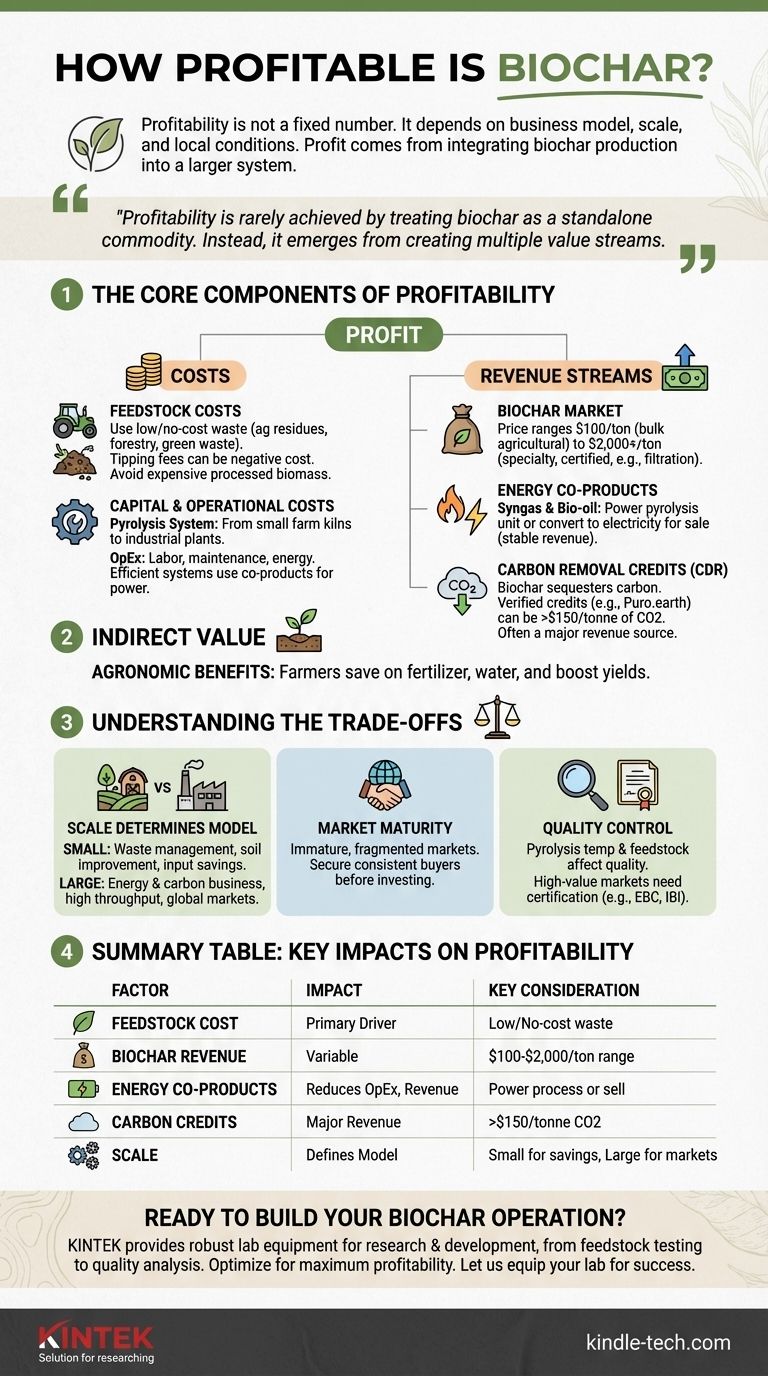
At its core, the profitability of biochar is not a single, fixed number. It is a highly variable outcome that depends entirely on your specific business model, operational scale, and local market conditions. Profit can range from modest returns based on agricultural cost savings to significant revenue from the combined sale of biochar, energy co-products, and carbon credits.
The central truth of biochar economics is this: profitability is rarely achieved by treating biochar as a standalone commodity. Instead, it emerges from integrating its production into a larger system to create multiple value streams—reducing waste, generating energy, improving soil, and sequestering carbon.

The Core Components of Biochar Profitability
To determine if biochar can be profitable for you, you must analyze the complete financial picture. Profit is a function of your costs and your total revenue, which often comes from more than just the biochar itself.
H3: Feedstock Costs: The Starting Point
Your single most critical cost factor is feedstock—the biomass you convert into biochar. The ideal feedstock is low-cost or even negative-cost, such as agricultural waste, forestry residues, or municipal green waste for which you can charge a "tipping fee" to accept.
Sourcing expensive, processed biomass like wood pellets will almost certainly make your operation unprofitable from the start.
H3: Capital & Operational Costs: The Pyrolysis System
The technology you use for pyrolysis represents your main capital expenditure (CapEx). This can range from a few thousand dollars for a small, on-farm kiln to millions for a large-scale, continuous industrial plant.
Operational costs (OpEx) include labor, maintenance, and the energy required to run the system. Highly efficient systems use their own energy co-products to power the process, dramatically reducing operational costs.
H3: Revenue Stream 1: The Biochar Market
The sale price of biochar varies dramatically, from $100 per ton for bulk, uncertified agricultural grades to over $2,000 per ton for high-purity, certified products used in specialty applications like filtration or cosmetics.
Your ability to command a higher price is directly tied to the quality, consistency, and certification of your product.
H3: Revenue Stream 2: Energy Co-products
Pyrolysis does not just produce char; it also generates syngas (synthesis gas) and bio-oil. These are valuable energy co-products.
Syngas can be used to power the pyrolysis unit itself, making the operation self-sustaining. Excess energy can be converted to electricity and used on-site or sold to the grid, creating a stable, predictable revenue stream.
H3: Revenue Stream 3: Carbon Removal Credits
Biochar is a form of carbon sequestration. By producing it and applying it to soil, you are durably removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This service has a market value.
Through verification platforms like Puro.earth, producers can sell carbon dioxide removal (CDR) credits, often for over $150 per tonne of CO2 removed. For many modern biochar operations, revenue from carbon credits can be equal to or even greater than revenue from selling the physical biochar.
H3: Indirect Value: Agronomic Benefits
If you are a farmer, a major part of your return on investment comes from using the biochar yourself. This "profit" is realized through cost savings and increased revenue.
Applying biochar to your own fields can significantly reduce fertilizer needs, improve water retention (lowering irrigation costs), and boost crop yields, providing a powerful economic benefit independent of external sales.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Market Realities
A profitable biochar venture requires a clear-eyed view of the challenges and strategic choices involved. The most common failures stem from misunderstanding these key trade-offs.
H3: Scale Determines the Business Model
Small, on-farm operations and large, industrial plants are fundamentally different businesses.
A small-scale system is best viewed as a waste management and soil improvement tool. Its profitability is measured in reduced farm input costs and higher yields.
A large-scale industrial plant is an energy and carbon-credit business. Its profitability depends on massive throughput, efficient energy conversion, and access to the global carbon markets.
H3: The Challenge of Market Maturity
While awareness of biochar is growing, the market for it can be immature and fragmented in some regions. Finding consistent buyers willing to pay a premium for quality can be a significant hurdle.
Successful producers often identify and secure their end-market (e.g., a large compost facility, a specialty soil blender, a municipal water utility) before they invest in production equipment.
H3: Quality Control is Non-Negotiable
Not all biochar is created equal. The temperature of pyrolysis and the type of feedstock dramatically alter the final product's characteristics, making it suitable for some applications but useless for others.
Selling into high-value markets requires rigorous quality control and often demands third-party certification (e.g., from the European Biochar Certificate or International Biochar Initiative). This adds cost and complexity but is essential for building a premium brand.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To build a profitable biochar venture, you must first define your primary objective. Your strategy will flow directly from this goal.
- If your primary focus is improving farm sustainability: Invest in a small-scale system to process your agricultural waste into biochar for your own soil, with profitability measured in lower input costs and better yields.
- If your primary focus is creating a new business: Secure a cheap, long-term feedstock contract and identify specific buyers for your biochar, energy, and carbon credits before investing in equipment.
- If your primary focus is large-scale carbon removal: Your business model must be built around industrial efficiency, long-term energy sales agreements, and fully accredited carbon credit sales.
Ultimately, biochar's profitability is achieved through strategic integration, not by simply selling a single product.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Profitability | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Feedstock Cost | Primary cost driver | Use low/no-cost waste materials (e.g., agricultural residues) |
| Biochar Revenue | Variable | Price ranges from $100/ton (agricultural) to $2,000/ton (specialty) |
| Energy Co-products | Reduces OpEx, creates revenue | Syngas/bio-oil can power the process or be sold |
| Carbon Credits (CDR) | Major revenue stream | Can exceed $150 per tonne of CO2 removed via platforms like Puro.earth |
| Scale | Defines business model | Small-scale focuses on farm savings; large-scale on energy & carbon markets |
Ready to Build Your Profitable Biochar Operation?
Navigating the complexities of pyrolysis technology and market strategy is critical to your success. KINTEK specializes in providing robust lab equipment and consumables essential for researching and developing your biochar production process. From testing feedstock properties to analyzing final biochar quality, our tools help you optimize for maximum profitability.
Let us equip your lab for success. Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your journey from R&D to a profitable, sustainable biochar venture.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does graphite react to heat? Unlocking Its Unique High-Temperature Strengths
- Why can graphite withstand heat? Unlocking Its Extreme Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What is the maximum working temperature of graphite? Unlock High-Temp Performance with the Right Atmosphere
- What is the temperature resistance of graphite? Unlocking Its High-Temp Potential in Your Lab
- How much temperature can graphite withstand? Unlock its true potential up to 3000°C



















