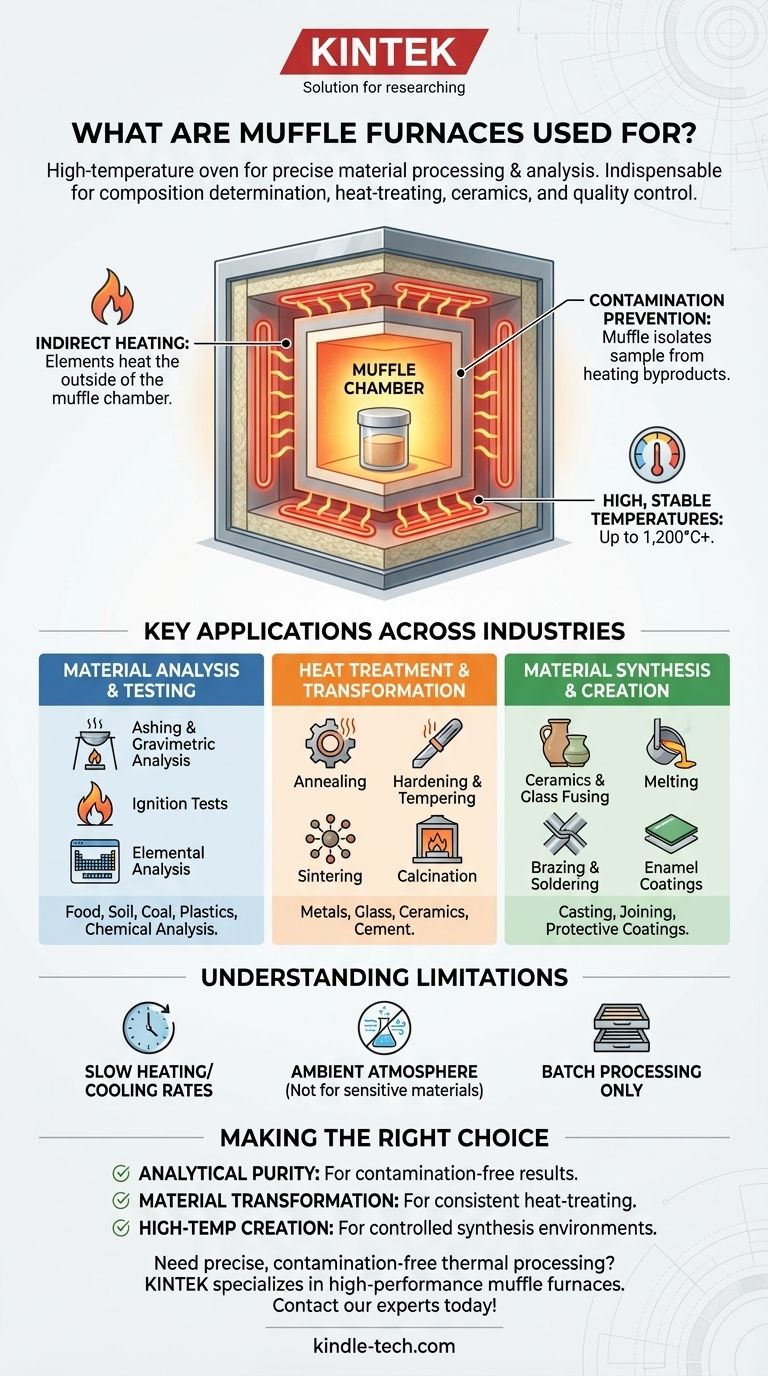
At its core, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven used for precise material processing and analysis. It is indispensable in laboratories and industries for a vast range of applications, including determining a sample's composition, heat-treating metals, creating ceramics, and performing quality control tests.
The defining feature of a muffle furnace is its design. The heating elements are physically separated from the internal chamber by an insulating "muffle," which ensures the sample is protected from contamination and receives highly uniform, stable heat. This makes it the ideal tool for tasks where purity and thermal accuracy are non-negotiable.
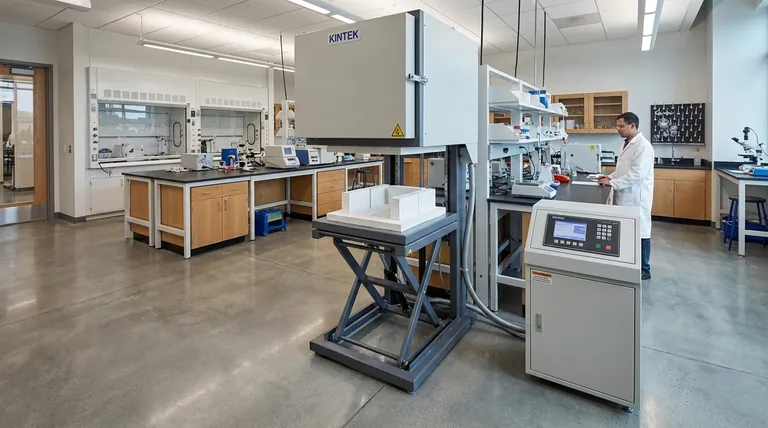

The Core Principle: Why a "Muffle" Matters
A muffle furnace is not just any oven; its specific construction is what makes it so valuable for technical applications. Understanding its design reveals why it's chosen for so many critical processes.
The Power of Indirect Heating
The term "muffle" refers to the furnace's inner chamber, which is made from a high-temperature, non-contaminating ceramic. This chamber encloses the sample completely.
The heating elements, whether electric coils or gas flames, heat the outside of this muffle. Heat then radiates into the chamber, providing extremely uniform and stable temperatures without exposing the sample to combustion byproducts or direct electrical interference.
Preventing Contamination
This separation is the furnace's primary advantage. For applications like ashing or gravimetric analysis, where the goal is to burn away organic material to weigh the inorganic residue, any contamination from the heat source would invalidate the results. The muffle ensures that what you put in is the only thing being heated.
Achieving High, Stable Temperatures
Muffle furnaces are designed to operate reliably at very high temperatures, typically ranging from 1,000°C to 1,200°C (1832°F to 2192°F), with some models reaching even higher. The heavy insulation allows the furnace to maintain a set temperature with high precision for extended periods.
Key Applications Across Industries
The unique capabilities of a muffle furnace make it a workhorse in materials science, analytical chemistry, engineering, and metallurgy. Its uses can be grouped into three main categories.
1. Material Analysis and Testing
This is a primary function in most laboratories. The goal is to alter a sample with heat to reveal its fundamental properties or composition.
- Ashing and Gravimetric Analysis: Burning a sample to determine its inorganic content, a common test for food, soil, coal, and plastics.
- Ignition Tests: Assessing the performance and fire resistance of materials at extreme temperatures.
- Elemental Analysis: Preparing samples for further chemical analysis to determine their elemental makeup.
- Coal Quality Analysis: Measuring moisture, volatile matter, and ash content in coal samples.
2. Heat Treatment and Transformation
In these applications, heat is used to intentionally change a material's physical or chemical properties without melting it.
- Annealing: Heating and slowly cooling metal or glass to soften it, improve ductility, and relieve internal stresses.
- Hardening and Tempering: Controlled heating and cooling cycles used to increase the hardness and durability of steel.
- Sintering: Heating powdered materials (like ceramics or metals) below their melting point until their particles bond together to form a solid piece.
- Calcination: Decomposing a material through heat to drive off volatile substances, such as creating cement from limestone.
3. Material Synthesis and Creation
Here, the furnace provides the energy needed to create new materials or assemble components.
- Ceramics and Glass Fusing: Firing clay to create ceramics or heating pieces of glass until they melt and fuse together.
- Melting: Liquefying small batches of metals or glass for casting or analysis.
- Brazing and Soldering: Joining metal components using a filler metal that is melted in the furnace.
- Enamel Coatings: Fusing a layer of powdered glass onto a metal substrate to create a durable, protective coating.
Understanding the Limitations
While incredibly versatile, a standard muffle furnace isn't the right tool for every high-temperature task. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Atmosphere Control is Not Standard
A typical muffle furnace operates in an ambient air atmosphere. This is fine for many processes but problematic for materials that oxidize (rust) or react with air at high temperatures. For those cases, a specialized vacuum furnace or atmosphere-controlled furnace that can be filled with an inert gas like argon is required.
Heating and Cooling Rates
The same heavy insulation that provides excellent temperature stability also means muffle furnaces heat up and cool down relatively slowly. They are not suited for applications requiring rapid thermal cycling.
Batch Processing Only
Muffle furnaces are designed for processing materials in batches. They are not intended for continuous, high-volume industrial production, which would require a conveyor-style tunnel furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the right thermal processing tool, clarify your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is analytical purity: A muffle furnace is ideal for ashing, gravimetric analysis, or preparing samples because its isolated chamber prevents contamination.
- If your primary focus is material transformation: Use a muffle furnace for annealing, hardening, or sintering, as its stable and uniform heat ensures consistent and predictable results.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature creation: The furnace provides the controlled thermal environment needed for crafting ceramics, fusing glass, or brazing components.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace is the definitive tool when your process demands a clean, stable, and precisely controlled high-temperature environment.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Uses | Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Material Analysis & Testing | Ashing, Gravimetric Analysis, Ignition Tests | Up to 1,200°C |
| Heat Treatment & Transformation | Annealing, Hardening, Sintering, Calcination | Up to 1,200°C |
| Material Synthesis & Creation | Ceramics, Glass Fusing, Brazing, Melting | Up to 1,200°C |
Need precise, contamination-free thermal processing? KINTEK specializes in high-performance muffle furnaces and lab equipment designed for analytical chemistry, materials science, and quality control. Our solutions ensure uniform heating and pure results for applications like ashing, sintering, and heat treatment. Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the use of muffle furnace in food analysis? Master Ashing for Accurate Mineral Content
- What is a muffle furnace for laboratory use? A Guide to Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the difference between an oven and a muffle furnace? A Guide to Selecting the Right Thermal Equipment
- What is the use of muffle furnace in soil laboratory? Essential for Accurate Soil Organic Matter Analysis
- What is the point of a muffle? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temperature Processes



















