Seed | Acts as a template for the crystal structure. |
| 2. Environment | Vacuum Chamber | Creates a low-pressure, high-temperature environment. |
| 3. Carbon Source | Methane (CH₄) Gas | Provides the carbon atoms for diamond growth. |
| 4. Growth Agent | Hydrogen (H₂) Gas | Etches non-diamond carbon and stabilizes the surface. |
| 5. Process | Ionization (Plasma) | Breaks down gases so carbon atoms can bond to the seed. |
Ready to bring precision engineering to your lab? The CVD process is a marvel of controlled material science. At KINTEK, we specialize in the high-performance lab equipment and consumables that make such innovations possible. Whether you're in research, quality control, or advanced manufacturing, our solutions are designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern laboratories.
Let's discuss how we can support your next breakthrough. Contact our experts today to find the perfect equipment for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? Achieve Precision Coating for Complex Geometries
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor
- What function does CVD equipment serve in rhodium-modified coatings? Achieve Deep Diffusion and Microstructural Precision
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit



















