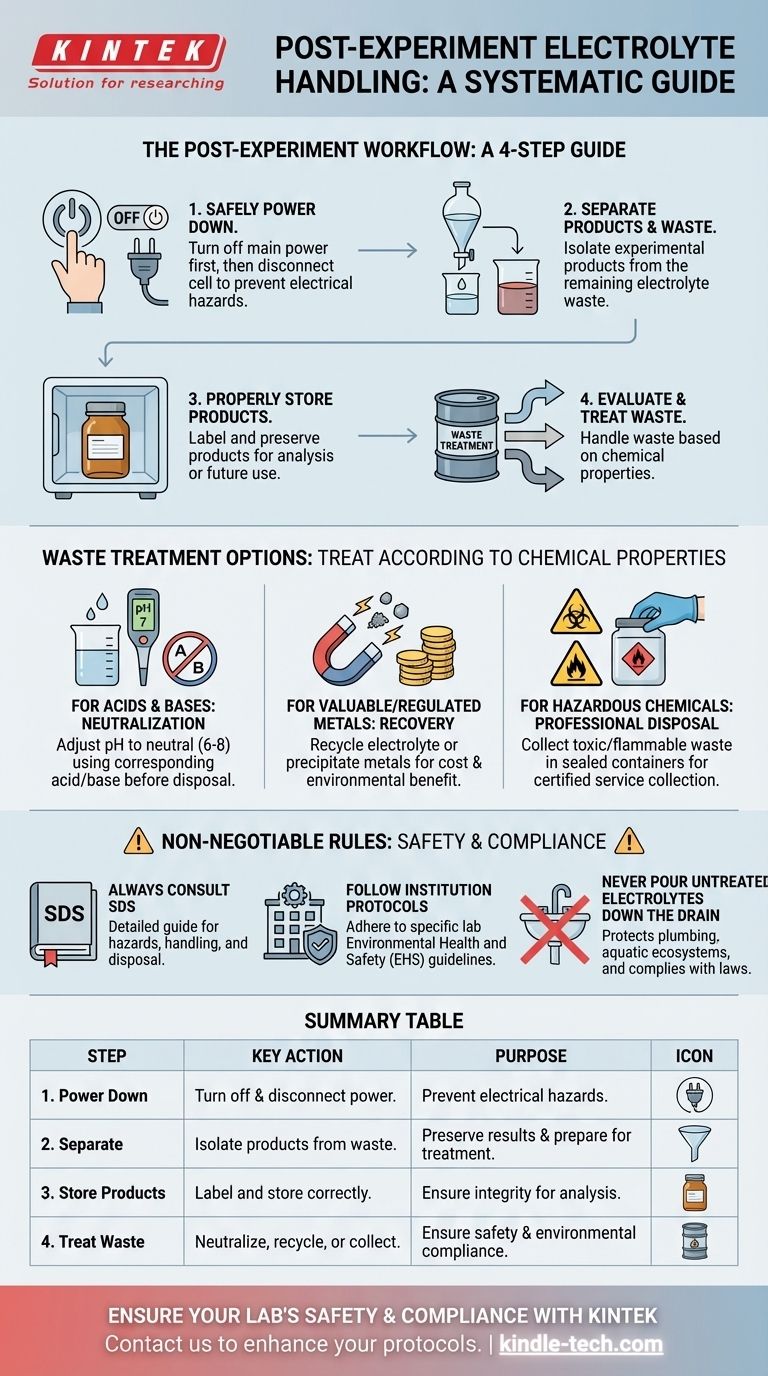
At the conclusion of an experiment, the electrolyte must be handled through a systematic process that prioritizes safety, environmental protection, and the integrity of your results. The first step is to always turn off the power source before disconnecting the cell. Afterward, you must separate any products from the waste liquid and treat the waste according to its specific chemical properties, which may involve neutralization, recycling, or collection for professional disposal.
The core challenge is not just disposing of a chemical, but executing a post-experiment protocol. This ensures personal safety from electrical hazards, preserves the experiment's products for analysis, and guarantees full compliance with environmental regulations.

The Post-Experiment Workflow: A Step-by-Step Guide
Properly concluding an electrochemical experiment involves more than just cleaning up. Following a clear sequence of steps is crucial for safety and scientific rigor.
Step 1: Safely Power Down the System
Before any handling occurs, the immediate priority is electrical safety.
Always turn off the main power supply first. Only after the power is off should you physically disconnect the electrolytic cell from the power source. This prevents the risk of electrical arcs, shocks, or other safety incidents.
Step 2: Separate Products from Waste Electrolyte
Your experiment has generated both a desired outcome (the product) and a byproduct (the waste liquid). These must be managed differently.
Carefully remove the products and the remaining electrolyte, now considered waste liquid, from the cell. This segregation is the critical next step.
Step 3: Properly Store Experimental Products
If the products of your experiment require further processing or analysis, they must be preserved correctly.
Store the isolated products in a clearly labeled, appropriate container to prevent contamination or degradation. This ensures the validity of any subsequent measurements.
Step 4: Evaluate and Treat the Waste Electrolyte
The waste electrolyte cannot simply be discarded. It must be treated based on its composition and your institution's rules.
This liquid must be handled according to strict environmental protection requirements to avoid pollution. The specific method depends entirely on its chemical properties.
Understanding Your Waste Treatment Options
The phrase "treat according to chemical properties" translates into several distinct paths. Your choice is dictated by the chemical nature of the electrolyte.
For Acids and Bases: Neutralization
If your electrolyte is a strong acid or base, the most common treatment is neutralization.
This involves carefully adding a corresponding base or acid to bring the pH to a neutral level (typically between 6 and 8) before it can be considered for further disposal.
For Valuable or Regulated Metals: Recovery
Some electrolytes contain expensive or environmentally sensitive materials, such as heavy metal ions.
In these cases, the goal may be to recycle the electrolyte or recover the valuable components through processes like precipitation. This minimizes both cost and environmental impact.
For Hazardous Chemicals: Professional Disposal
Many electrolytes contain components that are toxic, flammable, or otherwise hazardous and cannot be neutralized or recycled in a standard lab.
These materials must be collected in designated, sealed waste containers. They are then handed over to a certified environmental waste management service for proper disposal according to local and federal regulations.
The Non-Negotiable Rules: Safety and Compliance
Mistakes in handling electrolytes can have serious consequences. Adhering to established safety protocols is not optional.
Always Consult the Safety Data Sheet (SDS)
The SDS for your specific electrolyte is your most important guide. It contains detailed information on hazards, handling, and disposal procedures.
Follow Your Institution's Protocols
Every laboratory, university, or company has its own set of Environmental Health and Safety (EHS) guidelines. You must know and follow these rules, as they are designed to ensure compliance and safety in your specific environment.
Never Pour Untreated Electrolytes Down the Drain
This is a critical rule. Disposing of untreated chemicals down the sink can damage plumbing, harm aquatic ecosystems, and violate environmental laws.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision-making process for handling post-experiment electrolytes should be clear and systematic.
- If your electrolyte is a simple acid or base: Your first step is almost always neutralization before proceeding with disposal according to lab guidelines.
- If your electrolyte contains valuable or heavy metals: Investigate your lab's protocols for chemical recovery or precipitation to reclaim materials and protect the environment.
- If your electrolyte is toxic, organic, or otherwise hazardous: It must be collected as chemical waste for professional disposal, with no exceptions.
Properly managing your electrolyte after an experiment is the hallmark of a responsible and meticulous scientific professional.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Power Down | Turn off and disconnect the power source. | Prevent electrical hazards. |
| 2. Separate | Isolate products from the waste electrolyte. | Preserve results and prepare for treatment. |
| 3. Store Products | Label and store products correctly. | Ensure integrity for analysis. |
| 4. Treat Waste | Neutralize, recycle, or collect for disposal. | Ensure safety and environmental compliance. |
Ensure Your Lab's Safety and Compliance with KINTEK
Proper electrolyte handling is critical for protecting your team and the environment. KINTEK specializes in providing the reliable lab equipment and consumables you need to perform these procedures safely and efficiently.
Let us help you enhance your lab's protocols. Our experts can assist you in selecting the right tools for neutralization, waste collection, and more.
Contact us today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover how KINTEK's solutions can support your commitment to safety and excellence.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- How does the lab autoclave work? Achieve Complete Sterilization with High-Pressure Steam
- What is a lab autoclave? Your Guide to Sterilization with Pressurized Steam
- What temperature must be reached for sterilization in 10-12 minutes? Achieve Rapid, Reliable Sterility with Flash Autoclaving
- What are the advantages of autoclaving in hospitals? Achieve Unmatched Sterilization for Patient Safety
- Can autoclave sterilize liquid? Master Safe and Effective Liquid Sterilization



















