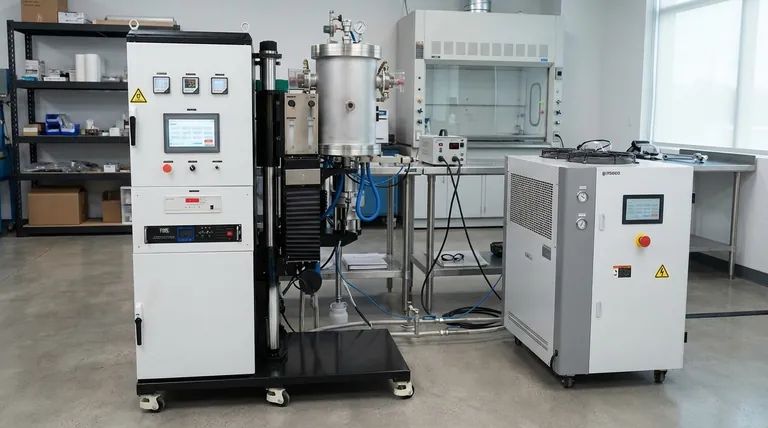
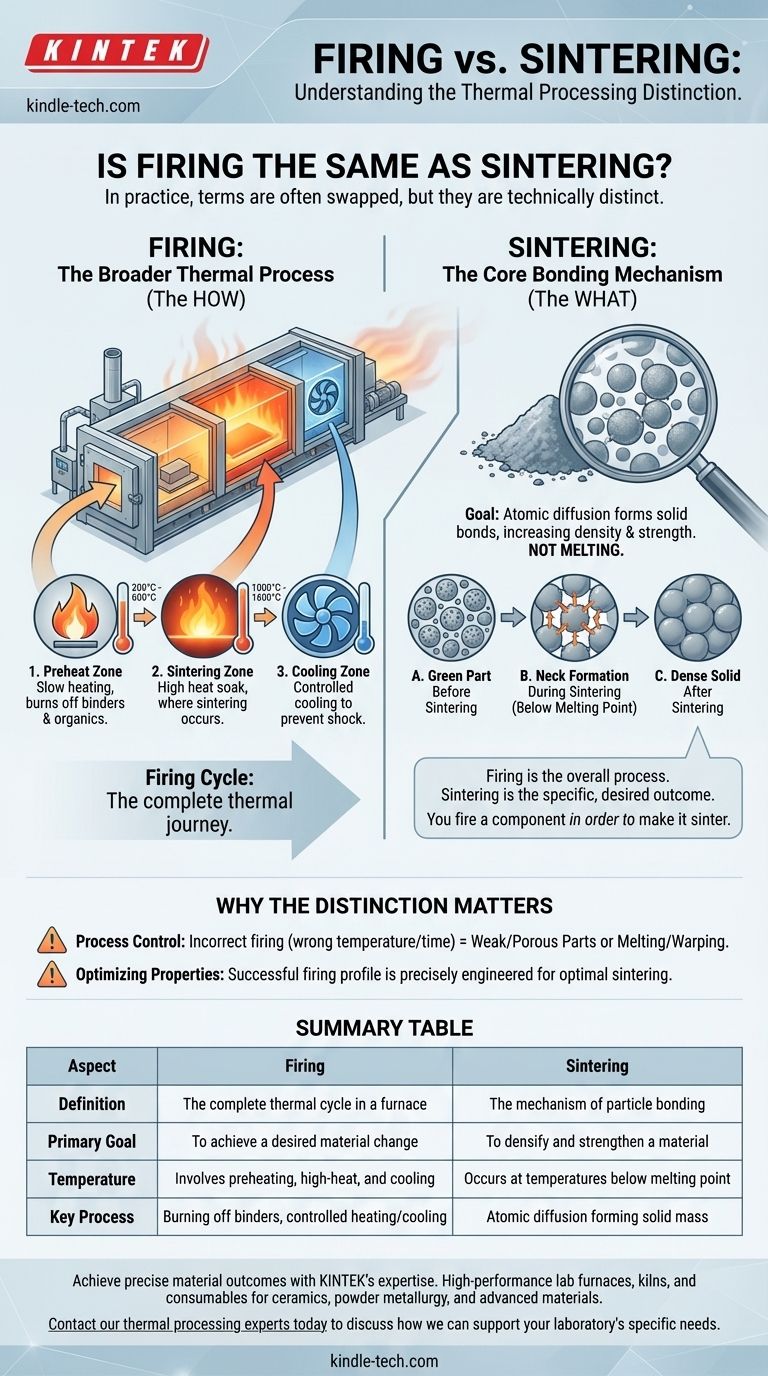
In practice, the terms "firing" and "sintering" are often used interchangeably, but they are not technically the same. Firing is the broad process of heating a material (like a ceramic or powdered metal) in a kiln or furnace to achieve a desired change. Sintering is a specific physical mechanism that often occurs during the firing process, where particles bond together to form a solid mass without melting.
The simplest way to understand the difference is to think of "firing" as the overall process and "sintering" as the specific, desired outcome. You fire a component in order to make it sinter.

What is Firing? The Broader Thermal Process
Firing refers to the entire, controlled thermal cycle a material undergoes in a furnace. This cycle is more than just heating; it consists of several distinct stages.
A General Term for High-Heat Treatment
In industries like ceramics and powder metallurgy, "firing" is the common verb used to describe putting a "green" (unprocessed) part into a furnace and subjecting it to a specific temperature profile.
The Three Stages of a Firing Cycle
A typical industrial firing process, such as in a tunnel kiln, involves three key zones:
- Preheat Zone: This initial, lower-temperature stage is designed to slowly heat the part and burn off any lubricants, binders, or organic materials used during forming.
- Sintering Zone: This is the high-heat stage where the part is held at a precise temperature for a specific duration. This is where the actual sintering mechanism takes place.
- Cooling Zone: The part is cooled in a controlled manner to prevent thermal shock, cracking, or the development of unwanted internal stresses.
What is Sintering? The Core Bonding Mechanism
Sintering is the scientific phenomenon that gives a fired part its strength and density. It is a process of consolidation driven by atomic-level changes, not by melting.
Bonding Below the Melting Point
The defining characteristic of sintering is that it occurs at a temperature below the material's melting point. The goal is not to liquefy the material, which would cause it to lose its shape, but to encourage solid-state bonding.
The Science of Atomic Diffusion
During sintering, the intense heat energizes the atoms within the individual powder particles. These atoms begin to migrate, or diffuse, across the boundaries where the particles touch.
This diffusion first creates small connections, or "necks," between adjacent particles. As the process continues, these necks grow, pulling the particles closer, eliminating the pores between them, and fusing the powder into a dense, solid object.
Why the Distinction Matters
While the terms are often used interchangeably in conversation, understanding the difference is critical for process control and achieving desired material properties.
Firing is the "How," Sintering is the "What"
You can fire a component incorrectly and fail to achieve proper sintering. If the temperature is too low or the time is too short, the part will be weak and porous. If the temperature is too high, it will begin to melt, warp, and lose its dimensional accuracy.
Therefore, a successful firing profile is one that is precisely engineered to optimize the sintering mechanism for a specific material.
Avoiding Confusion with Other Processes
Sintering is fundamentally different from both welding and melting. Welding typically involves localized melting and fusion, while sintering is a bulk process that avoids liquefaction entirely. This distinction is crucial for controlling the final microstructure and properties of the component.
Applying the Right Terminology
Use the term that best fits the context of your discussion to ensure clarity and precision.
- If your primary focus is the entire manufacturing step involving a furnace: Use "firing" to describe the complete thermal cycle of preheating, high-heat soaking, and cooling.
- If your primary focus is the specific science of how particles bond into a solid: Use "sintering" to describe the mechanism of atomic diffusion that occurs at high temperatures.
- If you are speaking with a general technical audience: Acknowledge that the terms are often swapped, but clarify that sintering is the specific goal of the firing process.
Mastering this distinction is key to controlling material outcomes and communicating effectively within any technical field.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Firing | Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The complete thermal cycle in a furnace | The mechanism of particle bonding |
| Primary Goal | To achieve a desired material change | To densify and strengthen a material |
| Temperature | Involves preheating, high-heat, and cooling stages | Occurs at temperatures below the melting point |
| Key Process | Burning off binders, controlled heating/cooling | Atomic diffusion forming solid mass |
Achieve precise material outcomes with KINTEK's expertise.
Understanding the nuances of thermal processes like firing and sintering is critical for developing strong, durable components. Whether you're working in ceramics, powder metallurgy, or advanced materials, the right equipment and consumables are essential for success.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces, kilns, and consumables designed to deliver the exact temperature control and consistency your sintering processes demand. Our solutions help you optimize your firing cycles for superior results.
Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the muffle furnace 1800 degree? High-Temp Precision for Advanced Materials
- What are the primary functions of a laboratory forced air drying oven in the multi-step deposition of hydrophobic coatings?
- How does tempering affect hardness? A Guide to Balancing Hardness and Toughness in Steel
- Why is a High-Temperature Muffle Furnace used for 600°C TiO2 Calcination? Optimize Catalyst Purity and Phase Stability
- What is the role of a high-temperature box resistance furnace in the heat treatment of 316L stainless steel? Achieve Peak Corrosion Resistance
- What is the role of a high-temperature box furnace in BZY20 densification? Achieve 94% Density with Precision
- What roles do specialized drying and sintering furnaces play in slip casting? Achieve High-Strength Composite Density
- What temperature is needed for sintering pottery? A Guide to Perfect Firing for Durability



















