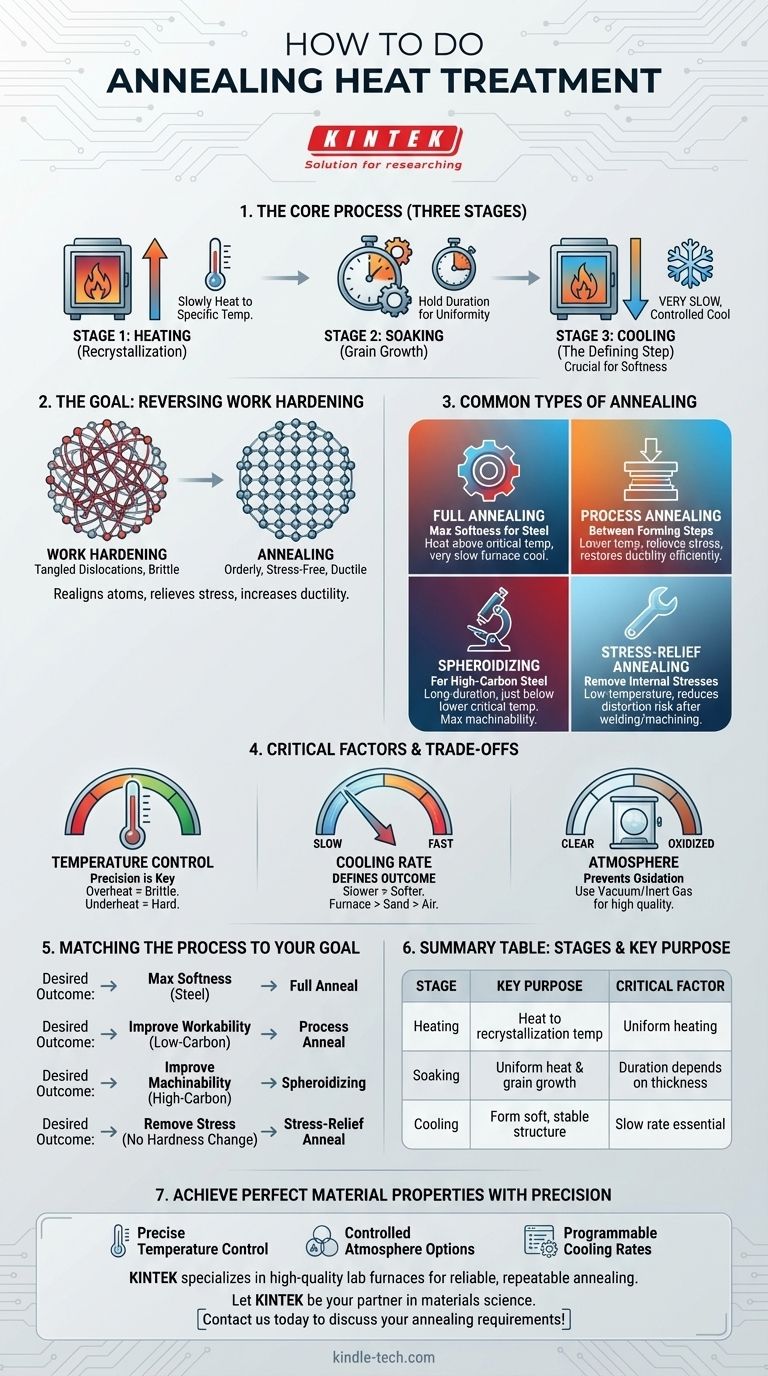
At its core, the annealing heat treatment process involves three distinct stages: heating a metal to a specific temperature, holding it there for a set duration, and then cooling it back down at a very slow, controlled rate. This procedure is designed to alter the material's internal microstructure, primarily to increase its ductility and reduce its hardness, making it easier to work with.
The central purpose of annealing is to reverse the effects of work hardening. By using a precise cycle of heating and, most importantly, slow cooling, you relieve internal stresses and create a softer, more uniform grain structure within the metal.
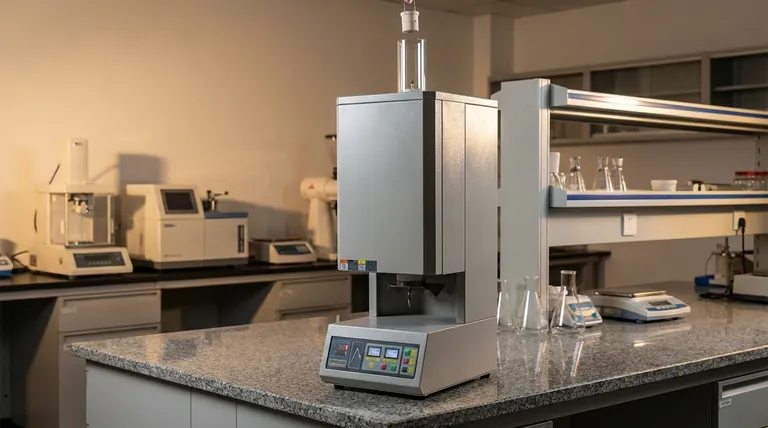

The Goal of Annealing: Reversing Work Hardening
To understand how to perform annealing, you must first understand why you are doing it. The primary goal is to undo the effects of "work hardening" or "cold working."
What is Work Hardening?
When you bend, roll, or hammer a piece of metal at room temperature, it becomes progressively harder and more brittle.
Internally, this plastic deformation creates a tangled, chaotic network of microscopic defects called dislocations. This tangled structure makes it difficult for atoms to slip past one another, which is what we perceive as increased hardness and reduced ductility.
How Annealing Solves the Problem
Annealing provides the thermal energy necessary for the atoms within the metal's crystal lattice to rearrange themselves into a more orderly, stress-free state.
This process eliminates the dense network of dislocations, effectively resetting the material's properties and restoring its softness and ability to be formed.
The Three Critical Stages of Annealing
Every annealing process, regardless of the specific type, follows the same fundamental three-stage pattern. The exact temperatures and times are highly dependent on the specific alloy.
Stage 1: The Heating Phase (Recrystallization)
The first step is to slowly and uniformly heat the material to its recrystallization temperature.
This is the critical temperature at which new, strain-free grains begin to form within the deformed microstructure. Heating too quickly can cause thermal stress and cracking, while not heating high enough will result in an incomplete anneal.
Stage 2: The Soaking Phase (Grain Growth)
Once the material reaches the target temperature, it is "soaked" or held there for a specific duration.
The purpose of soaking is twofold: to ensure the entire part, including its core, reaches a uniform temperature, and to allow the new, stress-free grains to fully form and grow. Soaking time depends on the material's thickness and composition.
Stage 3: The Cooling Phase (The Defining Step)
This is the most crucial stage and what truly defines annealing. The material must be cooled very slowly.
This slow cooling rate is essential to allow the microstructure to form into its most stable and softest state. For many steels, this means leaving the part inside the furnace and turning the furnace off, allowing it to cool over many hours or even days. Fast cooling (quenching) would produce a hard structure, the opposite of the desired outcome.
Common Types of Annealing Processes
While the three stages are universal, specific applications require different variations of the annealing process.
Full Annealing
This is the "classic" process used on steels to achieve maximum softness. The steel is heated above its upper critical temperature (A3 or Acm), transforming the grain structure completely into austenite, and then cooled extremely slowly in the furnace.
Process Annealing
Also known as subcritical annealing, this is a lower-temperature process used on low-carbon steels between forming operations. It relieves stress and restores ductility without the time and expense of a full anneal, making manufacturing processes more efficient.
Spheroidizing
This is a specialized, long-duration annealing process for high-carbon steels. It is performed just below the lower critical temperature (A1) to transform the hard iron carbide (cementite) into small, round spheres within the iron matrix. This structure gives the steel maximum softness and machinability.
Stress-Relief Annealing
This is a low-temperature heat treatment used to remove internal stresses caused by welding, casting, or heavy machining. The goal is to reduce the risk of distortion or cracking without significantly altering the material's hardness or other mechanical properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Factors
Successfully annealing a material requires careful control over several variables. Missteps can lead to undesirable results.
Temperature Control is Paramount
Using the correct temperature for the specific alloy is non-negotiable. Overheating can cause excessive grain growth, which can make the material brittle. Underheating will result in an incomplete anneal, leaving the material harder than desired.
Cooling Rate Defines the Outcome
The rate of cooling is the single most important variable that determines the final properties. The slower the cooling, the softer the final product. Furnace cooling is slowest, followed by burying the part in an insulating material like sand or vermiculite, followed by still air cooling.
Atmosphere Can Be Critical
For many materials, heating to high temperatures in the presence of oxygen will cause a layer of oxide scale to form on the surface. For high-carbon steels, it can also lead to decarburization (loss of carbon from the surface), which is often undesirable. Using a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere furnace prevents these issues.
Matching the Process to Your Goal
Choose your annealing method based on the material you are working with and your desired final outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum softness and ductility for steel: A full anneal with very slow furnace cooling is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is improving workability between forming steps: Process annealing offers a faster, more economical solution for low-carbon steel.
- If your primary focus is improving the machinability of high-carbon steel: Spheroidizing is the specific, long-duration treatment required.
- If your primary focus is removing internal stresses without changing hardness: A low-temperature stress-relief anneal is the best approach.
Ultimately, mastering annealing is about precisely controlling temperature and time to reshape a material's internal structure for your specific need.
Summary Table:
| Annealing Stage | Key Purpose | Critical Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Heating | Heat metal to its recrystallization temperature | Uniform heating to avoid thermal stress |
| Soaking | Hold at temperature for uniform heat and grain growth | Duration depends on material thickness |
| Cooling | Cool slowly to form a soft, stable microstructure | Slow cooling rate is essential for softness |
Achieve perfect material properties with precise annealing.
The right lab furnace is critical for controlling the heating, soaking, and slow cooling stages of annealing. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and equipment designed for reliable, repeatable heat treatment processes.
We provide solutions for:
- Precise Temperature Control: Ensure your material reaches and holds the exact temperature required for recrystallization and grain growth.
- Controlled Atmosphere Options: Prevent oxidation and decarburization with vacuum or inert gas furnaces for high-quality results.
- Programmable Cooling Rates: Achieve the slow cooling necessary for a full anneal with our advanced furnace systems.
Let KINTEK be your partner in materials science. Whether you're performing full annealing, process annealing, or stress relief, we have the equipment to meet your laboratory's specific needs.
Contact us today to discuss your annealing requirements and find the ideal furnace for your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation



















