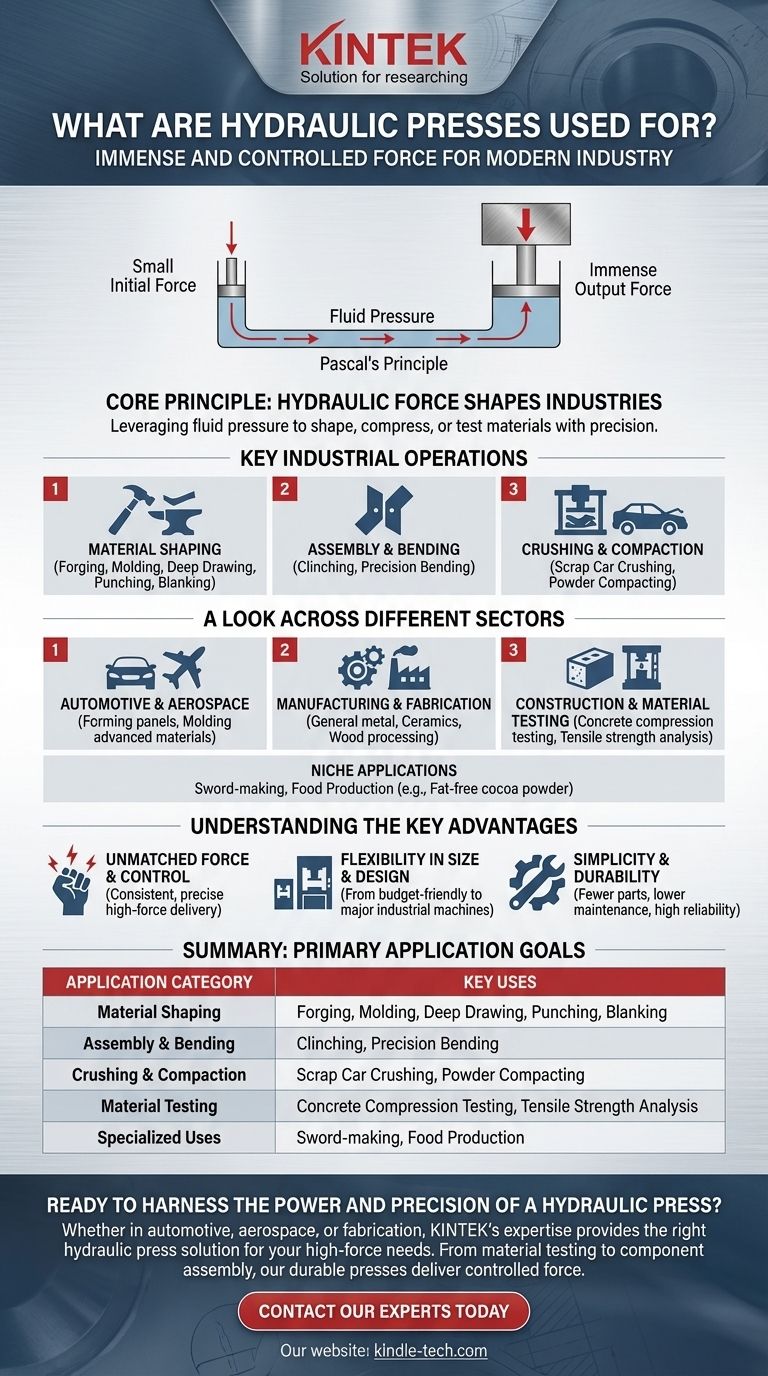
At its core, a hydraulic press is used for any task that requires immense and controlled force. These machines are the workhorses of modern industry, employed for a vast range of operations including forging, molding, crushing, blanking, punching, deep drawing, and assembling various materials.
The fundamental purpose of a hydraulic press is to leverage Pascal's principle—using fluid pressure to multiply a small initial force into an immensely powerful output—to shape, compress, or test materials with exceptional precision.

The Core Principle: How Hydraulic Force Shapes Industries
The versatility of the hydraulic press stems from its simple yet powerful method of operation. By applying force to a confined liquid, it generates a massive output force capable of altering even the most robust materials.
Key Industrial Operations
The most common applications involve shaping metal. Operations like forging (shaping metal with compressive force), punching (creating holes), blanking (cutting shapes from a sheet), and deep drawing (stretching sheet metal into a die) are fundamental in manufacturing.
Assembling and Bending
Beyond shaping raw material, these presses are used for clinching (joining sheet metal without fasteners) and precisely bending components into their final form. This is critical for creating complex parts in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Material Crushing and Compaction
The sheer power of a hydraulic press makes it ideal for size reduction and compaction. This includes large-scale tasks like crushing cars for scrap metal and more refined processes like powder compacting to form solid parts from powders.
A Look Across Different Sectors
The adaptability of hydraulic presses means they are integral to nearly every heavy industry, from manufacturing consumer goods to building advanced technology.
Automotive and Aerospace
These sectors rely on hydraulic presses for everything from forming car body panels to molding advanced materials like thermoplastics, composites, and carbon fiber for lightweight and high-strength components.
Manufacturing and Fabrication
As the backbone of many mechanical industries, hydraulic presses are used in general metal fabrication, ceramics manufacturing, and even wood processing. Their precision is essential for producing consistent, high-quality parts.
Construction and Material Testing
In construction, hydraulic presses are used in a laboratory setting to perform concrete compression testing. The data on tensile strength gathered from these tests is crucial for adjusting and validating concrete formulas to ensure structural integrity.
Niche and Specialized Applications
The versatility of the technology leads to some unique uses. These include the ancient craft of sword-making, where presses forge blades, and food production, such as making fat-free cocoa powder by pressing out the cocoa butter.
Understanding the Key Advantages
While other types of presses exist, the hydraulic press offers a unique combination of benefits that makes it indispensable for certain tasks.
Unmatched Force and Control
The primary advantage is the ability to deliver a massive amount of force consistently through the full length of the stroke. This force can be precisely controlled, allowing for complex operations that require both power and finesse.
Flexibility in Size and Design
Hydraulic presses can be built in a vast range of sizes. This includes small, budget-friendly electric hydraulic presses suitable for smaller metalworking tasks, all the way up to enormous machines that form the centerpiece of major industrial operations.
Simplicity and Durability
Compared to complex mechanical presses, a hydraulic system has fewer moving parts. This often translates to higher durability, lower maintenance requirements, and greater reliability for demanding, high-force applications.
How to Frame the Right Application
To understand where a hydraulic press fits, it's best to think in terms of the primary goal of the operation.
- If your primary focus is high-force material shaping: A hydraulic press is ideal for forging, molding, and deep drawing metal into complex forms.
- If your primary focus is material reduction or disposal: Its immense power is perfectly suited for crushing cars, scrap baling, and other compaction tasks.
- If your primary focus is precision testing: The controlled application of force is essential for tasks like testing the tensile strength of concrete or preparing laboratory samples.
- If your primary focus is component assembly: Hydraulic presses provide the controlled force needed for clinching, bending, and fitting parts together with high precision.
Ultimately, the hydraulic press is a foundational tool that transforms raw materials into the functional components that build our world.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Uses |
|---|---|
| Material Shaping | Forging, Molding, Deep Drawing, Punching, Blanking |
| Assembly & Bending | Clinching, Precision Bending |
| Crushing & Compaction | Scrap Car Crushing, Powder Compacting |
| Material Testing | Concrete Compression Testing, Tensile Strength Analysis |
| Specialized Uses | Sword-making, Food Production (e.g., Cocoa Powder) |
Ready to harness the power and precision of a hydraulic press for your operations?
Whether you're in automotive manufacturing, aerospace, or general fabrication, KINTEK's expertise in lab and industrial equipment can provide the right hydraulic press solution for your high-force needs. From material testing to component assembly, our durable and reliable presses deliver the controlled force you require.
Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK hydraulic press can enhance your productivity and precision!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- How does a laboratory hydraulic press improve XRF accuracy for catalyst samples? Enhance Precision & Signal Stability



















