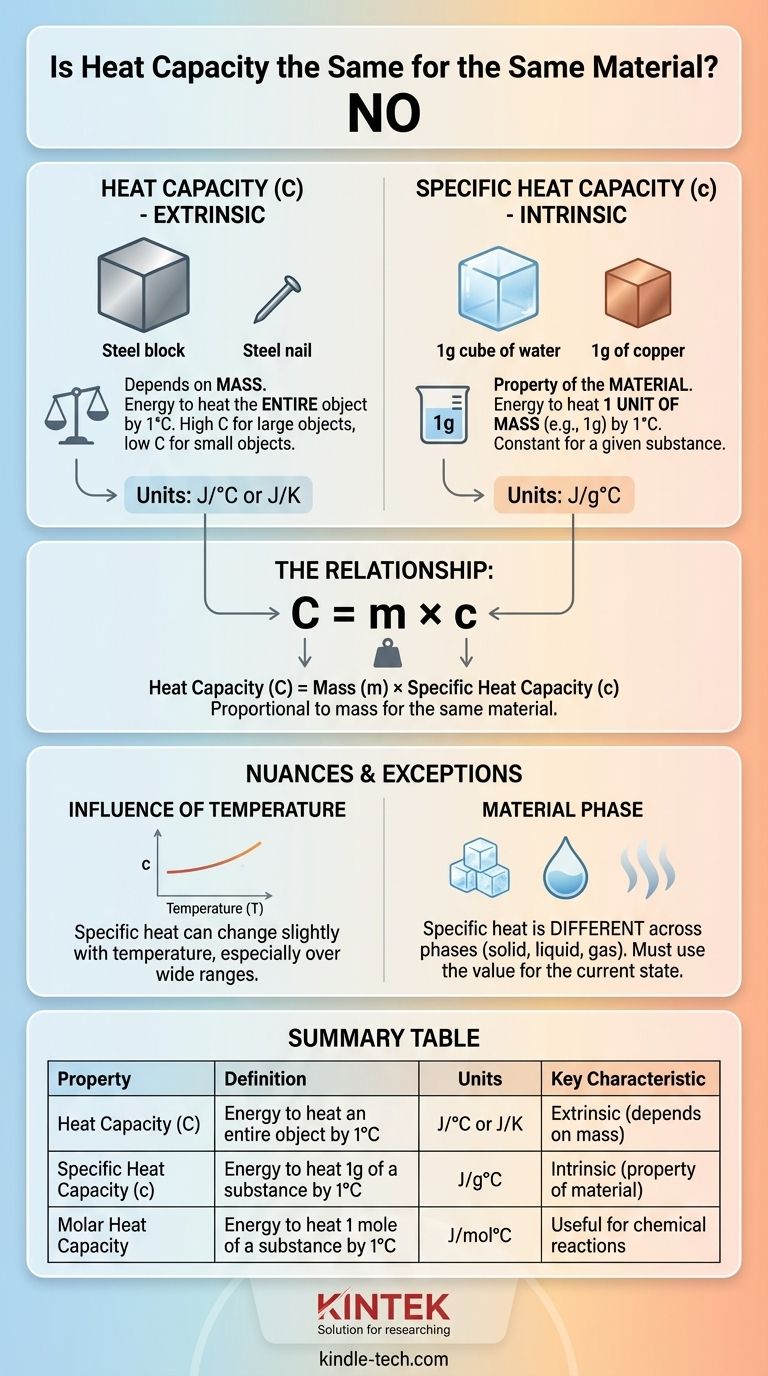
In short, no. The heat capacity of an object is not the same for the same material if the amount of material is different. Heat capacity depends directly on the mass of an object, so a large block of steel will have a much higher heat capacity than a small steel nail. The property you are thinking of, which is constant for a material, is called specific heat capacity.
The core distinction is this: heat capacity is an extrinsic property of a specific object (how much energy to heat the whole thing), while specific heat capacity is an intrinsic property of a substance (how much energy to heat a set amount, like one gram). Mistaking one for the other is a common source of confusion.

Defining the Key Concepts: Heat Capacity vs. Specific Heat
To solve problems involving thermal energy, you must first be precise with your terms. The difference between "heat capacity" and "specific heat capacity" is fundamental.
What is Heat Capacity (C)?
Heat capacity is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of an entire object by one degree (Celsius or Kelvin).
Think of it as the thermal inertia of a particular object. A large swimming pool requires a massive amount of energy to warm up by one degree, so it has a high heat capacity. A small cup of water requires far less energy, so it has a low heat capacity.
Because it depends on the size of the object, heat capacity is an extrinsic property. Its unit is typically Joules per degree Celsius (J/°C) or Joules per Kelvin (J/K).
What is Specific Heat Capacity (c)?
Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of one unit of mass (like one gram or one kilogram) of a substance by one degree.
This is the value you find in reference tables for materials. It allows for a fair comparison between substances. For example, water has a very high specific heat capacity (4.184 J/g°C), while copper has a low one (0.385 J/g°C).
This means it takes much more energy to heat one gram of water than to heat one gram of copper. Because it's standardized per unit of mass, specific heat is an intrinsic property of a substance.
The Mathematical Relationship
The connection between these two properties is simple and direct. The heat capacity of an object is its mass multiplied by the material's specific heat capacity.
Heat Capacity (C) = mass (m) × specific heat capacity (c)
This formula clearly shows that if you have two objects made of the same material (same c), the one with the larger mass (m) will have a proportionally larger heat capacity (C).
Understanding the Nuances and Exceptions
While specific heat is considered a constant for a given material, this assumption has important limits in real-world engineering and scientific applications.
The Influence of Temperature
For most everyday calculations, specific heat is treated as constant. However, in reality, the specific heat of a material can change slightly with temperature.
In high-precision fields like aerospace or materials science, engineers must account for how a material's specific heat changes as it heats up or cools down over a wide range.
The Critical Role of Material Phase
A substance's specific heat capacity is not the same across its different phases (solid, liquid, gas).
The most common example is water. The specific heat of solid ice is different from that of liquid water, which is also different from that of gaseous steam. When performing calculations, you must use the value corresponding to the material's current state.
Molar Heat Capacity: A Different Perspective
In chemistry, it is often more useful to measure the amount of a substance in moles rather than in mass.
Molar heat capacity is the energy required to raise one mole of a substance by one degree. This is particularly useful when analyzing chemical reactions, where the number of molecules is the key factor.
How to Apply This Knowledge Correctly
Choosing the right term depends entirely on what you are trying to describe or calculate.
- If your primary focus is a specific object: Use heat capacity (C) to understand the total energy needed to heat that entire object, such as an engine block, a heatsink, or a cooking pan.
- If your primary focus is a substance or material: Use specific heat capacity (c) to compare the inherent thermal properties of different materials, like choosing between aluminum and copper for a particular application.
- If your primary focus is a chemical reaction: Consider using molar heat capacity, as it relates energy changes directly to the number of molecules involved in the process.
Distinguishing between the property of an object and the property of a substance is the key to mastering thermal calculations.
Summary Table:
| Property | Definition | Units | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heat Capacity (C) | Energy to heat an entire object by 1°C | J/°C or J/K | Extrinsic (depends on mass) |
| Specific Heat Capacity (c) | Energy to heat 1g of a substance by 1°C | J/g°C | Intrinsic (property of the material) |
| Molar Heat Capacity | Energy to heat 1 mole of a substance by 1°C | J/mol°C | Useful for chemical reactions |
Accurate thermal analysis is critical for your lab's success.
Understanding the precise thermal properties of your materials is fundamental to reliable research, development, and quality control. Whether you are characterizing new materials, optimizing a thermal process, or selecting the right equipment, precise heat capacity data is non-negotiable.
KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need to perform these critical measurements with confidence. From calorimeters to temperature control systems, our solutions are designed to deliver the accuracy and reliability that laboratories demand.
Let KINTEK be your partner in precision. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover how our products can enhance your thermal analysis capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
- 10L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Glassy Carbon Sheet RVC for Electrochemical Experiments
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a constant temperature water bath? Ensure Reliable Dental Resin Conversion Rates
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is the primary role of a constant temperature water bath in biomass washing? Optimize Poplar Pretreatment.
- Why is a recirculating thermostatic bath required for high-precision CV testing? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Data
- What is the importance of an automatic temperature control circulation device? Ensure Reliable Electrochemical Data



















