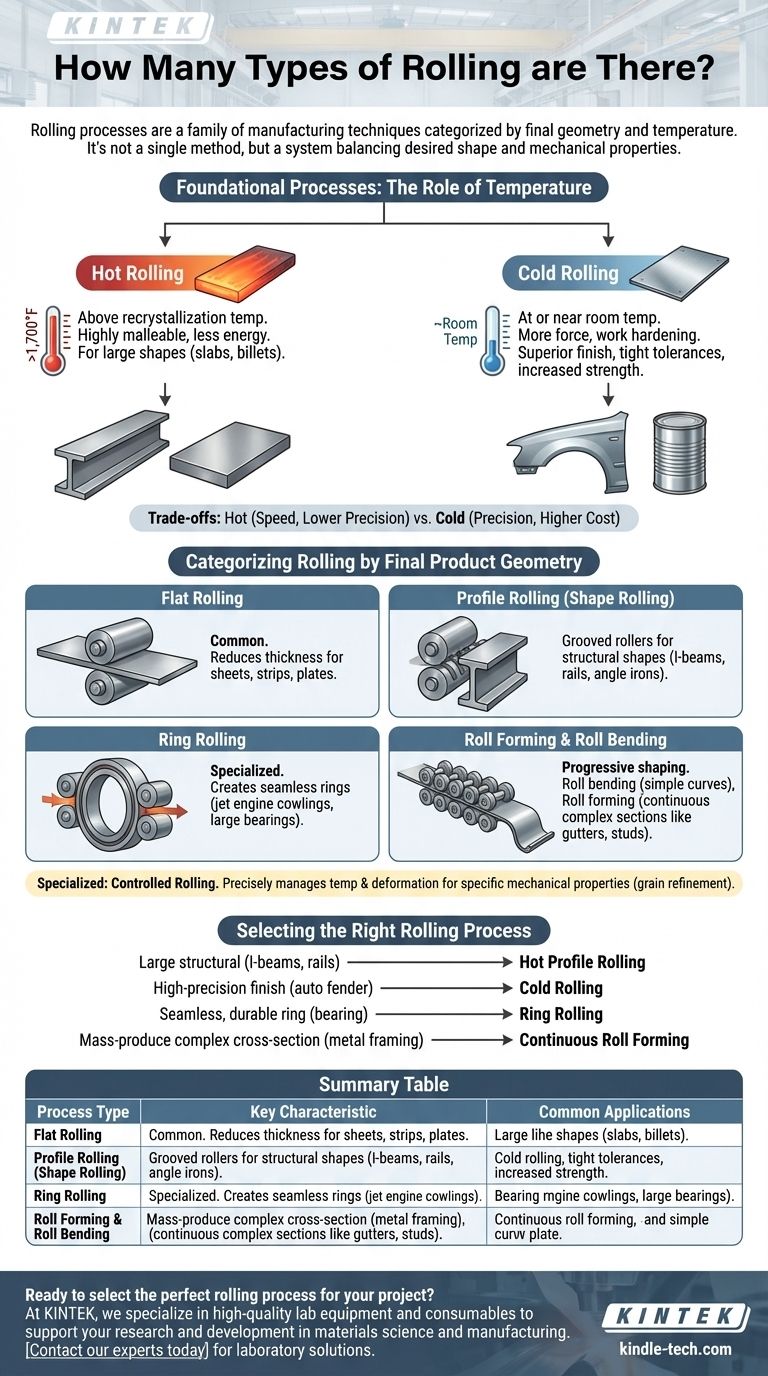
Rather than a fixed number, rolling processes are best understood as a family of manufacturing techniques categorized by the final geometry of the product and the temperature at which it is formed. Major types include hot and cold rolling, which define the material properties, and more specialized processes like profile rolling, ring rolling, and roll forming, which define the final shape.
The key to understanding rolling is to see it not as a single method, but as a system. The choice of process is dictated by two factors: the desired final shape and the required mechanical properties, which are largely controlled by temperature.
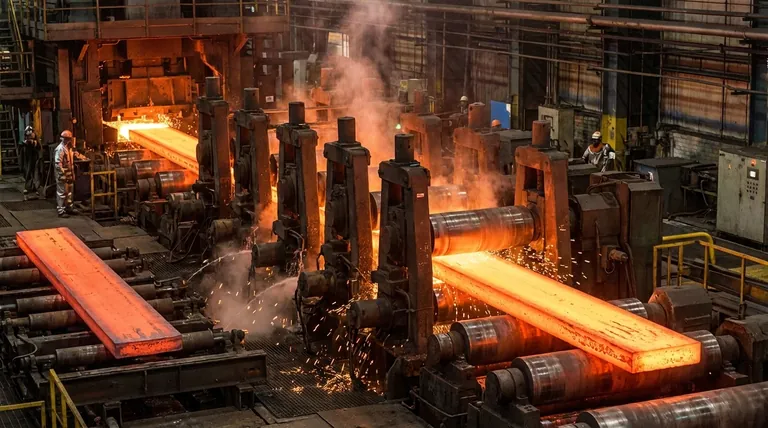

Foundational Processes: The Role of Temperature
Before examining shape, the most fundamental distinction in rolling is temperature. This choice impacts everything from the metal's ductility to the final product's strength and surface finish.
Hot Rolling
Hot rolling involves processing metal at a temperature above its recrystallization point (over 1,700°F or 926°C for steel). At this temperature, the metal is highly malleable and can undergo significant shape changes with less energy.
This process is ideal for creating large, simple stock shapes like slabs, billets, and blooms, which are the starting materials for many other manufacturing operations.
Cold Rolling
Cold rolling is performed at or near room temperature. Because the metal is not heated, it requires much more force to deform.
This process is used to create products with a superior surface finish, tighter dimensional tolerances, and increased strength through a phenomenon called work hardening. Automotive body panels and tin cans are common examples.
Categorizing Rolling by Final Product Geometry
Once the temperature条件 is established, the specific rolling process is chosen based on the desired final shape. This is where the diversity of rolling becomes apparent.
Flat Rolling
This is the most common type of rolling. It involves passing a piece of metal, such as a slab or billet, through a pair of opposing rollers to reduce its thickness and create flat products like sheets, strips, and plates.
Profile Rolling (Shape Rolling)
Profile rolling, or shape rolling, uses specially grooved rollers to form metal into specific cross-sectional shapes. This is the process used to create structural components like I-beams, railway tracks, and angle irons.
Ring Rolling
This specialized process creates seamless rings. It starts with a thick, hollow, donut-shaped workpiece that is rotated between rollers, which apply pressure to reduce its wall thickness and increase its diameter. This method is critical for manufacturing parts like jet engine cowlings, large bearings, and turbine wheels.
Roll Forming and Roll Bending
Both processes start with flat sheet metal and progressively shape it. Roll bending typically creates simple curves or large-radius cylinders.
Roll forming, however, is a continuous process that uses a long series of roller pairs to gradually bend flat metal strip into complex, specific cross-sections, such as gutters, door frames, or metal studs.
Controlled Rolling
Controlled rolling is a highly specialized thermomechanical process, most often a type of hot rolling. The temperature and deformation are precisely managed to refine the metal's grain structure. The goal is not just to shape the metal but to achieve specific mechanical properties, such as high strength and fracture toughness, without the need for later heat treatment.
Understanding the Core Trade-offs
No single rolling process is universally superior. The choice always involves balancing cost, precision, speed, and final material properties.
Hot Rolling: Speed vs. Precision
The primary advantage of hot rolling is its ability to deform large amounts of metal quickly and with less energy. However, as the metal cools, it shrinks unevenly, leading to less precise dimensional accuracy and a rougher surface finish covered in scale.
Cold Rolling: Precision vs. Cost
Cold rolling delivers exceptional surface finish and tight tolerances. The work hardening effect also increases the material's strength. The downside is a much higher cost due to the immense power required, slower processing speeds, and the metal's reduced ductility.
Selecting the Right Rolling Process
Your choice of rolling process should be driven directly by the requirements of your final product.
- If your primary focus is producing large structural components like I-beams or rails: Hot profile rolling is the industry standard for its efficiency in large-scale deformation.
- If your primary focus is a high-precision, smooth-finished product like an automotive fender: Cold rolling is essential to achieve the required surface quality and dimensional accuracy.
- If your primary focus is creating a seamless, durable ring for a high-stress application like a bearing: Ring rolling is the specialized process designed for this exact purpose.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing long parts with a complex cross-section, like metal framing: Continuous roll forming is the most cost-effective and efficient method.
Understanding these categories empowers you to select the precise manufacturing technique required to achieve your engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Process Type | Key Characteristic | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Hot Rolling | High temperature, high malleability | Slabs, billets, structural beams |
| Cold Rolling | Room temperature, high precision | Automotive panels, tin cans |
| Profile/Shape Rolling | Grooved rollers for specific shapes | I-beams, railway tracks |
| Ring Rolling | Creates seamless rings | Bearings, turbine wheels |
| Roll Forming | Continuous bending of sheet metal | Gutters, door frames, metal studs |
Ready to select the perfect rolling process for your project? The right equipment is crucial for achieving the desired material properties and final product geometry. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to support your research and development in materials science and manufacturing. Whether you're testing material behavior under different rolling conditions or scaling up production, our solutions can help ensure precision and efficiency. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- What does a hydraulic heat press do? Achieve Industrial-Scale, Consistent Pressure for High-Volume Production
- What is a hydraulic hot press? Unlock the Power of Heat and Pressure for Advanced Materials
- How does a hydraulic hot press machine work? Unlock Precision in Material Bonding and Forming
- What is a hydraulic hot press? A Guide to Precision Heat and Pressure for Manufacturing
- What is a hydraulic hot press machine? A Guide to Force and Heat for Material Transformation



















